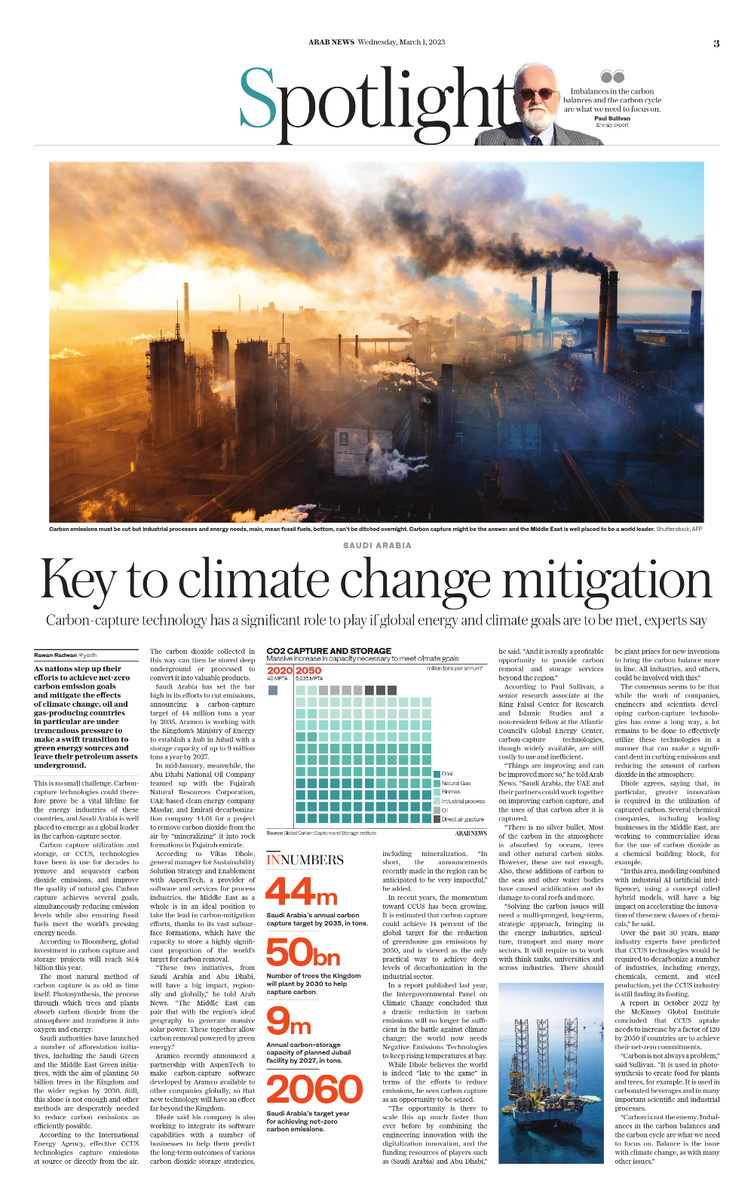
RIYADH: As nations step up their efforts to achieve net-zero carbon emission goals and mitigate the effects of climate change, oil and gas-producing countries in particular are under tremendous pressure to make a swift transition to green energy sources and leave their petroleum assets underground.
This is no small challenge. Carbon-capture technologies could therefore prove be a vital lifeline for the energy industries of these countries, and Saudi Arabia is well-placed to emerge as a global leader in the carbon-capture sector.
Carbon capture utilization and storage, or CCUS, technologies have been in use for decades to remove and sequester carbon dioxide emissions, and improve the quality of natural gas. Carbon capture achieves several goals, simultaneously reducing emission levels while also ensuring fossil fuels meet the world’s pressing energy needs and providing a mechanism to help meet net-zero goals by 2050.
According to Bloomberg, global investment in carbon capture and storage projects will reach $6.4 billion this year.
The most natural method of carbon capture is as old as time itself: Photosynthesis, the process through which trees and plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and transform it into oxygen and energy.

Saudi authorities have launched a number of afforestation initiatives, including the Saudi Green and the Middle East Green initiatives, with the aim of planting 50 billion trees in the Kingdom and the wider region as part of the Middle East Green Initiative, in partnership with the countries. Still, this alone is not enough and other methods are desperately needed to reduce carbon emissions as efficiently possible.
According to the International Energy Agency, effective CCUS technologies capture emissions at source or directly from the air. The carbon dioxide collected in this way can then be stored deep underground or processed to convert it into valuable products.
The IEA is aware of more than 300 carbon-capture facilities being developed worldwide, including the Gorgon Carbon Dioxide Injection Project in Australia; two capture facilities linked to the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line in Canada; the first large-scale bioenergy and carbon-capture project in Japan; capture facilities at the Sinopec chemical plant and at the Guohua Jinjie coal-fired power plant in China; and Saudi Aramco’s Uthmaniyah project and Hawiyah gas plant.
Saudi Arabia has set the bar high in its efforts to cut emissions, announcing a carbon-capture target of 44 million tons a year by 2035. Aramco is working with the Kingdom’s Ministry of Energy to establish a hub in Jubail with a storage capacity of up to 9 million tons a year by 2027.
In mid-January, meanwhile, the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company teamed up with the Fujairah Natural Resources Corporation, UAE-based clean energy company Masdar, and Emirati decarbonization company 44.01 for a project to remove carbon dioxide from the air by “mineralizing” it into rock formations in Fujairah emirate.
According to Vikas Dhole, general manager for Sustainability Solution Strategy and Enablement with AspenTech, a provider of software and services for process industries, the Middle East as a whole is in an ideal position to take the lead in carbon-mitigation efforts, thanks to its vast subsurface formations, which have the capacity to store a highly significant proportion of the world’s target for carbon removal.
“These two initiatives from Saudi Arabia and Abu Dhabi will have a big impact, regionally and globally,” he told Arab News. “The Middle East can pair that with the region’s ideal geography to generate massive solar power. These together allow carbon removal powered by green energy.”

