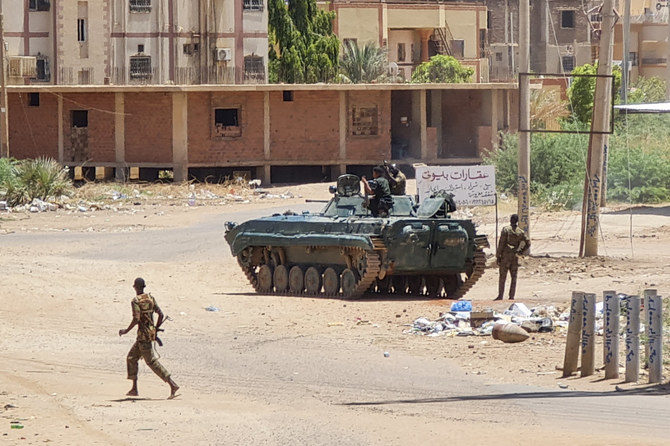
DUBAI: The power struggle between Sudan’s de-facto ruler and commander of the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF), Gen. Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan, and Gen. Mohamed Dagalo and his Rapid Support Forces (RSF), has now been raging for three brutal weeks.
What began as tensions over the planned integration of Dagalo’s paramilitary group into the Sudanese military reached a flashpoint on April 15, when the two former allies, who had worked together to oust dictator Omar Al-Bashir less than four years ago, fell out, plunging the country into chaos.
Among the many questions on the minds of Africa analysts and geopolitical experts is whether a protracted, bitter feud between the two generals will do to Sudan what similar internecine conflicts in recent decades have done to two large, now largely ungoverned countries in North Africa — Libya and Somalia.
For the past 25 years, US administrations have regarded as Sudan as geostrategically important to their interests in both Africa and the Middle East. In the early 1990s, under the influence of the National Islamic Front (NIF), Sudan had a government hospitable to militant groups of all stripes, notably Al-Qaeda.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
In 1993, the US placed Sudan on its list of state sponsors of terrorism, but by 1996, the country was viewed as a refuge, nexus and training hub for a number of international terrorist organizations, primarily of Middle Eastern origin. That year, following the passage of three critical UN Security Council resolutions, Sudan ordered the expulsion of Al-Qaeda chief Osama bin Laden from its soil in May.
