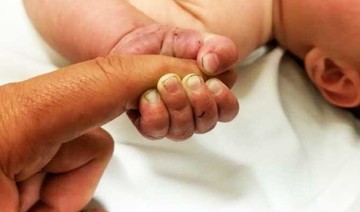
HELENA, Montana: A grizzly bear pulled a woman from her tent in a small Montana town in the middle of the night and killed her, wildlife officials said.
Then fellow campers used bear spray to force the bruin out of the area.
Leah Davis Lokan, 65, of Chico, California, was on a long-distance bicycling trip and had stopped in the western Montana town of Ovando when she was killed early Tuesday, said Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks officials as they provided more details about the attack.
Lokan was killed on the bear’s second visit to the site where she and two fellow bicyclists were camping near the post office, officials said.
The approximately 400-pound (181-kilogram) grizzly first awakened the campers about 3 a.m., officials said. They took food out of their tents, secured it and went back to sleep, they said.
Surveillance video from a business in town showed the bear about a block from the post office about 15 minutes later, wildlife officials said.
About 4:15 a.m., the sheriff’s office received a 911 call after two people in a tent near the victim’s were awakened by sounds of the attack, Powell County Sheriff Gavin Roselles said. They discharged their bear spray, and the bear ran away.
The bear is also believed to have entered a chicken coop in town that night, killing and eating several chickens.
Efforts to find and kill the bear entered a third day Thursday. Wildlife officials stopped the helicopter flights that were used in the initial search for the grizzly and set five large traps — made out of culverts and baited with roadkill — in and around Ovando. That included traps near the chicken coop that the bear raided the night Lokan was killed.
Investigators got DNA left by the bear at the scene of the attack and could compare it with any bruin they are able to trap. Bear specialists and game wardens also were stationed near the traps to shoot the animal if the opportunity arises, said Greg Lemon, Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks spokesperson.
“Our best chance would be if the bear comes back and tries to get another chicken or some more food around town,” Lemon said. “Our wardens, they feel like they could readily identify the bear that they saw on the (surveillance footage) and if they saw that bear at the trap and had a clear shot at it, they might choose to do that.”
Lokan, a registered nurse who had worked at a hospital in Chico, had looked forward to the Montana bike trip for months, said Mary Flowers, a friend of the victim’s from Chico. Lokan had taken previous long-distance bike trips and on this one was accompanied by her sister and a friend, Flowers said.
“She was talking about her summer plans — this wonderful wild adventure, riding her bike on, I don’t know, a 400-mile trip or something,” Flowers said. “A woman in her 60s, and she’s doing this kind of stuff — she had a passion for life that was out of the ordinary.”
People who camp in grizzly bear country — whether deep in the woods or in a developed campground — are advised to keep food and scented products like toothpaste away from their campsites at all times and to cook elsewhere.
If a bear comes through a campsite, it’s important to stay on lookout for the animal to return, Lemon said.
“You’ve secured your food, stay awake, stay vigilant and be ready,” he said. “Having bear spray is important, and they did, but we don’t know if the victim did.”
Grizzly bears have run into increasing conflict with humans in the Northern Rockies over the past decade as the federally protected animals expanded into new areas and the number of people living and recreating in the region grew. That has spurred calls from elected officials in Montana and neighboring Wyoming and Idaho to lift protections so the animals could be hunted.
Ovando, about 60 miles (97 kilometers) northwest of Helena, is a community of fewer than 100 people at the edge of the sprawling Bob Marshall wilderness.
North of Ovando lies an expanse of forests and mountains, including Glacier National Park that stretches to Canada and is home to an estimated 1,000 grizzlies. It’s the largest concentration of the bruins in the contiguous US
Fatal attacks are rare in the region. There have been three in the last 20 years, including Tuesday’s mauling, according to the US Fish and Wildlife Service.
In 2001, a hunter was killed by a grizzly with two cubs while he was gutting an elk at a wildlife management area west of Ovando. The three animals were shot and killed by wildlife officials days later. Over the past 20 years, there have been eight fatal maulings of people by grizzlies from a separate population of about 700 bears in and around Yellowstone National Park. In April, a backcountry guide was killed by a grizzly bear while fishing along the park’s border in southwestern Montana.
