RIYADH: Another week, another huge green hydrogen project announcement in the Middle East. This time, it was Egypt’s turn. The most populous Arab nation is planning to invest up to $4 billion in a project to create hydrogen through electrolysis powered by renewable energy, Egyptian Minister of Electricity and Renewable Energy Mohamed Shaker said on June 14.
The disclosure follows a flurry of announcements last month, including Oman’s plan for the biggest green hydrogen plant in the world, to be built over the coming 27 years along with 25 GW of solar and wind power.
Also in May, Dubai launched the region’s first industrial scale solar-powered green hydrogen plant, a demonstration facility built by Siemens Energy and Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA).
Later in the month, Abu Dhabi got in on the act as it revealed plans for a $1 billion facility with capacity to produce 200,000 tons of green ammonia from 40,000 tons of green hydrogen (hydrogen is turned into ammonia for long-distance transport before being transformed back for use).
As for Saudi Arabia, it unveiled plans in July last year for a green hydrogen facility powered by 4 GW of wind and solar, the world’s largest such project at the time. The $5 billion plant will be built by Air Products, ACWA Power and Neom and will be capable of producing 650 tons of green hydrogen a day, enough to run about 20,000 hydrogen-fueled buses.
“The Middle East has joined the green hydrogen wave with mega project announcements,” said Flor Lucia De la Cruz, a senior research analyst for hydrogen and emerging technologies at Wood Mackenzie. “The Middle East has now positioned itself to become a key player in the green hydrogen economy leveraging its solar and wind capabilities and strategic position in between the European and Asian markets.”
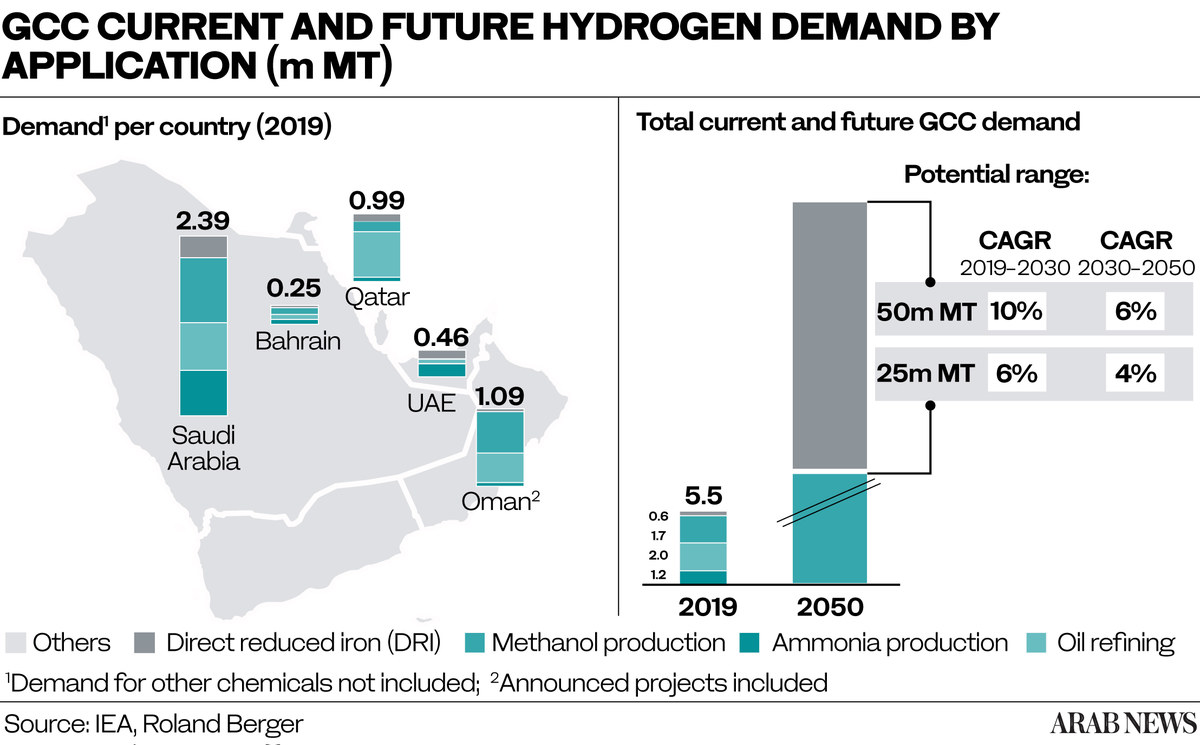
The region has the potential to be one of the most competitive globally for green hydrogen production thanks to its abundant wind and solar resources, industrial infrastructure and its location as an export hub, Dii Desert Energy and Roland Berger said in a report on the industry this month.