Two years later, in retaliation for the deadly Aug. 7 bombings of two US embassies in East Africa, the Bill Clinton administration ordered cruise missile strikes on a pharmaceutical plant in Khartoum, claiming that the site was used by Al-Qaeda to produce ingredients for chemical weapons.
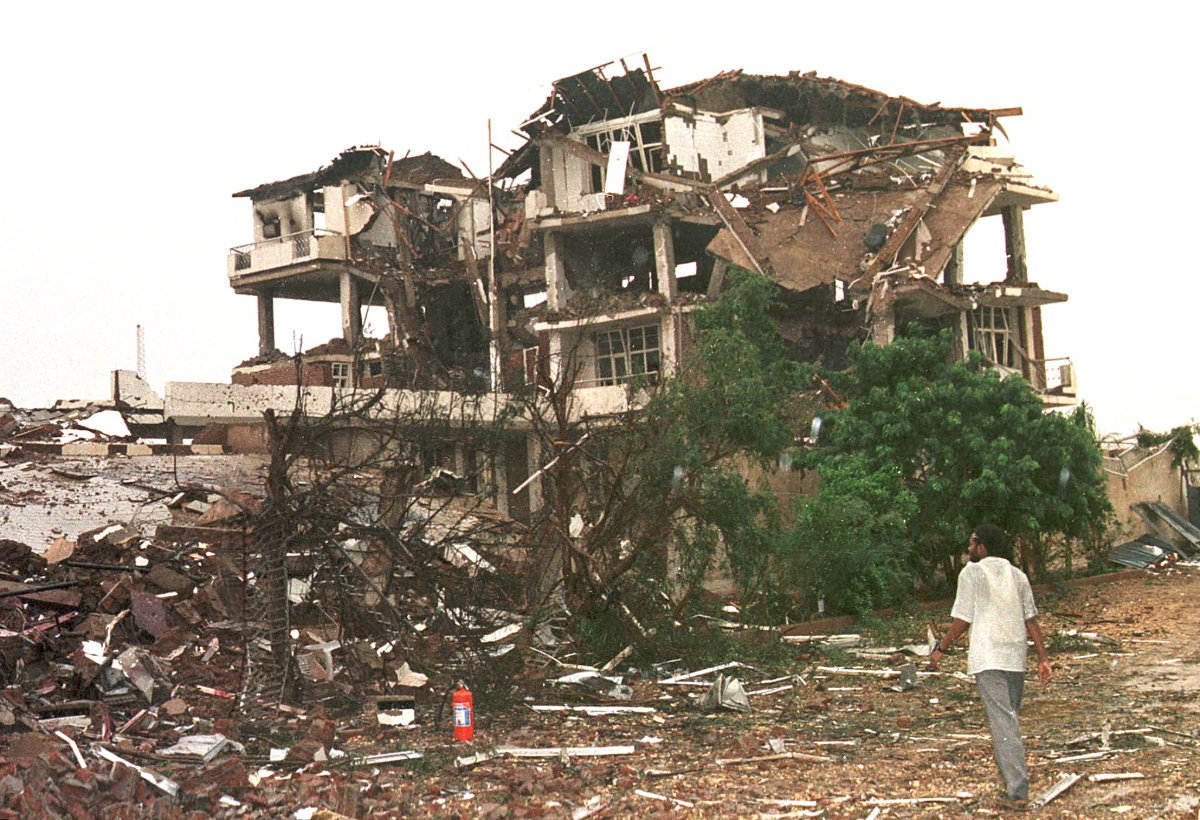

A view of the al-Shifaa pharmaceutical plant in Khartoum after it was bombed by a US jets on August 20, 1998. (AFP File)
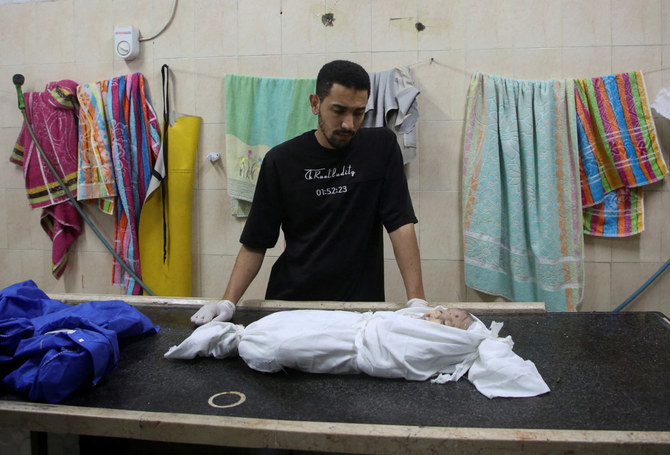
Over the past decade, however, Sudan has adhered to its commitments in peace deals in both Darfur and what became South Sudan, and has maintained counterterrorism cooperation with its international partners. But these achievements are in peril as the impoverished country of 45 million people sinks into a morass of lawlessness, organized criminality and economic collapse.
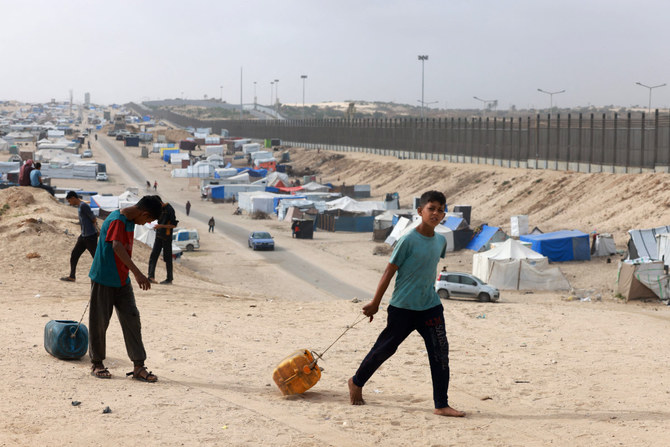
In recent weeks, parts of Khartoum have become war zones and civilians have poured into neighboring countries, whose own conditions are fragile owing to the risks and vulnerabilities they face. The UN refugee agency recently estimated that 800,000 people are expected to flee the conflict — many of them refugees from other countries.
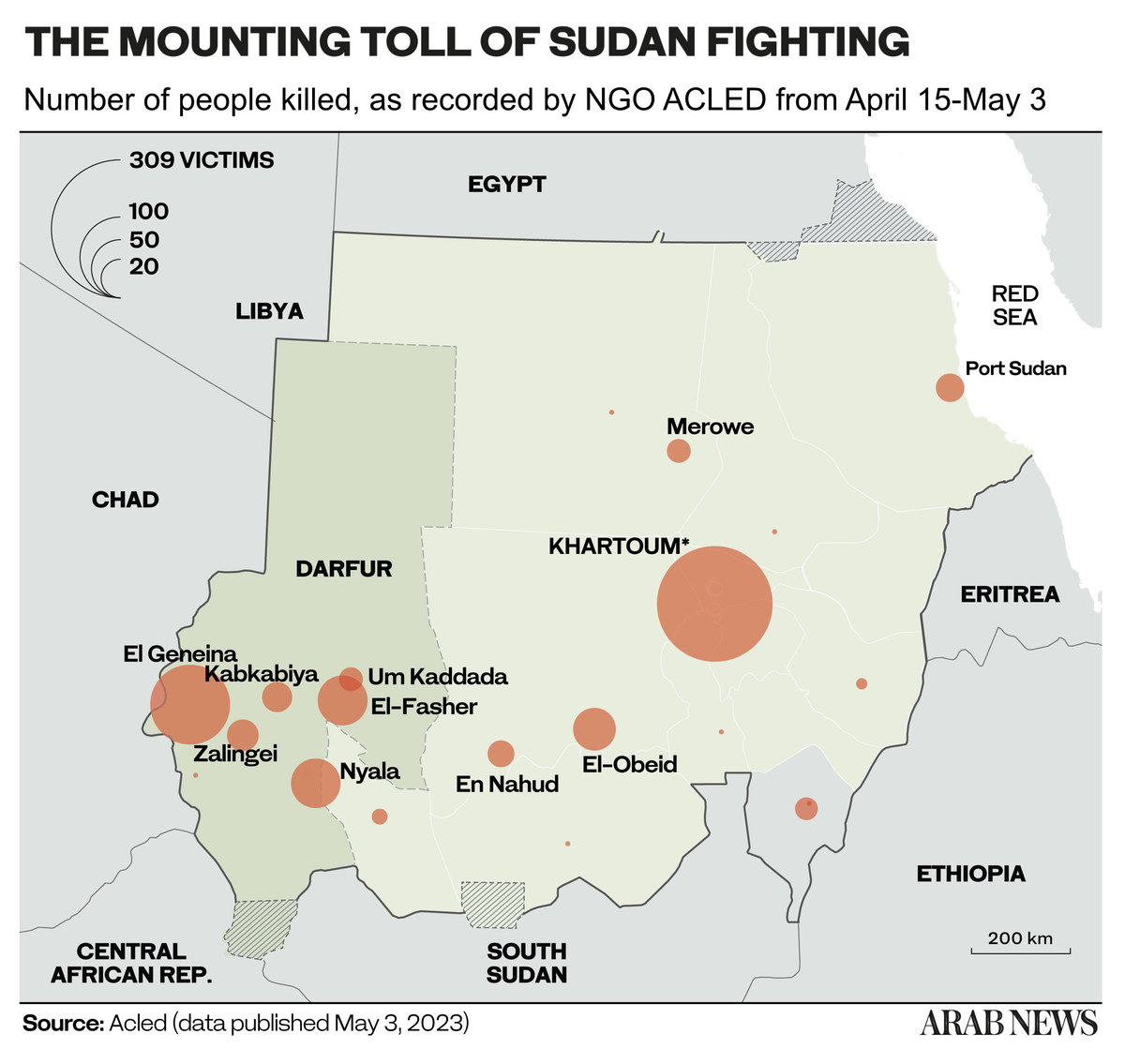
The clashes have killed about 700 people so far, most of them in Khartoum and the western Darfur region, according to the Armed Conflict Location and Event Data Project (ACLED).
INNUMBERS
800,000 Total number of people expected to flee the conflict in Sudan, as estimated by the UN refugee agency.
700 Death toll in the conflict, according to the non-profit organization Armed Conflict Location and Event Data Project (ACLED).