Bears that attack people are not always killed if the mauling resulted from a surprise encounter or the bear was defending its young. But the bear involved in Lokan’s death is considered a public safety threat because of the circumstances of the attack, Lemon said.
Bear pulls woman out of her tent, kills her in Montana
https://arab.news/bykp7
Bear pulls woman out of her tent, kills her in Montana

- Leah Davis Lokan, 65, of California, was on a long-distance bicycling trip and had stopped in Montana when she was killed Tuesday
- The bear also entered a chicken coop in town that night, killed and ate several chickens
Turkiye and Germany in spicy feud over doner kebab

- The humble doner has its origins in Turkiye but is also beloved in Germany after being introduced there by Turkish migrants
BERLIN: A spicy row has erupted between Turkiye and Germany over what constitutes a doner kebab, with Berlin objecting to a Turkish push for protected status for the iconic snack.
The humble doner, made with thinly sliced meat cooked on a vertical rotisserie, has its origins in Turkiye but is also beloved in Germany after being introduced there by Turkish migrants.
In April, the International Doner Federation (Udofed), based in Turkiye, filed an application to the European Commission to grant the doner kebab Traditional Speciality Guaranteed (TSG) status.
From the exact meat and spices to the thickness of the knife used to slice the meat, Udofed wants the definition of the doner to adhere to a strict list of criteria.
If successful, the application would bar businesses in the European Union from using the name doner kebab unless it met the criteria, giving it the same protected status as Italy’s bufala mozzarella or Spain’s Serrano ham.
In its application, Udofed hails the doner’s origins during the Ottoman Empire, citing a recipe found in manuscripts dating from 1546.
But that has sparked an uproar in Germany, where the doner has become an emblem of the country’s large Turkish community, descended from “guest workers” invited under a massive economic program in the 1960s and 70s.
The German capital even claims the doner kebab to be “a Berlin invention.”
“It happened in Berlin: Legend has it, Kadir Nurman was the first to put the meat in flatbread in 1972 and invented the version of doner that is so beloved in Germany,” according to the city’s website.
“The doner belongs to Germany. Everyone should be allowed to decide for themselves how it is prepared and eaten here. There is no need for any guidelines from Ankara,” said Agriculture Minister Cem Ozdemir, whose parents migrated from Turkiye.
Germany’s agriculture ministry viewed Turkiye’s application “with astonishment,” a spokesman said.
If this “imprecise” and “contradictory” proposal is accepted by the commission, “the economic consequences for the German gastronomic sector would be enormous,” the spokesman said.
The DEHOGA hotel and catering union also warned of a “lack of clarity and transparency,” “difficulties with legal definitions” and “a raft of future disputes.”
The German government lodged an objection to the Turkish application just ahead of the European deadline on Wednesday.
In Berlin, where the doner has long surpassed the sausage as the convenience snack of choice, Birol Yagci is concerned that the Turkish version only allows beef, lamb or chicken.
“Here it’s different. The traditional recipe is made with veal,” the chef at a Turkish restaurant in the city’s Kreuzberg district said.
Behind him, two columns of meat glisten on their spits, one ironically made from turkey — the bird — which would also not be allowed under the new definition.
“People eat doners all over the world. Turkiye can’t just dictate to others what they should do,” said the 50-year-old.
“My customers won’t want to eat lamb. It has a very particular taste,” said Arif Keles, 39, owner of a doner kiosk, whose customers include Germany’s national football team.
Keles too said he would sooner charge the name of his products than alter his recipes.
“My customers know what they’re eating, so as long as the quality is there it doesn’t matter what you call it,” he said.
Germany accounts for two-thirds of doner kebab sales in Europe with the market worth 2.4 billion euros ($2.6 billion) a year, according to the Association of Doner Manufacturers in Europe (ATDID).
In April, German President Frank-Walter Steinmeier even took Keles with him on a visit to Turkiye as a symbol of the close ties between the two countries.
Keles arrived to serve his wares at an official reception armed with a huge spit of veal, much to the “curiosity” of his guests.
