JEDDAH: Hajj, the annual pilgrimage to the holy shrines in Makkah, is one of the oldest regular movements of people over long distances and one of the largest reoccurring religious mass gatherings globally.
Prior to the current coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, Hajj was affected by various infectious diseases throughout history, which at times suspended the pilgrimage, limited pilgrims’ travel to the holy city, and claimed victims from among the pilgrims as well as from Makkah’s population.
One of the first historically recorded plagues in Makkah was mentioned by prominent Muslim scholar and historian Ibn Kathir. In his book, “Al-Bidāya wa-n-Nihāya” (“The Beginning and the End”), he said that an epidemic known as Al-Mashri hit the city of Makkah in 968, killing many people as well as travelers’ camels, while pilgrims who were able to complete their pilgrimage died soon thereafter.
Several historians indicated that convoys of pilgrims witnessed a significant decline during that period, especially from regions hit by the epidemic, due to the deteriorating social and economic circumstances caused by the disease or other diseases in later periods.
Hajj was later transformed by a global revolution in transportation in the 19th century. New means of transportation facilitated movements of larger groups of people worldwide, making the transmission of diseases faster and severely unmanageable.
That same century was plagued with epidemics, and global life expectancy declined to just 29 years of age as different diseases spread and killed millions throughout the world. The Hijaz region saw its share of these epidemics, particularly cholera, which repeatedly hit the area through India’s pilgrims.
Muslims have long known about the efficacy of quarantine, since the Prophet Muhammad said in the hadith, “If you get wind of the outbreak of plague in a land, do not enter it; and if it breaks out in a land in which you are, do not leave it.” Pilgrims were often quarantined upon their return in some countries during epidemics, such as in Egypt during the Ottoman Empire.
Quarantine measures were not yet part of a widespread public health policy back then, however, and the world was not familiar with global disease breakouts. Unlike the plague, cholera was a completely new disease, of which humanity only had very limited knowledge.
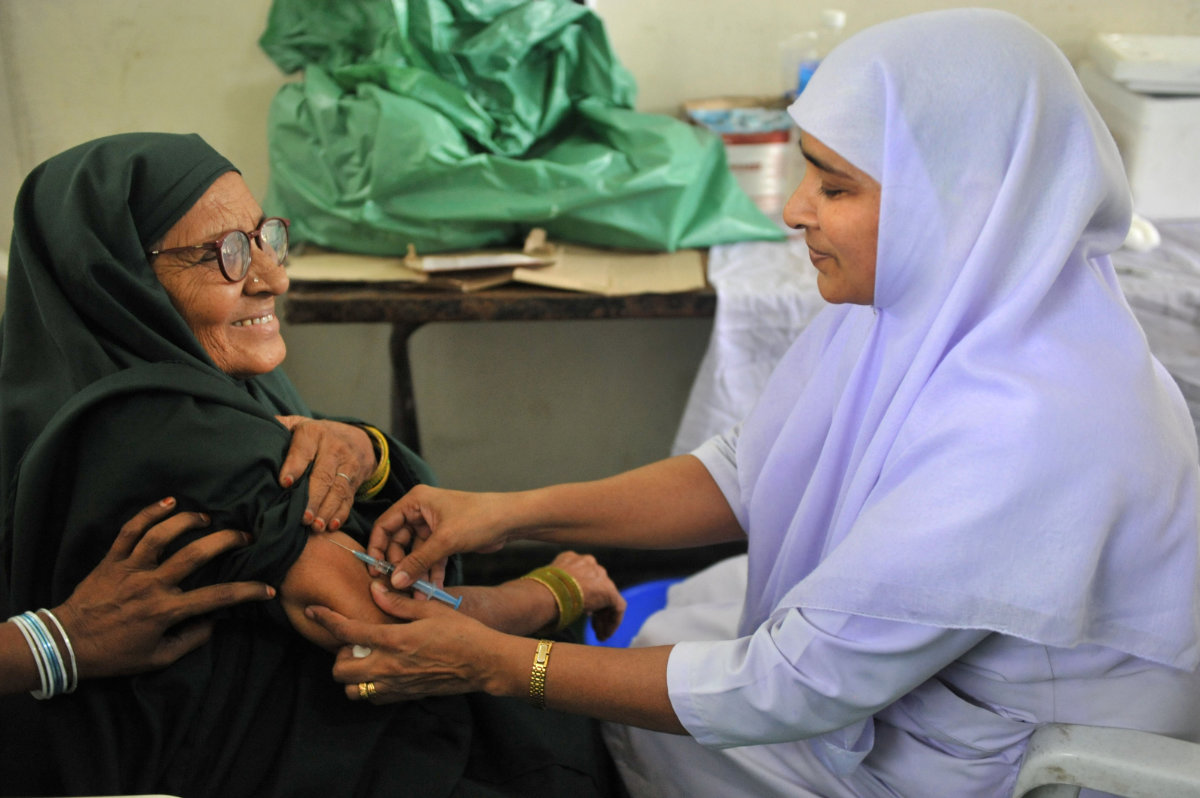
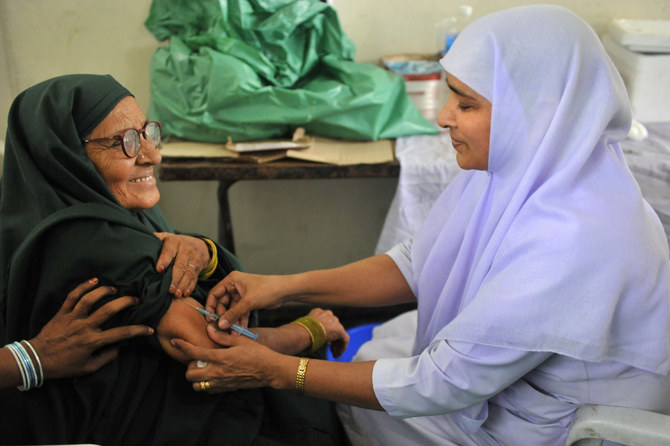
An Indian health worker (R) administers a meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine to a Hajj pilgrim in Hyderabad, 2010. (Getty Images/AFP)
Cholera threatened Islamic pilgrimage routes, especially after the opening of the Suez Canal, which facilitated the spread of diseases through ships and railways and forced pilgrims to stay in quarantine for 15 days in the canal or in the Red Sea before heading to Hijaz.