1,700 Number of people wounded during the first 11 days of the conflict, as estimated by ACLED.
While the numbers of casualties and the displaced continue to rise and horrify the world, some analysts warn that the conflict may be a harbinger of a grim consequence — Sudan’s transformation into a hotbed of terrorism.
They say that if the fighting continues and troop losses mount, it is bound to create not only ungoverned spaces for terrorists to exploit, but also tempt the two feuding factions to cut deals with regional militant groups and set the stage for a spiral of warfare and lawlessness.
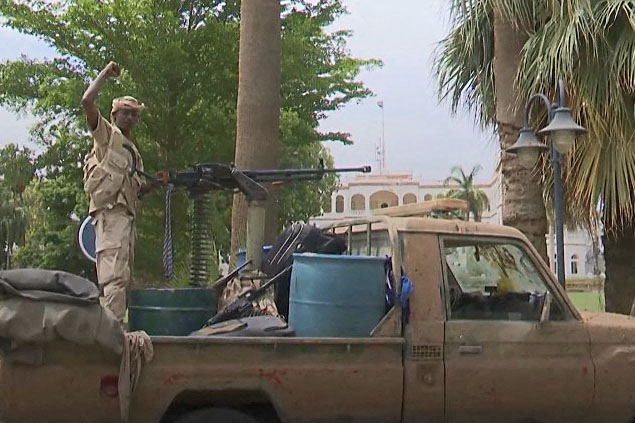

An RSF patrol is seen near the presidential palace in Khartoum in this photo taken on May 1, 2023. (Rapid Support Forces handout via AFP)
Hafed Al-Ghwell, a senior fellow at Johns Hopkins Schools of Advanced International Studies, says the combination of a fragile security situation, economic crisis, social unrest and unstable neighborhood creates the perfect conditions for the emergence of extremist groups.
Given Sudan’s history of harboring extremist groups as well as growing instability, terrorist organizations such as Daesh and Al-Qaeda may set their eyes on the country as a potential new base. “Both the militant Islamic groups have operated in Sudan in the past. The potential for Daesh’s emergence in the country is compounded by its geographic location,” Al-Ghwell told Arab News.
“Sharing a border with Libya, Chad and Somalia, where violent extremist groups continue to operate, the porous borders and weak security infrastructure in the region create perfect conditions for terrorists to relocate and move weapons, contraband and other illicit supplies.”