The Gulf alone could create a $200 billion green hydrogen industry by 2050, generating up to one million jobs, the report said as it predicted a long-term renewable energy deployment of up to 1,000 GW, 500 GW of electrolyzer capacity producing 100 million megatons of hydrogen.
“The GCC region is on the verge of a new era similar to the discovery of oil decades ago,” Vatche Kourkejian, a partner at Roland Berger, wrote in the report. Green hydrogen could allow the Gulf to continue being the main energy supplier to the world in a sustainable manner, he said.
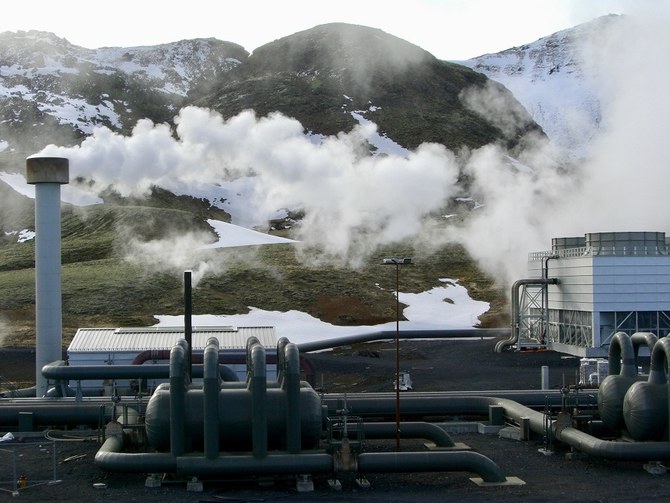
The majority of the world’s hydrogen today (about 95 percent) is considered brown or gray, in that it is produced by steam reforming of natural gas, partial oxidation of methane or coal gasification. While the end product is a clean fuel, the production process uses huge amounts of energy and creates significant amounts of carbon dioxide.
So-called blue hydrogen uses the same process as gray hydrogen, but captures the carbon. Green hydrogen creates the gas through splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen via electrolysis and powering the process with renewable energy, leaving no dirty byproducts.
As well as allowing for the storage of intermittent wind and solar power, hydrogen can also be used to heat homes and cook as a replacement for natural gas, power vehicles, including planes and ships as well as cars, trucks and trains, and be used in industry to reduce the environmental impact of making metals, chemicals and refining oil.
However, the Middle East is not the only region looking to green hydrogen for future industrial development.
So far, 17 countries, (including Japan, South Korea, Canada and UK) have announced a hydrogen roadmap, strategy or vision, according to Wood Mackenzie.
Last year, the EU’s Green Recovery Package earmarked €150 billion ($178 billion) for green hydrogen, including targets for 6 GW of electrolyzer capacity in the first phase between 2020 and 2024, with 40 GW to be installed by the end of the second phase in 2030.
“The last year has seen a decisive pivot toward decarbonization globally, which is extremely positive for zero-carbon technologies,” said Ben Gallagher, lead analyst, emerging technologies at Wood Mackenzie. “Green hydrogen is a key beneficiary, with this pivot pushing it to the fore ahead of other methods for producing the gas. In fact, electrolysis-based low-carbon production now makes up 67 percent of the overall pipeline for hydrogen.”
