The disease first appeared in the Arabian Peninsula in 1821. Yet, it did not reach Hijaz until 1831, when it broke out for the first time in Makkah, causing the death of at least three-quarters of the pilgrims arriving at the time. It was called the “Indian epidemic,” and it moved with astonishing swiftness.
According to the book “Histories of Health in South Asia” published by Indiana University Press, cholera killed 20,000 people in Makkah in 1831, and subsequent epidemics came to the region of the holy cities in 1841, 1847, 1851, 1856–57, and 1859.
In 1840, the Ottoman Empire enforced quarantine, organizing stops at border crossings and in cities near the holy shrines.
Politics was never too far from the medical policies of Hajj in Hijaz. The massive outbreak of the disease forced British and European colonial powers to pay attention to this crisis and include it in their international politics agenda — not so much to protect the pilgrims as to safeguard their colonies and geopolitical and economic interests. This continued throughout the colonial period, from the late 19th into the early 20th century.
Colonial powers pushed for a series of large-scale international meetings to deal with the threat of cholera. The first was held at Constantinople in 1866, and it eventually became known simply as the Cholera Conference.
British policy, however, contradicted the scientific findings of the Cholera Conference. For a long time, the British held that Indian cholera was not a contagious disease, denying the efficacy of cordons and the quarantine of ships following the opening of the Suez Canal, which resulted in a huge loss of life that could have been avoided.
FASTFACT
20,000 people were killed by cholera in Makkah in 1831.
Therefore, although pilgrims were often blamed for being the source of cholera, the worldwide spread of the disease was caused by colonialism, capitalism and new technologies, with pilgrims unwittingly carrying the disease and falling victim to it.
In 1895, the first directorate of health was established in Makkah. Gradually, with the development first of sanitation and then of countermeasures like vaccines and antibiotics, the way the world interfaced with epidemics drastically changed.
In the early 1950s, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia built a quarry for pilgrims outside the city of Jeddah, the location of what would later come to be the King Abdul Aziz Hospital.
Between Saudi Arabia’s internationally recognized success in handling the COVID-19 health crisis and the death of tens of thousands due to cholera in 1865, the Kingdom has earned over 95 years of experience in managing disease.
“Saudi Arabia has acquired extensive experience in public health, especially as it has been hosting large numbers of pilgrims during Hajj and Umrah seasons over the years,” Dr. Wael Bajahmoom, consultant in infectious diseases and head of the internal medicine departments at King Fahd Hospital in Jeddah, told Arab News.