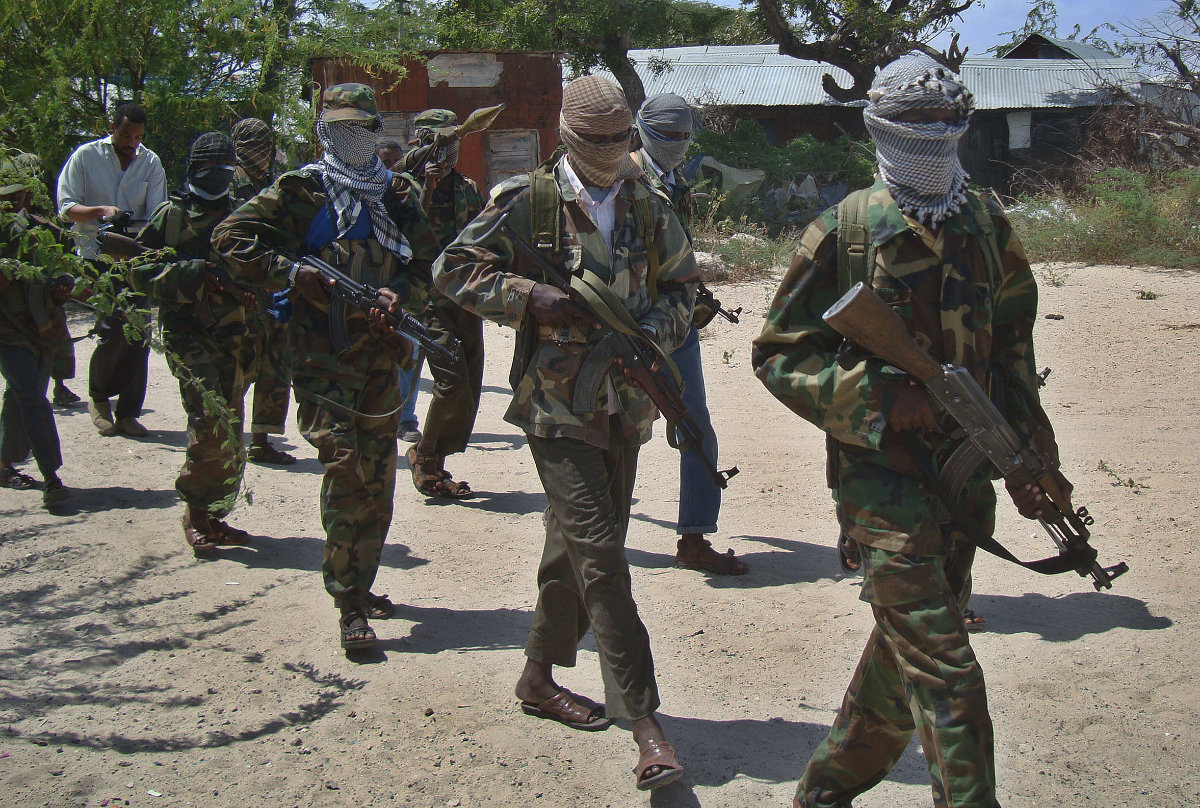

Al-Qaeda-linked Al-Shabab recruits walk down a street on March 5, 2012 in the Deniile district of Somalian capital, Mogadishu, following their graduation. (AFP File Photo)
All this, according to Al-Ghwell, is a cause for concern not only in the Middle East, but also in Europe and the world at large.
Sudan’s strategic location, bordering the Red Sea, the Horn of Africa and the Sahel region, has seen it affected by regional disputes. For example, the country’s relationship with neighboring Ethiopia has been strained over tensions related to disputed farmlands along the border.
The African continent is also home to terrorist groups such as Boko Haram in Nigeria, Al-Shabaab in Somalia, and Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM), which operates in northwest Africa and the Sahel region. Moreover, Boko Haram and Al-Shabaab also have ties to Al-Qaeda.

An image made available by propaganda Islamist media outlet Welayat Tarablos on February 18, 2015, shows Daesh militants parading in a street in Libya's coastal city of Sirte. (AFP)
Al-Ghwell says that a comeback by the Muslim Brotherhood, which was previously one of the Sudanese regime’s strongest backers, is a potential cause for concern.
“It is crucial that the international community remains vigilant in monitoring the activities of the Muslim Brotherhood and its affiliates. Past escalations in Sudan, even including a failed military coup attempt in September 2021, have been blamed on the Muslim Brotherhood,” he said.
“While it is difficult to predict with some certainty the exact likelihood of the Muslim Brotherhood’s return, there are several factors that suggest that the group could make a comeback in Sudan.”
The Muslim Brotherhood has a history in the country dating back to the 1950s, when the group established its first Sudanese branch. Over the next several decades, it continued to strengthen its presence in Sudan, reaching its zenith in 1989 when the Muslim Brotherhood-backed NIF seized power.
