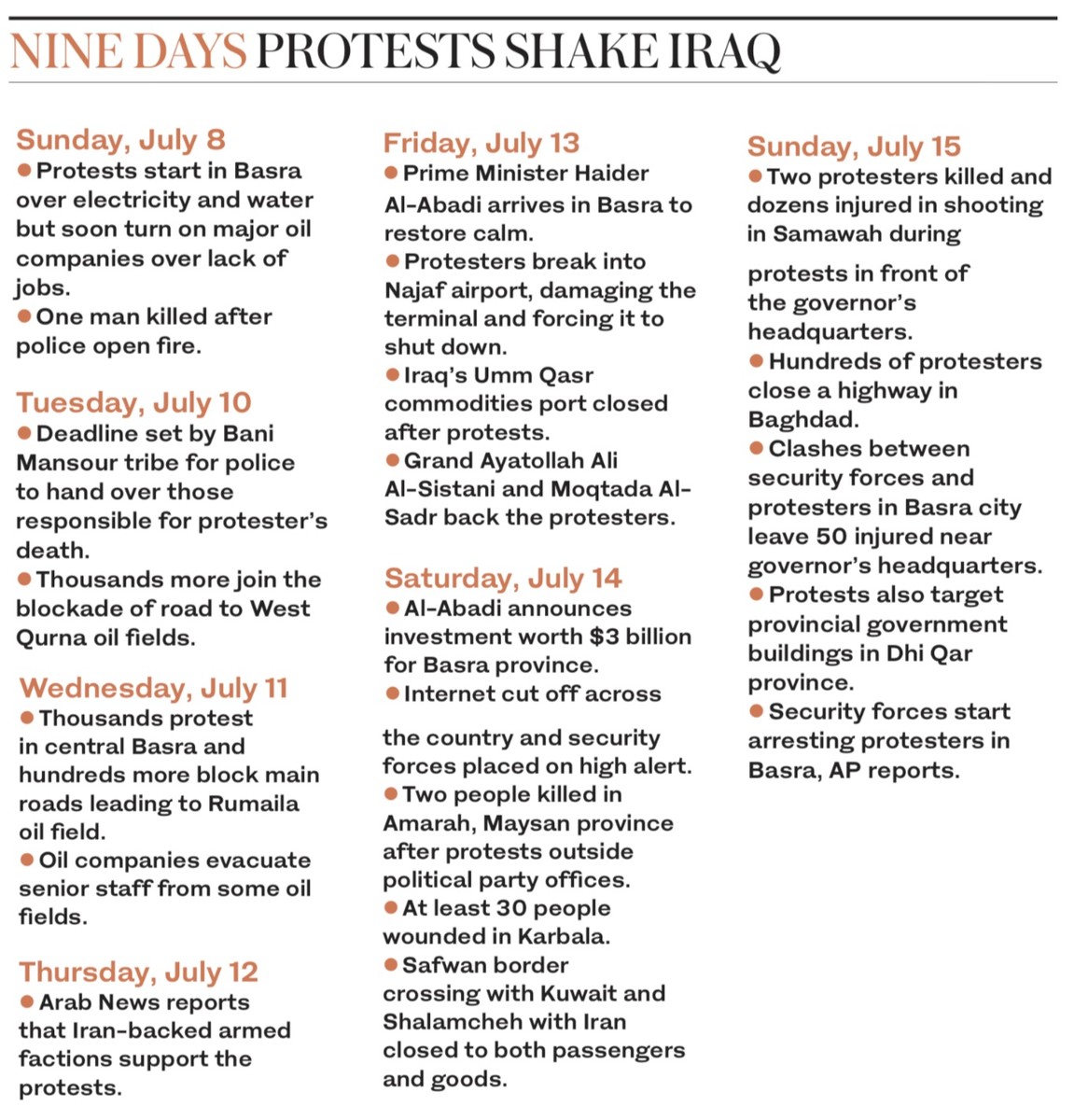
BAGHDAD: Regional and local players have been blamed for spreading violent protests across southern provinces
Demonstrations that have spread through Iraq’s southern provinces against the lack of basic services, poverty and unemployment have been driven by multiple local and regional players to achieve their own political goals.
In the oil hub of Basra, where hundreds of foreign and Arab oil companies operate, the protesters called for jobs. In Najaf, they demanded an end to corruption, while in Sammawa, Ammara and Dhi Qar, demonstrations called for clean drinking water and regular electricity.
The protests, which entered a second week on Monday, started in Basra city with gatherings outside provincial government buildings and the blocking of roads to key oil fields.
But they escalated and turned increasingly violent over the weekend after large groups stormed oil sites in northern Basra and set fire to a number of government buildings in Nasiriyah, Amara and Diwaniya.
On Friday, a mob stormed Iraq’s fourth busiest airport in Najaf and burned several headquarters belonging to some of the Shiite political forces.
In the nine days of unrest, eight protesters have been killed and hundreds wounded, half of whom were policemen, medics and security, sources told Arab News.
