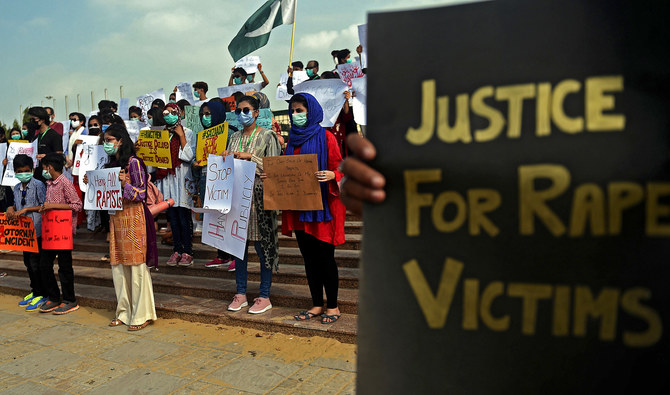ISLAMABAD: It’s no surprise the Pakistani street wants faster, harsher justice for sexual crimes following the gang-rape of a woman on a highway last week that has caused uproar in the South Asian nation but rights advocates say the government should focus on strengthening the criminal justice system to ensure ‘certainty of punishment’ instead of making calls for public hangings and chemical castrations.
Last week, a mother of two was driving along a major highway near Lahore when her car ran out of fuel. As she waited for help along the road, at least two men arrived, dragged the woman out of her car and raped her at gunpoint, in front of her children.
In an interview aired on Monday, Prime Minister Imran Khan said he believed the culprits should be hanged publicly or chemically castrated.
Rights advocates and lawyers have cried foul at the suggestion, saying Pakistan needs better policing and prosecutions, not new laws or punishments that will trample fundamental rights in the government’s rush to be in tune with popular rage.
“In most countries that allow chemical castrations, these are only carried out in a regulated manner against perpetrators of child sexual abuse, in consultation with doctors and psychologists,” Reema Omer, legal adviser South Asia for International Commission of Jurists, told Arab News.
She said that the punishment is “often voluntary and a condition for such offenders to get parole.”
“Their objective is rehabilitation and preventing repeat offenses,” the lawyer said. “They are not viewed as exemplary punishment of all kinds of sexual offenses, which appears to be what the prime minister is considering for Pakistan.”
Rape is a criminal offense in Pakistan, with punishment ranging from up to 25 years in prison to the death penalty. No official data is available for the number of rape cases in the country, though experts estimate they are in the thousands each year.
In Pakistan, the conviction rate in rape cases is under three percent, according to the Karachi-based War Against Rape (WAR).
Omer said that every time a rape grabbed headlines in Pakistan, there was public outrage and an ‘erroneous focus’ on enhancing the sentence: “Even the most severe penalty won’t be a deterrent for such crimes if perpetrators know there is less than five percent chance they will be convicted,” she said.
If Pakistan enacts laws to make chemical castration of sexual abusers legal, it will join a small group of nations that allow such a punishment, including Indonesia, Poland, Russia, and Estonia, as well as some states in the United States. In 2011, South Korea became the first Asian country to use chemical castration as a punishment.
The procedure involves using a drug to reduce testosterone levels and affect the sex drive.
Sarah Zaman, former director at War Against Rape, said rape was prevalent in Pakistan because of “impunity” and systematic flaws in the criminal justice system that helped culprits escape accountable.
“We need to defeat the culture in our society that encourages such crimes instead of raising the punishments,” she told Arab News, adding that the government need to work on increasing conviction rates in rape cases.
“It’s ignorant, short-sighted and non-serious,” Zaman said when asked about the PM’s suggestion that rapists be chemically castrated. “Also, this won’t help reduce impunity to the criminals.”
Dr. Qibla Ayaz, chairman of the Council of Islamic Ideology, a body that advices the government on the compatibility of laws with Islam, said the council had recommended that the government establish special courts that could hear cases of heinous crimes like rape.