The Kingdom’s history has equipped modern Saudi authorities with significant experience in managing crowds and controlling diseases.
A recently issued report by the Hajj and Umrah Research Institute indicated that infectious diseases still represent a real threat to the current Hajj seasons.
It showed that between 26-60.5 percent of reported cases in previous Hajj seasons were respiratory diseases such as colds and pneumonia, while the rest were digestive diseases such as intestinal flu, diarrhea and meningitis. The death rate due to infectious diseases during Hajj ranged from 1.08-13.67 percent, with an average of 7.1 percent.
Bajahmoom noted that Saudi Arabia favors the policy of “prevention is better than cure,” which was especially highlighted in its exemplary handling of the COVID-19 pandemic, during which the government limited Hajj to immune local pilgrims.
“The Kingdom is keen on maintaining the safety of worshipers and visitors to the holy sites, and one of the basics of safety is prevention, which is vaccination. The important role vaccines have played in light of many medical crises over the decades is undeniable,” Bajahmoom added.
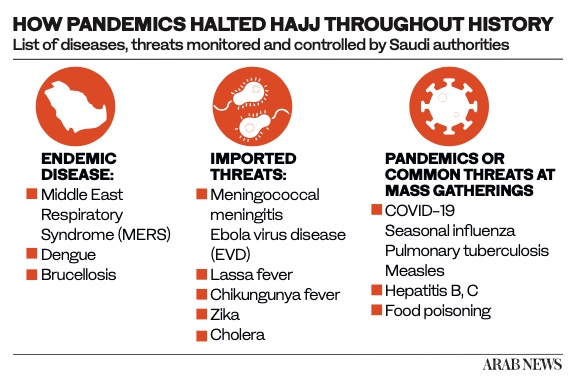
One such crisis was meningitis, which is highly transmissible in gatherings such as those at the holy sites in Makkah. Vaccines were essential in curbing its spread.
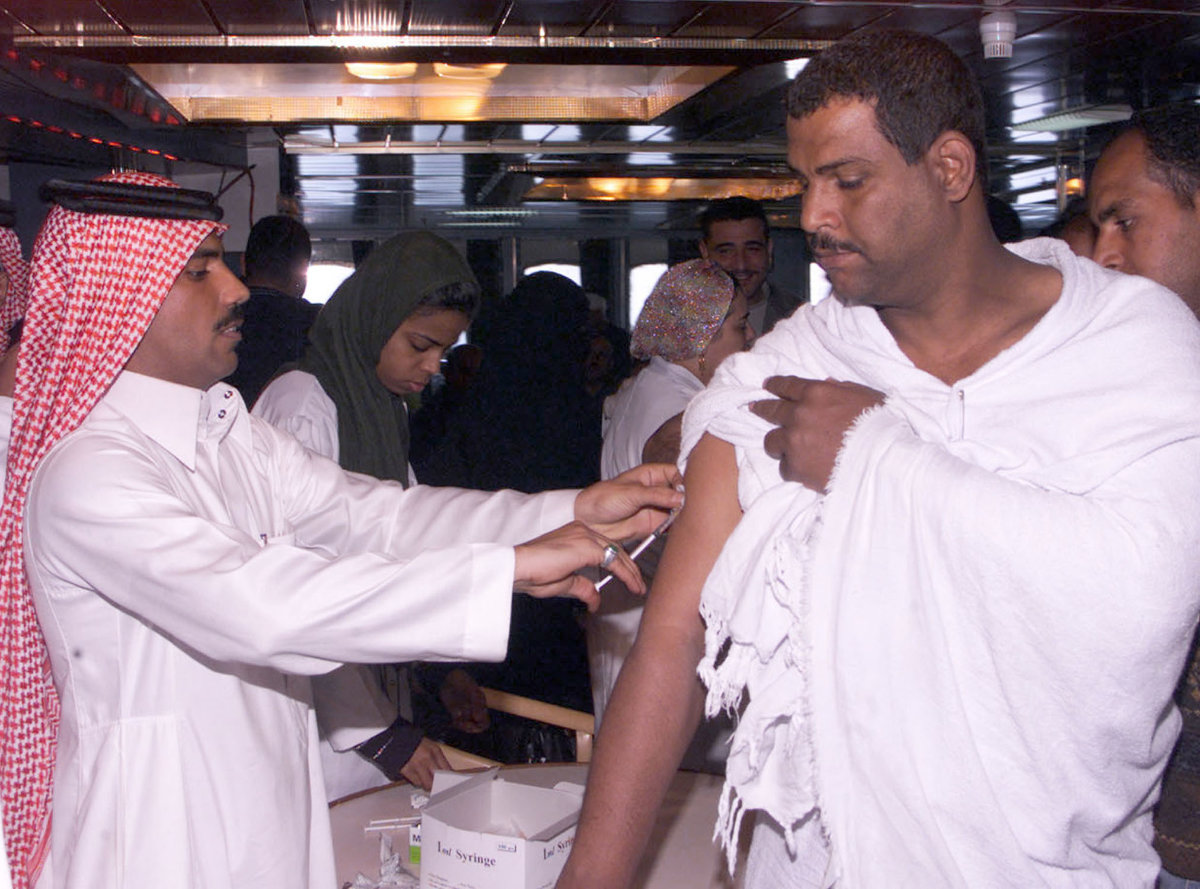
According to the UK-based Meningitis Research Foundation, epidemics of meningitis have been linked to the Hajj pilgrimage, with cases of the disease also occurring worldwide after pilgrims returned to their own countries. Since then, Saudi Arabia has made vaccination against the disease compulsory for entry into the Kingdom during Hajj and Umrah since 2002. No Hajj-related outbreaks of the disease have been reported ever since.
The Public Health Concerns 2019 report by the Saudi Ministry of Health, the year in which the Kingdom received international pilgrims for the last time before the current COVID-19 pandemic, indicated that the meningitis vaccine was mandatory for everyone in the Hajj area; that polio and yellow fever vaccines were required for pilgrims from certain countries; and that the seasonal influenza vaccine was optional but highly recommended.
Other viruses and diseases that the Ministry of Health warned of included dengue fever, polio, pulmonary tuberculosis, hemorrhagic fevers including Ebola and Lassa fever, measles, Zika virus, blood-borne viruses, and food and water-borne diseases.
Bajahmoom explained that the vaccine lists for pilgrims were determined by specific factors, such as the widespread nature of an epidemic in a given region or its presence in the world as a whole, and environmental factors that would facilitate the spread of certain diseases such as a particular season or weather changes.