Middle East is well placed to be a world leader in carbon capture. (AFP)
Aramco recently announced a partnership with AspenTech to make carbon-capture software developed by Aramco available to other companies globally, so that new technology will have an effect far beyond the Kingdom.
Dhole said his company is also working to integrate its software capabilities with a number of businesses to help them predict the long-term outcomes of various carbon dioxide storage strategies, including mineralization.
“In short, the announcements recently made in the region can be anticipated to be very impactful,” he added.
In recent years, the momentum for CCUS has been growing. It is estimated that carbon capture could achieve 14 percent of the global target for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 2050, and is viewed as the only practical way to achieve deep levels of decarbonization in the industrial sector.
In a report published last year, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change concluded that a drastic reduction in carbon emissions will no longer be sufficient in the battle against climate change; the world now needs Negative Emissions Technologies to keep rising temperatures at bay.
While Dhole believes the world is indeed “late to the game” in terms of the efforts to reduce emissions, he sees it as an opportunity to be seized.
“The opportunity is there to scale this up much faster than ever before by combining the engineering innovation with the digitalization innovation, and the funding resources of players such as (Saudi Arabia) and Abu Dhabi,” he said. “And it is really a profitable opportunity to provide carbon removal and storage services beyond the region.
INNUMBERS
• 44m Saudi Arabia’s annual carbon capture target by 2035 in tons.
• 50bn Number of trees the Kingdom will plant by 2030 to help capture carbon.
• 9m Annual carbon storage capacity of planned Jubail facility by 2027 in tons.
• 2060 Saudi Arabia’s target year for achieving net-zero carbon emissions.
“Carbon-capture utilization and storage are now proven, technologically, and rapidly improving, economically. They will become one of the key ‘silver bullets,’ if they are funded to the extent that the projects can be done in a completely digital manner, so that the earlier projects will inform future projects to keep improving technology-wise, economics-wise, and speed of execution-wise.
“This all can be done with an end-to-end digital pathway, as AspenTech has introduced to the industry.”
According to Paul Sullivan, a senior research associate at the King Faisal Center for Research and Islamic Studies and a non-resident fellow at the Atlantic Council’s Global Energy Center, carbon-capture technologies, though widely available, are still costly to use and inefficient.
“Things are improving and can be improved more so,” he told Arab News. “Saudi Arabia, the UAE and their partners could work together on improving carbon capture, and the uses of that carbon after it is captured. There is no silver bullet.
“Most of the carbon in the atmosphere is absorbed by oceans, trees and other natural carbon sinks. However, these are not enough. Also, these additions of carbon to the seas and other water bodies have caused acidification and do damage to coral reefs and more.
“Solving the carbon issues will need a multipronged, long-term, strategic approach, bringing in the energy industries, agriculture, transport and many more sectors. It will require us to work with think tanks, universities and across industries. There should be giant prizes for new inventions to bring the carbon balance more in line. All industries, and others, could be involved with this.”
The consensus seems to be that while the work of companies, engineers and scientists developing carbon-capture technologies has come a long way, a lot remains to be done to effectively utilize these technologies in a manner that can make a significant dent in curbing emissions and reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.

Imbalances in the carbon balances and the carbon cycle are what we need to focus on,” said Paul Sullivan, Energy expert.
Dhole agrees, saying that in particular, greater innovation is required in the “utilization” of captured carbon. Several chemical companies, including leading businesses in the Middle East, are working to commercialize ideas for the use of carbon dioxide as a chemical building block, for example.
“In this area, modeling combined with industrial AI (artificial intelligence), using a concept called hybrid models, will have a big impact on accelerating the innovation of these new classes of chemicals,” he said.
Over the past 30 years, many industry experts have predicted that CCUS technologies would be required to decarbonize a number of industries, including energy, chemicals, cement, and steel production, yet the CCUS industry is still finding its footing.
A report in October 2022 by the McKinsey Global Institute concluded that CCUS uptake needs to increase by a factor of 120 by 2050 if countries are to achieve their net-zero commitments.
The 2015 Paris climate agreement calls for a balance between reductions in carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and earthbound carbon sinks, in an effort to reduce the confusion over the relative qualities and benefits of carbon in its various forms.
“Carbon is not always a problem,” said Sullivan. “It is used in photosynthesis to create food for plants and trees, for example. It is used in carbonated beverages and in many important scientific and industrial processes.
“Carbon is not the enemy. Imbalances in the carbon balances and the carbon cycle are what we need to focus on. Balance is the issue with climate change, as with many other issues.”