“Sufficient laws and strict punishments regarding rape already exist, and we just need to ensure their implementation to deter the crime,” he told Arab News.
Maliha Zia Lari, a human rights activist and lawyer, also suggested that the government focus on “certainty of the punishment” through cogent reforms in the criminal justice system.
“We need to understand that rape is a power offense and not a lust crime,” she said. “We need to change the patriarchal mindset to curb sexual violence against women.”
Rights advocates wary as Pakistan suggests public executions, chemical castration after gang-rape
https://arab.news/jyv5z
Rights advocates wary as Pakistan suggests public executions, chemical castration after gang-rape

- Activists and legal experts urge government to strengthen criminal justice system, ensure ‘certainty of punishment’ rather than opt for stopgap solutions
- Council of Islamic Ideology says adequate laws and punishments regarding rape already exist and need to be implemented properly
Pakistan presses UN to prevent Afghan soil from being used against neighboring countries

- Pakistan, which faces a renewed surge in militancy, has frequently accused Afghanistan of allowing militant groups on its soil, an allegation Kabul denies
- Islamabad’s UN envoy says the UN Security Council has spoken with a unanimous voice and ‘it is for the Taliban to decide what path they wish to choose’
ISLAMABAD: Pakistan on Thursday urged the United Nations (UN) to prevent the use of Afghan soil by militant groups to threaten neighboring countries, saying “efforts must be made to prevent external spoilers from exploiting the situation.”
Pakistan, which has been witnessing a renewed surge in militant violence, has frequently accused Afghanistan of allowing militant groups, including the Tehreek-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP) and the Baloch Liberation Army (BLA), to operate on its soil and India of backing them in attacks against Pakistan. Kabul and New Delhi deny the allegations.
The surge in militant violence in Pakistan triggered one of the worst skirmishes between Pakistan and Afghanistan in Oct. last year, after Islamabad hit what it called TTP targets inside Afghanistan. Pakistan has since suspended all trade with Afghanistan, despite a ceasefire reached between the neighbors in Doha that same month.
On Thursday, Pakistan voted in favor of a UN Security Council resolution that extended for 12 months the mandate of the team tasked with monitoring sanctions against the Taliban and their associated groups and individuals, welcoming the unanimous adoption of the resolution that is both “timely and necessary.”
“Pakistan remains seriously concerned by the active presence of terrorist groups on Afghan soil,” Islamabad’s permanent representative to UN Asim Iftikhar Ahmad said, while addressing the Council.
“We reiterate our call that Afghan territory must not be used for terrorism against neighboring countries and efforts must be made to prevent external spoilers from exploiting the situation.”
There was no immediate comment from the Afghan side to the statement, which came days after a suicide attack on a mosque in the Pakistani capital of Islamabad killed at least 32 people and injured dozens more. Officials said while the suicide attacker was a Pakistani national, he was trained in Afghanistan ahead of the bombing claimed by Daesh.
Unanimously adopting resolution 2816, the 15-member UNSC decided that all states will continue to implement the sanctions measures imposed both on the Taliban and related “individuals, groups, undertakings and entities” that threaten Afghanistan’s peace, stability and security.
It further renewed the mandate of the monitoring team charged with assisting the Afghanistan Sanctions Committee, which was first established in resolution 2011, for a period of 12 months from the date of its expiration this month. Among other tasks, the Council directed the monitoring team to gather information on instances of non-compliance with sanctions, keep the Committee informed of such instances and to provide recommendations on actions to respond to non-compliance.
“The Council has spoken with a unanimous voice today by highlighting these problems and remains committed to reviewing these sanctions as and when appropriate while taking into account the ground realities in Afghanistan,” Ahmad said.
“It is for the Taliban to decide what path they wish to choose for Afghanistan; whether it is the path to isolation or the path to peace and prosperity as a responsible member of the international community.”