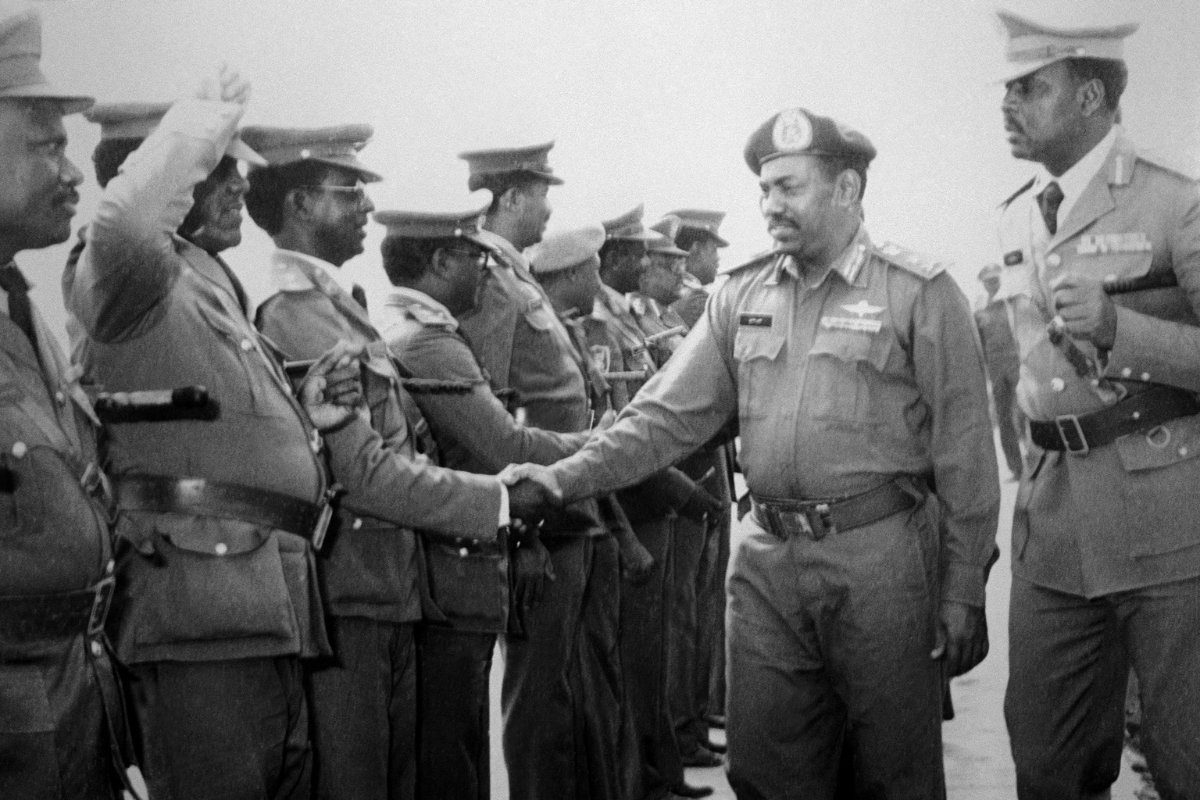

This photo taken on July 7, 1989 shows Sudanese military officials greeting General Omar Al-Bashir, who seized power from the civilian government of Prime Minister Sadiq Al-Mahdi in a coup on June 30, 1989. (AFP file)
Led by military officer and eventual Sudanese head of state Omar Al-Bashir, the NIF, which in the late 1990s changed its name to the National Congress Party (NCP), dominated Sudanese politics until the 2019 Sudanese coup d’etat. Al-Bashir’s government was accused of a litany of human rights violations, including supporting the infamous Janjaweed militias during the war in Darfur in 2004.
After 2019, the NCP was officially banned and forced underground. However, amid mounting chaos in Sudan, the country’s volatile political climate may provide favorable conditions for a return of the Muslim Brotherhood.
“If the Muslim Brotherhood were to successfully re-emerge in Sudan and consolidate its gains, it could pose a significant threat to the country itself and its neighbors. The group’s ideology could lead to a state-sanctioned crackdown on civil liberties and human rights in Sudan, stoking further unrest and potentially leading to more violence,” Al-Ghwell said.
