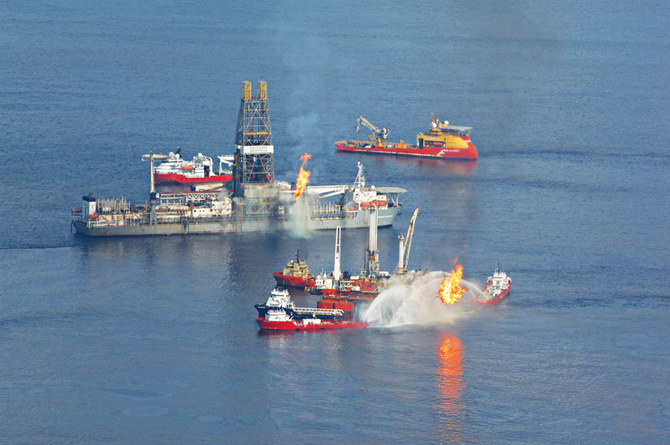
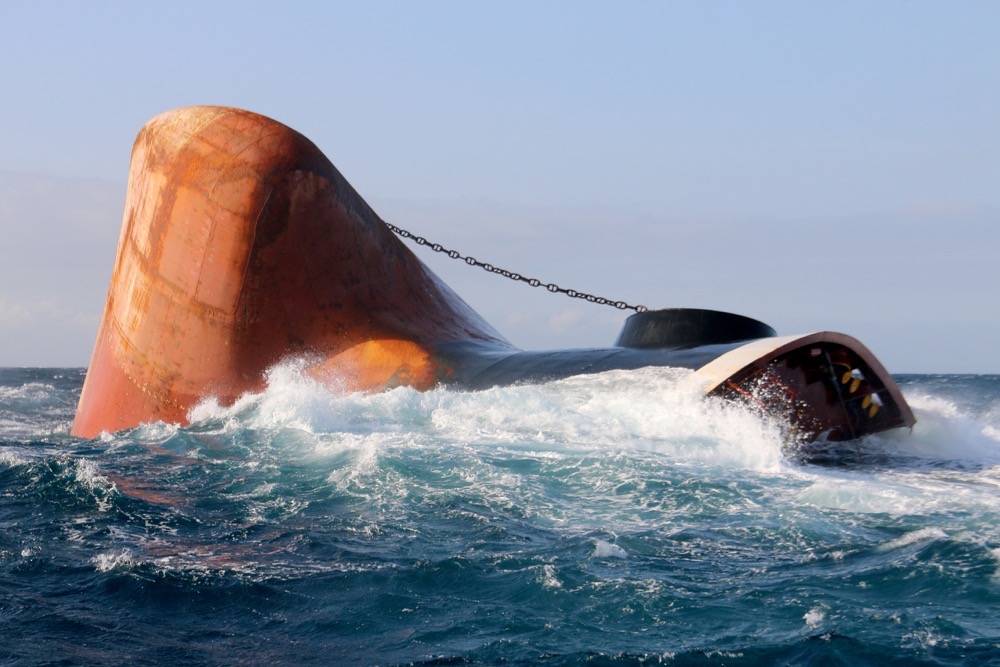
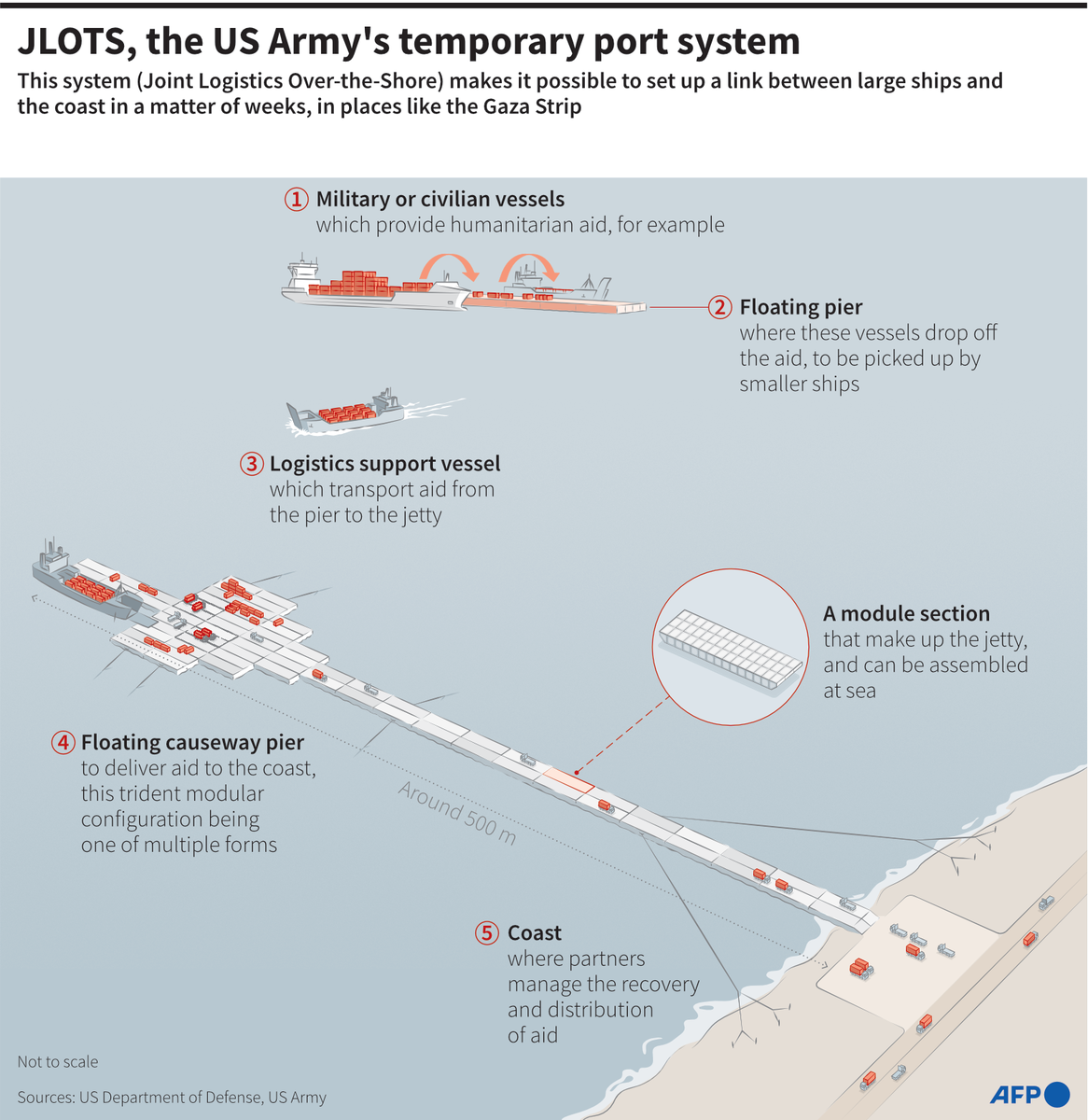
DUBAI: Sabotage attacks targeting four oil tankers off the coast of the UAE’s Fujairah port earlier this month not only highlighted a new threat to maritime traffic but also prompted a more immediate concern for environmentalists — the damage to marine ecosystems.
The warning comes after satellite imagery from the US-based Planet Labs and Finnish company Iceye showed oil leaking from the Saudi VLCC supertanker Amjad — one of the four vessels targeted — and spreading over a large area north of the Khor Fakkan section of the Arabian Gulf, with ocean trackers now monitoring the waters to determine the potential environmental aftermath of the incidents.
The attacks took place on May 12 east of Fujairah port, outside the Strait of Hormuz, a narrow waterway through which most Gulf oil exports pass and which Iran has threatened to block in the event of a military confrontation with the US. The attacks drew strong condemnation from the Arab League and governments around the world.

A photograph captured on May 14 by the European Space Agency shows oil leaking after the tanker attack in the Arabian Gulf. (ESA photo)
The ship was empty of crude oil, but it was carrying fuel oil onboard. The oil spill is estimated to be about 235 barrels, according to TankerTrackers.com, an oil tanker tracking service.
Its co-founder, Samir Madani, told Arab News: “We spotted this fuel oil spill on May 17 (the day after the image was captured) on Planet Labs satellite imagery (they have 300 satellites lined up in an orbit to line-scan the Earth’s surface on a daily basis) but waited a few more days before being able to confirm that it wasn’t something else. As we saw that on May 20, the spill had started dispersing over a larger area north of Khor Fakkan.”
Now experts have warned that the attacks may also threaten marine life and biodiversity.
Madani said that depending on the grade of oil, it will either float or sink based on density, but warned that it could have a longer-term impact on the surrounding marine environment.
“Fuel oil is heavier than the average barrel of crude oil, so there is a chance that it’ll settle to the bottom and pollute the marine life,” he said. “Crude oil can be treated with dispersants such as we’ve seen in incidents in Kuwait, but we don’t have enough knowledge of what impact such chemicals have on marine life, either.”
The radar images captured by Iceye’s X2 satellite also detected a long trail leading from the Amjad two days after the attack, although it cannot state how much oil was present. “Oil on top of seawater is visible on radar satellite imaging because it changes the way the water surface reflects radio waves,” explained Iceye CEO Rafal Modrzewski.

