TOKYO: Once forecast to become the world’s biggest economy, Japan slipped below Germany last year to fourth place, official data showed Thursday, although India is projected to leapfrog both later this decade.
Despite growing 1.9 percent, Japan’s nominal 2023 gross domestic product in dollar terms was $4.2 trillion, government data showed, compared with $4.5 trillion for Germany, according to figures released there last month.
The change in positions primarily reflects the sharp fall in the yen against the dollar, which slumped by almost a fifth in 2022 and 2023 against the US currency, including around seven percent last year.
This was in part because the Bank of Japan has maintained negative interest rates, unlike other major central banks, which have raised borrowing costs to fight soaring inflation.
Both economies rely heavily on exports, though Germany’s manufacturers have been hit particularly hard by soaring energy prices and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Europe’s biggest economy has also been hampered by the European Central Bank raising interest rates in the eurozone as well as uncertainty over its budget and chronic shortages of skilled labor.
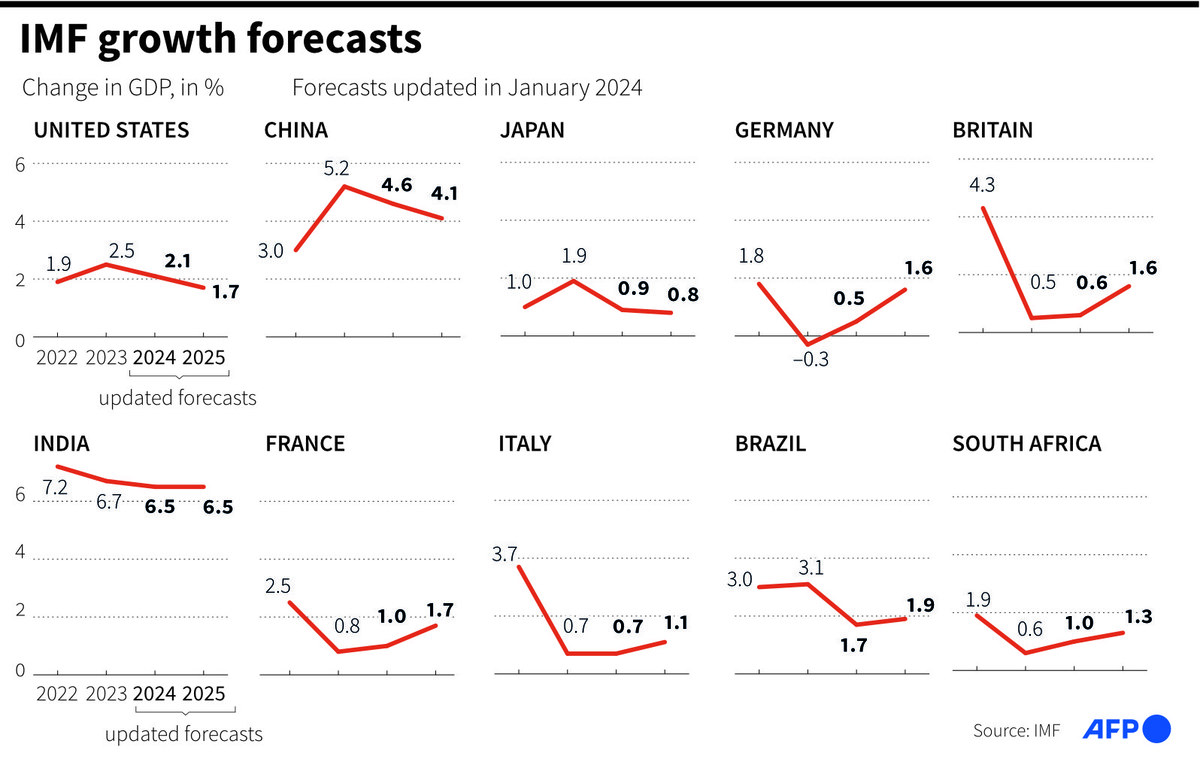
IMF forecast in January 2024. (AFP)
In January, German Finance Minister Christian Lindner dismissed accusations that his country was the “sick man” of Europe.
“Germany is a tired man after a short night and the low-growth expectations are partly a wake-up call,” he said.
Japan is also heavily reliant on exports, in particular cars, sales of which have been helped by the weak yen.
But it is suffering more than Germany in terms of worker shortages as its population falls and birth rates remain low.
Thursday’s data showed that its economy shrank 0.1 percent in the last quarter of 2023, missing market expectations of 0.2 percent growth.
Growth for the third quarter was also revised downwards to negative 0.8 percent.
Japan became the world’s second-largest economy behind the United States in the late 1960s, and during the boom years of the 1970s and ‘80s some projected it would become number one.
But the catastrophic bursting of Japan’s asset bubble in the early 1990s led to several “lost decades” of economic stagnation and deflation.
When in 2010 Japan was overtaken as number two by Asian rival China — whose economy is now around four times larger — it prompted major soul-searching.
While more down to the yen’s slide, falling behind Germany will still be a blow to Japan’s self-esteem and add to the pressure on unpopular Prime Minister Fumio Kishida.
Kishida, reeling from a string of scandals, has already reshuffled his cabinet twice and in November announced a stimulus package worth 17 trillion yen ($118.5 billion).
More pain is to come, as India’s economy, with a burgeoning young population, is projected to overtake Japan in 2026 — then Germany in 2027 — according to the International Monetary Fund.
The Nikkei financial daily said in an editorial last week that the German economy faces its own problems.
“Nevertheless, Japan has not made progress in raising its own growth potential. This situation should be taken as a wake-up call to accelerate neglected economic reforms,” the paper said.