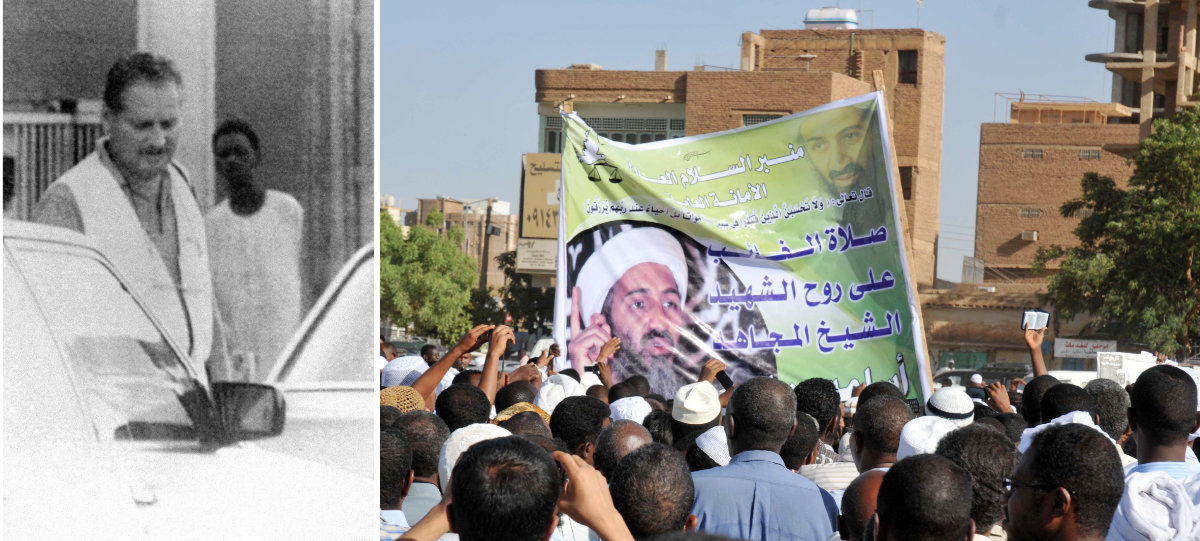

Sudan has a history of harboring terrorists and extremist groups. One was Carlos the Jackal (Ilich Ramirez Sanchez), who was captured by French agents in Sudan in 1994 (left frame). It also once harbored Al-Qaeda mastermind Osama Bin Laden, whose portrait is shown in this combo image with Sudanese sympathizers holding prayers on May 3, 2011, in Khartoum, after he was shot dead at this hide-out in Pakistani by US commandos. (AFP file photos)
“Furthermore, the Muslim Brotherhood has a history of supporting militant groups and extremist ideologies. If the group were to gain power in Sudan, it could provide a haven for terrorist organizations and pose a threat to regional stability.”
With the war in Yemen seemingly moving at a slower pace, Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) could emerge as another major threat if it seeks to move its operations to Sudan.
According to Al-Ghwell, the absence of a proper security infrastructure will make it relatively easy for AQAP to move fighters and weapons into Sudan to support cells there, or use the country as a transit point to sustain the operations of AQIM.
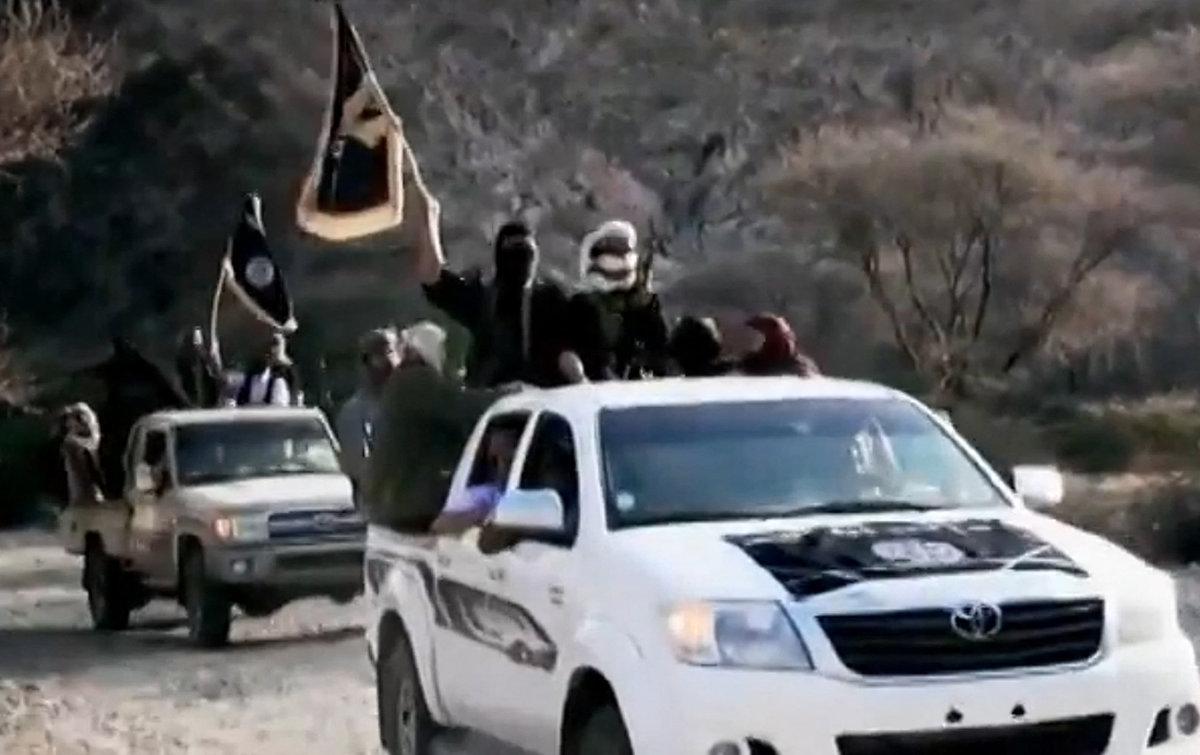

An image grab from a video released on March 29, 2014 by Al-Malahem Media, shows AQAP militants at an undisclosed location in Yemen. (AFP)
“A recent article in the Long War Journal says that an Al-Qaeda ideologue has called for holy war in Sudan and provided guidelines for supporters looking to join the fight. The book, which was compiled by the ideologue Abu Hudhayfah Al-Sudani and released by an extremist publishing house believed to be linked to AQAP, provides ideological justification and guidelines for waging holy war against the Sudanese state, as well as rules for prospective extremists to follow when forming a new entity,” he said.
