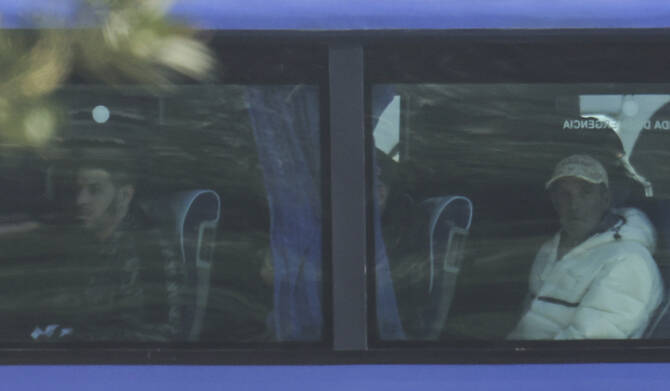
SHENGJIN: Italian authorities on Friday transferred 40 migrants with no permission to remain in the country to Italian-run migration detention centers in Albania.
It was the first time a EU country sent rejected migrants to a nation outside the EU that is neither their own nor a country they had transited on their journey, migration experts said.
A military ship with the migrants departed the Italian port of Brindisi and arrived hours later in the Albanian port of Shengjin, about 65 km northeast of the capital, Tirana.
FASTFACT
A military ship with the migrants departed the Italian port of Brindisi and arrived hours later in the Albanian port of Shengjin, about 65 km northeast of the capital, Tirana.
The migrants were seen being transferred in buses and minivans under heavy security to an Italian-run center in Shengjin, where they will be processed before being transferred to a second center in Gjader, also run by Italian authorities.
The Italian government has not released their nationalities or further details.
Both facilities in Shengjin and Gjader were initially built to process asylum requests of people intercepted in the Mediterranean Sea by Italy.
But since their inauguration in October, Italian courts have stopped authorities from using them, and small groups of migrants sent there have returned to Italy.
Italy’s government of Premier Giorgia Meloni approved a decree last month that expanded the use of the Albanian fast-track asylum processing centers to include the detention of rejected asylum-seekers with deportation orders.
It is not clear how long the migrants may be held in Albania. They can be detained in Italy for up to 18 months pending deportation.
Meloni’s novel approach to expel the migrants echoes US President Donald Trump’s recent deportations of migrants of various nationalities to Panama.
It’s also in line with a recent EU Commission proposal that, if passed, would allow EU members to set up so-called “return hubs” abroad.
Some experts and rights groups question the transfers Migration experts say it was unclear how legal Italy’s actions were.
Meghan Benton of the Migration Policy Institute said the move likely will be challenged in court.
Speaking from Toulouse, France, Benton said other EU countries are interested in doing the same, including the Netherlands with Uganda.
Francesco Ferri, a migration expert with ActionAid, who was among a group of nongovernmental organizations and Italian lawmakers visiting Albania to follow the migrant transfer, said Italian authorities have failed to clarify what happens to the migrants once they’re in Albania. He said there is no legislation in Italian law, EU law, or the Albania-Italy agreement that would allow rejected asylum-seekers to be deported directly from Albania, making the purpose of the transfer unclear.
“For us, it is unacceptable,” Ferri said.
The Albanian centers opened in October, but they remained substantially inactive due to legal hurdles and broad opposition from human rights associations, which believe they violate international laws and put migrants’ rights at risk.
The November 2023 agreement between Italy and Albania— worth nearly 800 million euros over five years — allows up to 3,000 migrants the Italian coast guard intercepted in international waters each month to be sheltered in Albania and vetted for possible asylum in Italy or repatriation.
Italy has agreed to welcome those migrants who are granted asylum, while those whose applications are rejected face deportation directly from Albania.
The first three groups of 73 migrants transferred there in October, November, and January spent only a few hours in Albania.
They were returned to Italy after Italian magistrates refused to validate their detention in a non-EU country.
So far this year, 11,438 migrants landed on Italian shores, less than the 16,090 who arrived in the same period last year.
According to the Italian Interior Ministry, most arrived from Bangladesh, followed by Syria, Tunisia, and Egypt. Irregular border crossings were 31 percent lower across the EU, according to figures released by the EU’s Border and Coast Guard Agency Frontex.