Iraqi security services arrested dozens of organizers of the demonstrations over the past two days to interrogate them “in an attempt to get an idea about the parties that guide the demonstrations and incited the demonstrators to attack and vandalize public facilities,” a security official told Arab News.
Basra
An intelligence official said that while the protests may have started organically, they have since been hijacked for political gain.
“No one denies that the services situation in Iraq is catastrophic and that the citizens suffer from a severe shortage of water and electricity at temperatures above 50C throughout the summer. This was the first spark that ignited these demonstrations,” the intelligence official told Arab News.
“But, later many local and regional sides have ridden the wave (of demonstrations).
“All I can reveal now is that a regional player was behind the demonstrations in Basra, but the rest were (stirred by) local players.”
While the official declined to name a regional player specifically, analysts said that Iran has the most to gain from disrupting oil supplies from Iraq.
Tehran, which wields significant influence in Iraq, particularly through paramilitary groups, faces suffocating economic sanctions imposed by the US administration after Donald Trump pulled America out of the Iran nuclear deal. The US has ordered all countries to stop buying Iranian oil from November.
Oil from Saudi Arabia and Iraq would be the main sources to compensate for the shortfall faced by the global oil markets.
“If you know who will be the beneficiary of stopping the export of Iraqi oil, you will know the regional player (behind the demonstrations in Basra),” the intelligent official said.
Rahman Al-Joubori, an Iraqi analyst based in Washington, told Arab News that Iran was sending a message to the international community.
“The message says that the Iraqi oil sector is not secure and you cannot rely on it,” he said.
Najaf
In Najaf, one of Iraq’s holiest cities and a center for pilgrimage, the story is different. Demonstrators stormed the air- powas responsible. Najaf airport, which opened in July 2008, is run by senior leaders of the Islamic Dawa Party.
Many complaints have been filed to Iraq’s Integrity Commission and the related government bodies suggesting the airport managers are corrupt and have not delivered the incomes of the airport to the government treasury.
The Iraqi cabinet led by Prime Minister Haider Al-Abadi, a Dawa member, last year issued a decision to dissolve the airport’s board and hand it over to the Civil Aviation Au- thority, but the directors refused to respond.
“The leaders of Dawa Party who do not benefit from the airport incomes have incited their followers against the leaders of Dawa Party who run the airport,” the Shiite leader said. “It is an internal fight,” he said, adding that Al-Abadi, was not involved in the protest and has been desperately trying to calm tensions.
The election
As the demonstrators left the airport, hundreds of others attacked and burned the headquarters of the most prominent paramilitary Shiite groups Najaf and Ammara. Buildings housing the Badr Organization, As-saib Ahl Al-Haq and Kataib Huzballah were all attacked.
Several security and political sources said that the followers of the influential Shiite cleric Moqtada Al-Sadr were behind the action.
Al-Sadr has emerged as kingmaker in Iraq since preliminary results of the May election showed that his alliance had won first place. He has been leading negotiations to form the biggest parliamentary bloc, which could then form a government.
His pro-Iranian arch Shiite rivals, who ran in the election under the Al-Fattah list, won second place and have been trying to block his way.
Fattah includes members of the Iran-backed paramilitaries, includ- ing Badr Organization and Assaib Ahl Al-Haq.
“We know that Sadrists (the followers of Al-Sadr) were behind the burning of our offices. It was an action and a reaction,” a senior Fattah leader told Arab News.
“Our guys (Badr, Assaib and Kattaib Huzballah) have set fire to the street in Basra and other provinces.”
High alert
Iraqi security forces are on high alert as more demonstrations are expected across the south of the country. Most foreign companies evacuated its senior staff from oil facilities in Basra province.
The demonstrators on Monday gathered in Al-Burjisiya town, southwestern Basra, threatening to attack the nearby giant pipeline that carries oil to the loading platforms for export. It marks a significant escalation compared to when the protests started on July 8 in Basra with a group of youths at the entrance of a foreign oil company in West Qurna — home of the biggest oil fields in Iraq.
The demonstrators had blocked the main road leading to the field and prevented employees of the compa- ny from reaching their work sites for two days. Police opened fire to dis-perse the demonstrators. A protester was killed and another three were wounded.
Bani Mansour, the tribe of the killed protester, asked the security forces to hand over the policemen responsible, but the government refused — sparking more anger.
By Wednesday, the 13 main Basra tribes said that they were backing the Bani Mansour and vowed “to paralyze” the oil companies.
Thousands of protesters took to the streets in Basra. All roads leading to the oil companies and fields were blocked either by protesters, dirt barriers or burning tires.
Although the Iraqi government sought to absorb the anger and sent them a ministerial committee to negotiate with them, the situation rapidly deteriorated and the demonstrators started attacking the sites of oil companies and stormed the headquarters of the government owned-Basra Oil Company and the Russian power giant Lukoil Company.
On Saturday, Al-Abadi, who led the country through one of its many dark chapters with the defeat of Daesh, offered $3 billion in investment in the province.
But it is hard to see how money alone will appease the anger which is being fueled by increasingly complex political forces.

