An Indian health worker (R) administers a meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine to a Hajj pilgrim in Hyderabad, 2010. (Getty Images/AFP)
“With the outbreak of COVID-19 this year, the primary vaccine for this Hajj season was the one against this disease,” he noted.
Saudi Arabia has faced various epidemics and virus outbreaks since meningitis. In 2009, with the spread of the swine flu, Saudi Arabia decided to prevent the elderly, children and pilgrims with chronic diseases from performing Hajj that year.
Moreover, with the escalation of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in 2013, Saudi Arabia urged elderly and chronically ill Muslims to refrain from performing Hajj, as the disease had already killed dozens of people in the Kingdom.
Furthermore, during the Ebola outbreak in Africa between 2014 and 2016, in which 11,300 people died, Saudi Arabia made specific contingency plans that included deploying medical staff at airports and setting up isolation units as nearly 3 million Muslims from across the world flocked to perform Hajj. It also suspended pilgrimage visas for Guinea, Sierra Leone, and Liberia — the three worst-affected countries.
With the spread of COVID-19 in early 2020, which claimed thousands of lives worldwide, dozens of workers began sterilizing the floors of the Grand Mosque in Makkah. Saudi Arabia also decided to suspend the entry of pilgrims to the country and enforced health measures for performing Umrah and Hajj — a decision that was welcomed by the World Health Organization (WHO).
“Saudi Arabia played a major role in combating epidemics both locally and internationally,” said Bajahmoom. “Its cooperation with the rest of the world did not stop with the exchange of research but also included medical and financial support to neighboring countries, as well as those farther away.”
One of the most important contributors to international scientific research is the Ministry of Health’s Global Center for Mass Gatherings Medicine, which works hand-in-hand with the WHO in the health management of mass gatherings and is considered one of the world’s few centers specialized in this area.
“Having almost two years of experience of controlling COVID-19 in addition to the Kingdom’s accumulated experience gives us extraordinary capabilities to combat any future health issues,” Bajahmoom said.
As Saudi Arabia approaches herd immunity within months, Bajahmoom hopes that the Kingdom will soon welcome international pilgrims again.
“This pandemic is only one of many crises that we have faced, and it will pass in time. We will look to it as a memory that will equip us with strength in the future.”