“In Turkiye, doner is eaten on a plate. I served it Berlin-style, on bread with sauce, and they loved it,” said the chef, whose grandfather emigrated from Turkiye to Germany.
But the European Commission must now decide whether doner diversity will win the day, according to the institution’s agriculture spokesman Olof Gill.
If the objection to the Turkish application is found to be admissible, the two parties will have a maximum of six months to reach a compromise, he said.
NASA telescope spots a super Jupiter that takes more than a century to go around its star

- The planet is roughly the same diameter as Jupiter, but with six times the mass
- One big difference: It takes this planet more than a century, possibly as long as 250 years, to go around its star
CAPE CANAVERAL, Florida: A super Jupiter has been spotted around a neighboring star by the Webb Space Telescope — and it has a super orbit.
The planet is roughly the same diameter as Jupiter, but with six times the mass. Its atmosphere is also rich in hydrogen like Jupiter’s.
One big difference: It takes this planet more than a century, possibly as long as 250 years, to go around its star. It’s 15 times the distance from its star than Earth is to the sun.
Scientists had long suspected a big planet circled this star 12 light-years away, but not this massive or far from its star. A light-year is 5.8 trillion miles. These new observations show the planet orbits the star Epsilon Indi A, part of a three-star system.
An international team led by Max Planck Institute for Astronomy’s Elisabeth Matthews in Germany collected the images last year and published the findings Wednesday in the journal Nature.
Astronomers directly observed the incredibly old and cold gas giant — a rare and tricky feat — by masking the star through use of a special shading device on Webb. By blocking the starlight, the planet stood out as a pinpoint of infrared light.
The planet and star clock in at 3.5 billion years old, 1 billion years younger than our own solar system, but still considered old and brighter than expected, according to Matthews.
The star is so close and bright to our own solar system that it’s visible with the naked eye in the Southern Hemisphere.
Don’t bet on life, though.
“This is a gas giant with no hard surface or liquid water oceans,” Matthews said in an email.
It’s unlikely this solar system sports more gas giants, she said, but small rocky worlds could be lurking there.
Worlds similar to Jupiter can help scientists understand “how these planets evolve over giga-year timescales,” she said.
The first planets outside our solar system — dubbed exoplanets — were confirmed in the early 1990s. NASA’s tally now stands at 5,690 as of mid-July. The vast majority were detected via the transit method, in which a fleeting dip in starlight, repeated at regular intervals, indicates an orbiting planet.
Telescopes in space and also on the ground are on the hunt for even more, especially planets that might be similar to Earth.
Launched in 2021, NASA and the European Space Agency’s Webb telescope is the biggest and most powerful astronomical observatory ever placed in space.
Cyprus displays once-looted antiquities dating back thousands of years

- The returned artifacts numbering around 60 were part of a larger haul of 250 antiquities that German authorities had seized from Turkish art dealer Aydin Dikmen in 1997
NICOSIA: Cyprus on Monday put on display artifacts — some of them thousands of years old — that were returned after a Turkish art dealer looted them from the ethnically divided island nation decades ago.
Aydin Dikmen took the artifacts from the country’s breakaway north in the years after Cyprus’ split in 1974, when Turkiye invaded following a coup mounted by supporters of union with Greece. The antiquities were kept in Germany after authorities there seized them in 1997, and protracted legal battles secured their repatriation in three batches, the last one this year.
Addressing the unveiling ceremony at Cyprus’ archaeological museum, President Nikos Christodoulides said the destruction of a country’s cultural heritage as evidenced in recent conflicts becomes a “deliberate campaign of cultural and religious cleansing that aims to eliminate identity.”
Among the 60 most recently returned artifacts put on display include jewelry from the Chalcolithic Period between 3500-1500 B.C. and Bronze Age bird-shaped idols.
Antiquities that Dikmen also looted but were returned years ago include 1,500-year-old mosaics of Saints Luke, Mark, Matthew and James. They are among the few examples of early Christian works to survive the Iconoclastic period in the 8th and 9th centuries when most such works were destroyed.
