LONDON: As more Saudis connect through their social media profiles and even begin to profit from these platforms, the Kingdom has launched a new licensing system to properly monitor the influencer industry.
From early October, every Saudi and non-Saudi content creator in the Kingdom who earns revenue through advertising on social media must first apply for an official permit from the General Commission for Audiovisual Media (GCAM).
For a fee of SR15,000 (roughly $4,000), content creators will receive a permit lasting three years, during which time they can work with as many private entities as they wish and promote any product or service, as long as it does not violate the Kingdom’s laws or values.
The incoming influencer license “is not a permit to censor or to block,” Esra Assery, CEO at GCAM, told Arab News. “It’s more of a permit to enable the maturity of the sector. We want to help those individuals grow, but grow in a professional way so they can make a career out of (social media revenue).”
The new regulations are being touted as legal protections, both for influencers and businesses wishing to advertise with them, so that rates and contractual obligations are standardized across the industry.
“The market is so unregulated,” said Assery. “We’re not against influencers or those individuals. Actually, we want to enable them. If you check out the new bylaw, it protects them also, because the bylaw regulates their relationship with the advertisers.”
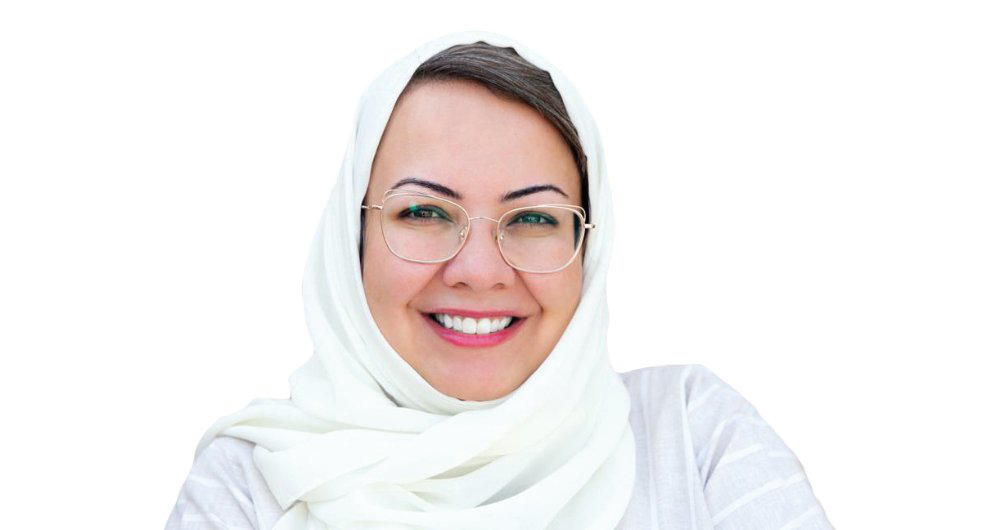

Esra Assery, CEO at Saudi Arabia's General Commission for Audiovisual Media. (Supplied)
Currently, anyone in Saudi Arabia is able to advertise on social media and earn money from deals with private entities — with payments per post climbing into the thousands of riyals, depending on the number of followers an influencer can reach.
Concern has been expressed that introducing permits and regulations will undermine how much money influencers can make and might even constitute censorship. However, GCAM insists the permits are designed to ensure transparency between influencers and their clients.
Saudi influencers, whether based in the Kingdom or abroad, must apply for the permit if they wish to work with a brand — local or international. However, non-Saudi residents in the country must follow a different track.
 After applying to the Ministry of Investment for a permit to work in the country, they can then apply for an influencer permit through GCAM. However, non-Saudi residents must be represented by specific advertising agencies.
After applying to the Ministry of Investment for a permit to work in the country, they can then apply for an influencer permit through GCAM. However, non-Saudi residents must be represented by specific advertising agencies.
“While some influencers may focus on the short-term loss of paying the license fee, there is a huge benefit to licensing coming in as it legitimizes the sector on a national level,” Jamal Al-Mawed, founder and managing director of Gambit Communications, told Arab News.
“This is crucial in the influencer industry as it has been a bit of a wild west for marketing in the past, with no clear benchmarking for rates or contracts.”
Al-Mawed said that the new measures can protect brands that are susceptible to fraud “when they pay huge budgets to influencers who are buying fake followers and fake engagements. This creates a vicious circle, as hard-working content creators are undermined by the bad apples.”
Although the new license is unlikely to solve every issue overnight, “it does create a foundation for more professionalism and accountability,” Al-Mawed added.
In June, non-Saudi residents and visitors to the Kingdom were prohibited from posting ads on social media without a license. Those who ignore the ruling face a possible five-year prison sentence and fines of up to SR5 million.
GCAM announced the ban after finding “violations by numerous non-Saudi advertisers, both residents and visitors, on social media platforms.”
“After checking their data, it was found that they had committed systemic violations, including lack of commercial registrations and legal licenses, and they are not working under any commercial entity or foreign investment license,” the commission said at the time.
Now, with a regulated license, such violations will be easier to monitor and the sector will be better regulated to ensure full transparency.

Businesses such as bakeries or hair salons that hold social media accounts and advertise their own products or services are not covered by the prohibition. (Shutterstock image)
Although Saudi influencers will be able to hold full-time jobs while earning on the side through promotional campaigns on their social media profiles, the law states that non-Saudis can work only in one specific role while residing in the Kingdom.
However, the system does not apply to businesses and entities — such as bakeries or hair salons — that hold social media accounts and advertise their own products or services on these platforms. Only individuals are affected by the new law.
There are certain exceptions, however, such as individuals who have been invited to the country by a ministry or government entity in order to perform, including musicians and entertainers.
With the rise of social media over the past decade, content creators and so-called influencers with thousands of followers on Instagram, TikTok, Snapchat and other platforms have drawn audiences away from traditional outlets, such as television, newspapers and magazines, to new and largely unregulated media.

Sensing the shift in content consumption, advertisers have followed the herd. Crystal-blue waters caressing white, sandy beaches at luxury resorts and scrumptious feasts at the finest restaurants are now commonplace on influencer profiles as businesses rush to take advantage of more “natural-feeling” product placement.
However, regulators have struggled to keep up with this rapid transformation, leaving the process open to legal disputes, exploitation and abuse. That is why authorities elsewhere in the world have also been exploring influencer permits.
Dubai, widely seen as the influencer hub of the Middle East, is among them.
In 2018, the UAE’s National Media Council launched a new electronic media regulation system, which required social media influencers to obtain a license to operate in the country.
The cost of the annual license is 15,000 AED (roughly $4,000). Those who fail to obtain or renew the license can face penalties including a fine of up to 5,000 AED, a verbal or official warning, and even closure of their social media accounts.
The rules apply to influencers visiting the UAE as well. They must either have a license or be signed up with an NMC-registered influencer agency to operate in the country.
With Saudi Arabia progressing in the entertainment and creative industries, the introduction of the license is viewed as a step in the right direction.
“It’s great news for the industry,” said Al-Mawed. “When someone is licensed by the government to offer their services, that gives them a level of safety and trust and can help filter out the scammers who prefer to fly under the radar.”





