Although multiple ceasefire agreements between the SAF and RSF have been reached since fighting first erupted in Sudan, they have quickly broken down, with the dueling factions trading blame for the collapse.
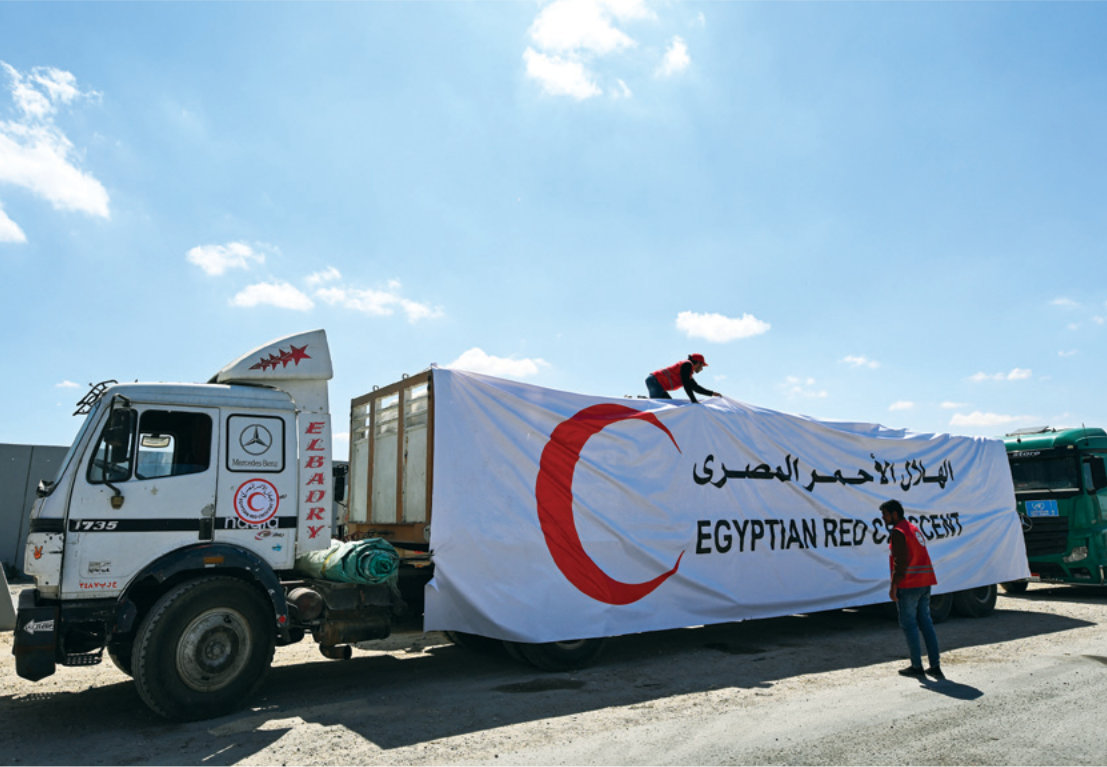
Al-Ghwell says that humanitarian aid such as water, shelter, food and medical assistance must be provided to fleeing civilians as well as the internally displaced, while financial support is vital to help stabilize the economy and nip a resurgence of extremism in the bud.
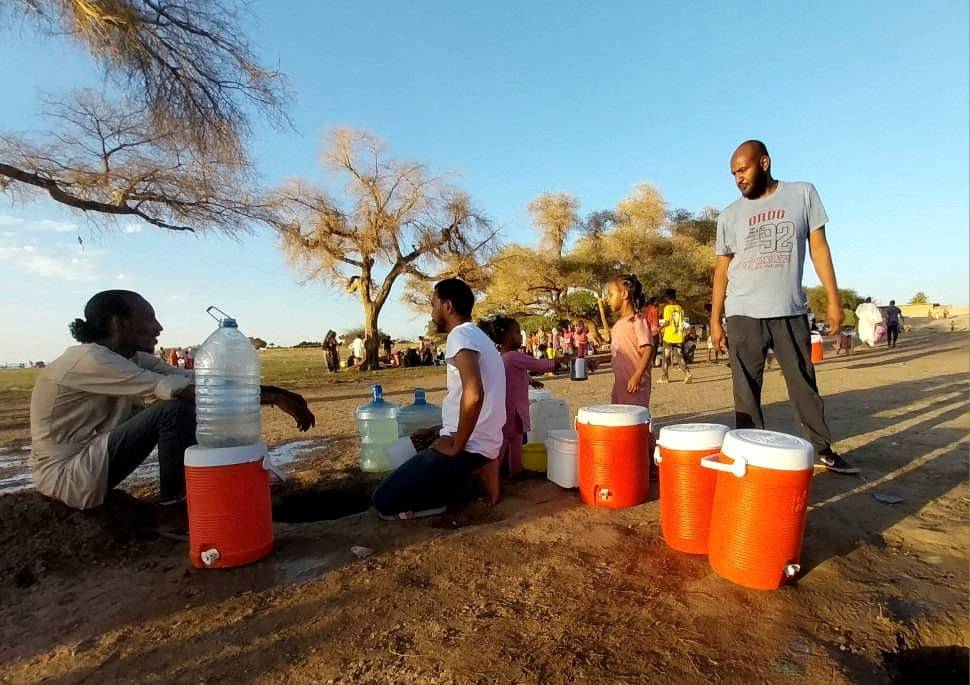

Sudanese citizens dig small holes at the shore to get potable water at the banks of the White Nile amid a water supply shortage as clashes continue in Khartoum on May 6, 2023. (REUTERS)
Looking to the future, he says, the international community should take pre-emptive action by sharing intelligence with, and training, Sudanese security forces to prevent the spread of extremist groups that could take advantage of the power vacuum.