Cyprus’ authorities and the country’s Orthodox Church for decades have been hunting for the island’s looted antiquities and centuries-old relics from as many as 500 churches in open auctions and on the black market.
The museum’s antiquities curator, Eftychia Zachariou, told the ceremony that Cyprus in recent years has benefited from a shift in thinking among authorities in many countries who now opt to repatriate antiquities of dubious provenance.
Baby flamingos saved from drought-decimated lake in Algeria

OUM EL BOUAGHI: Around 300 pink flamingo chicks were rescued by volunteers in eastern Algeria after the salt lake where they hatched dried up following years of high temperatures and drought.
Thousands of flamingos migrate each year to nest in Lake Tinsilt, located around 450 kilometers (about 280 miles) southeast of the capital Algiers.
It is one of the largest wetlands in the country, with an area of more than 20 square kilometers.
“Barely a month ago there was water here,” volunteer Mourad Ajroud told AFP on Friday, pointing to what is now a vast expanse of cracked earth littered with the carcasses of dead birds.
The disappearance of the lake, which locals and Algerian media attribute to high temperatures and a years-long drought, has driven the adult flamingos away.
They left behind their unhatched eggs and defenseless chicks, dozens of which have died from hunger, thirst, poaching and wolf attacks.
A group of volunteers provided their cars and trucks to transfer 283 pink flamingos about 50 kilometers away to Lake Mahidiya, about 50 kilometers away.
The wetland near Ain Mlila remains flush thanks to a steady flow of water from nearby rivers and lakes.
The rescue operation was initiated by local amateur photographer Tarek Kawajlia, who documents the wildlife in his area, and noticed the decrease in the size of the lake and the flight of birds.
The volunteers carry out “morning and evening patrols to follow the chicks until they recover and are able to fly, so that they can return next year to the sabkha (marsh) and life can resume its normal course,” Kawajlia told AFP.
Ajroud, 53, said the group was not able to save all the birds.
“We couldn’t transport them all,” he said sadly, as another volunteer takes an injured bird to a veterinary clinic.
A few hours after the chicks were released at their new habitat, some adult birds joined them.
“The operation was successful and the parents found their little ones in a magnificent scene,” Kawajlia said in a comment on one of his photos posted to Facebook.
Lake Tinsilt is one of the around 50 bodies of water in Algeria declared wetlands of international importance under the Ramsar international environment treaty to protect wetlands.
Last year, about a hundred pink flamingos died at Lake Telamine in western Algeria’s Oran province due to wastewater pollution, according to environmental activists.
Artist swaps British Museum coin with fake

- Ile Sartuzi said the idea came to him when he saw a museum volunteer handing visitors coins to handle
LONDON: A Brazilian conceptual artist swapped a historic British coin for a fake in the British Museum to highlight the large number of foreign objects it holds.
Ile Sartuzi said the idea came to him when he saw a museum volunteer handing visitors coins to handle.
He asked for an English Civil War-era silver coin because “It is one of the few British things in the British Museum” and then created a diversion while he swapped it for the fake.
Sartuzi told Reuters he deposited the original coin in the museum’s collection box on the way out. The Art Newspaper first reported his act, which he recounted in a video made for his master’s degree at Goldsmiths, University of London.
The British Museum said it would inform police about the incident, which took place in June.
“This is a disappointing and derivative act that abuses a volunteer led service aimed at giving visitors the opportunity to handle real items and engage with history,” a museum spokesperson said when asked for comment.
Sartuzi said institutions such as the British museum and France’s Louvre view themselves as the “holders of the treasures of humanity. The problem is that these institutions are the basis of imperialist cultures that looted a lot of these objects from the global south and world.”
The British Museum has been under scrutiny over the way it acquired some of the artefacts it holds, with some countries asking for pieces to be returned. Examples include the Parthenon Sculptures and Nigeria’s bronzes looted by British troops in 1897. It did not respond to Sartuzi’s allegations.
Sartuzi, who has exhibited in Brazil, Portugal and London, said he had sought advice from an art lawyer before swapping the coin.
The Museum dismissed an employee a year ago and ordered a review of security after it discovered hundreds of items had been stolen from its collection or were missing.