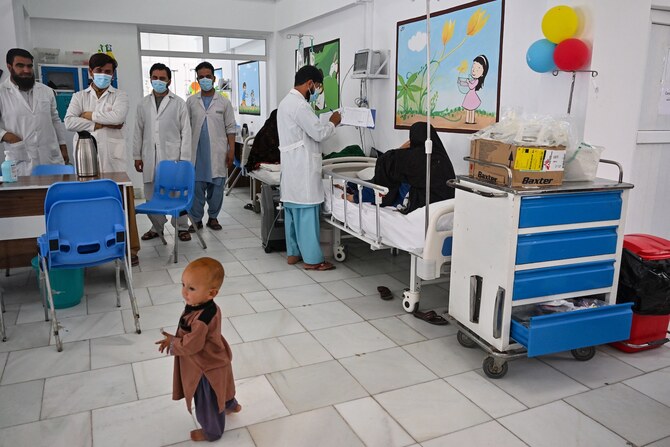
Kabul: Afghan doctors warn that new foreign funding cuts are depriving the country’s most vulnerable of healthcare, especially in rural areas, where aid-dependent NGOs are the sole providers.
The WHO announced last week that 206 health facilities across 28 provinces of Afghanistan were either suspended or closed due to a lack of financial support.
About 200 more clinics, health centers and mobile health and nutrition teams operating in remote areas of the country are set to close by June.
The UN health agency said that the funding shortfall, which comes amid massive US aid cuts since January, is leaving an additional 1.8 million Afghans without access to primary health care.
“The big hospitals in provincial capitals are primarily run by the government while most of the health centers in rural areas are operated by NGOs with funding from different donors,” Dr. Zobair Saljuqi, a doctor at Herat Regional Hospital, told Arab News.
Most of the rural population cannot afford to travel to provincial capitals or major cities for treatment. Health facilities in remote areas are also crucial for women, especially since their movement has been curtailed by the Taliban administration.
“If these health facilities don’t receive the needed financial aid, they cannot continue functioning even for a month because from staff salaries, through running costs, to medicines — all are provided by the donors,” Saljuqi said.
“Women will face severe challenges during pregnancies and children could die due to malnutrition or infectious diseases.”
The halt in US aid is another blow to Afghanistan’s humanitarian situation since the Taliban took over in 2021. Following the collapse of the country’s Western-backed regime, the US withdrew its troops and froze all projects overnight, after spending billions on two decades of military and development operations.
Afghanistan’s health sector relies on donor funds. UN estimates show that out-of-pocket expenses and external funding make up 97 percent of total health expenditure, while government contributions account for just 3 percent.
Dr. Ahmad Tariq, who works at a health center in Qarghayi district, Laghman province, said that almost everyone in his neighborhood depended on the facility.
“People here are very poor. They are all either farmers or daily laborers. They can’t afford to travel to the center of the province or buy medicine,” he told Arab News.
“Our small facility is helping tens of patients every day, men and women, children and elderly persons. They come for OPD consultations as well as vaccination and receive some medicine for free. If it wasn’t for this center most of the people would have been deprived of basic health services.”
According to Afghanistan’s Ministry of Health data, 72 percent of the rural population lacks access to primary and secondary healthcare services.
Of the country’s 400 districts, only 93 have operational hospitals, and almost 10 million people in more than 20,000 villages have limited or no access to basic health services.
Dr. Mohammad Nazar, a public health practitioner in Kabul, forecast that the sudden shortage of US-led funding would further devastate Afghanistan’s already fragile health system, which had endured decades of war and Soviet and American invasions.
“Almost all health centers across rural areas are supported by donors and humanitarian organizations,” he said.
“Tens of health facilities are already closing, which means more and more women, children, elderly persons, displaced persons ... will have no access to essential health services and mortality from preventable diseases would rise.”