When the fighting between Al-Burhan and Dagalo will end remains unclear. Both factions have claimed territorial control over key areas in Khartoum and other parts of the country.
Fayez, a Sudanese civilian who wanted to be identified only by his first name, recently shared with Arab News his thoughts on having to flee his homeland and his fears for the future. He was exhausted after completing a perilous journey from Sudan through the northern border into Egypt along with his new bride.
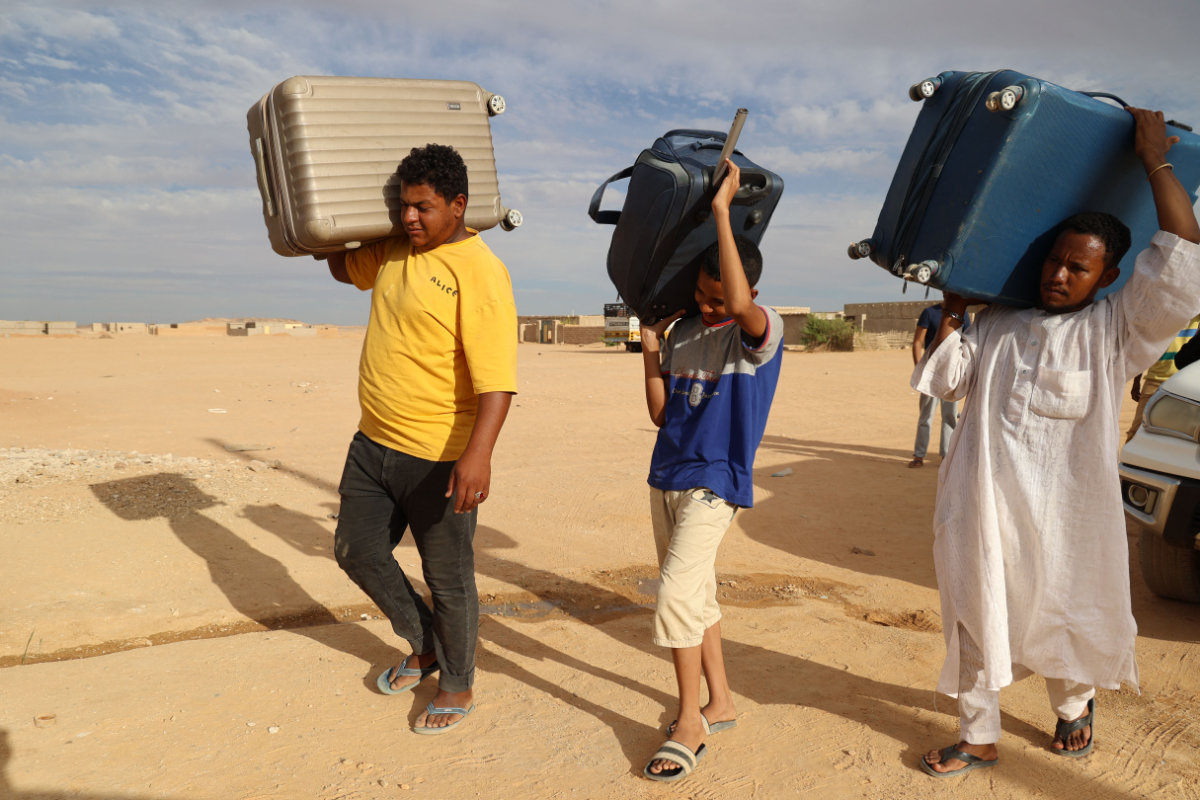

Sudanese people carry suitcases in the town of Wadi Halfa bordering Egypt on May 4, 2023 as they flee the fighting between rival Sudanese generals. (AFP)
“We managed, we survived. I don’t know what Sudan will turn into; I dread to think about it. Rather than waking up to the sound of prayer, my loved ones who are still stuck there are waking up to the sound of explosions,” Fayez said.
“I pray for their safety, I pray for my country, I pray we don’t turn into the worst version of ourselves and the worst, and wrong version of Islam, and kill each other under false ideologies.”