Iceye CEO Rafal Modrzewski
“Oil forms a layer on top of the seawater. This changes the water’s viscosity, flattening and making the surface smoother. As a result, oil on water appears on the image as a dark patch.”
According to the International Maritime Organization (IMO), oil tankers transport some 2,900 million tons of crude oil and oil products every year around the world by sea. Most of the time, oil is transported quietly and safely. Measures introduced by the IMO have helped to ensure that most oil tankers are operated safely and are constructed to reduce the amount of oil spilled in the event of an accident.
However, when an accident involving ships or oil rigs occurs, the ocean water becomes contaminated by liquid petroleum hydrocarbon, with oils spills not only killing fish, marine mammals and birds but also causing damage to beaches and wildlife habitats.
“We run into spills all the time, and they are mostly fuel oil,” said Madani. “The most notorious area in the Gulf region is off the coast of Iraq, at the Umm Qasr anchorage, where there are a lot of ship-to-ship transfers of fuel oil, and things get sloppy when there’s no third vessel (tugboat) to quarantine the spill with the help of an oil boom.”
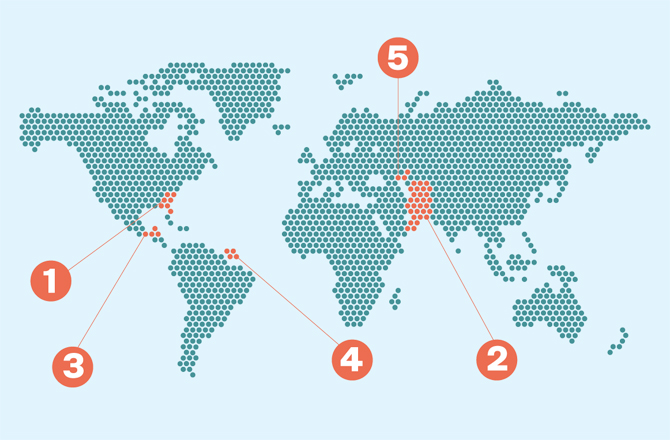
WORLD’S BIGGEST OIL SPILLS
1. DEEPWATER HORIZON Almost a decade on, it is still considered to be the largest oil spill in the petroleum industry’s history. In 2010, the accident began after a spill from a seafloor oil gusher, leading to the explosion of the BP oil rig, Deepwater Horizon, in its Macondo Prospect. An estimated 53,000 barrels flowed into the Gulf of Mexico every day for more than three months, killing more than 82,000 birds, 25,900 marine mammals, 6,000 sea turtles and tens of thousands of fish.
2. GULF WAR In 1991, Iraqi forces opened valves at the Sea Island oil terminal and dumped oil from several tankers into the Arabian Gulf. About 240 million gallons of oil were believed to have been discharged, killing hundreds of fish and marine mammals.
3. IXTOC I An exploratory oil well being drilled in the Bay of Campeche off the Gulf of Mexico, Ixtoc 1 suffered a blowout in 1979, and 10,000 to 30,000 barrels of oil were discharged into the sea over 10 months. The oil slick, which measured about 1,100 square miles, surrounded Rancho Nuevo, a nesting site for sea turtles.
4. ATLANTIC EXPRESS In 1979, two oil tankers collided in the Caribbean Sea during a tropical storm, causing the supertankers — the Atlantic Empress and Aegean Captain — to leak their cargo. According to reports, around 88.3 million gallons of crude oil were discharged into the sea, making it the world’s largest ship-sourced oil spill.
5. NOWRUZ FIELD During the Iran-Iraq war in 1983, an oil tanker hit the Nowruz Field platform in the Arabian Gulf, leading to a major spill. It is estimated that about 80 million gallons of oil flowed into the Gulf during a seven-month period, causing harm to marine life.
The waters of the Gulf have been affected a number of times in recent years, with Fujairah being pinpointed as a site that has had tankers causing oil spills; however, local measures have seen the number of incidents decrease.
Oil spills have long been one of the major concerns of the maritime world. According to Marine Insight, a substantial spill “can completely disturb an entire ecosystem for a substantial period of time.” It can take month-long oil cleaning operations to bring the areas back to normality.
No one has yet claimed responsibility for the incidents near Fujairah port, the main shipping route linking Middle East oil producers with the rest of the world. At any one time, many tens of ships will be anchored a few nautical miles from the port.
The official Saudi Press Agency reported the confirmation of the attack on the two vessels, quoting the Saudi Energy Minister. “Two Saudi oil tankers were subjected to a sabotage attack in the exclusive economic zone of the United Arab Emirates, off the coast of the Emirate of Fujairah, while on their way to cross into the Arabian Gulf,” SPA quoted Khalid Al-Falih as saying.
According to the International Tanker Owners Pollution Federation, which provides advice on effective response to spills, when oil is spilled at sea it normally spreads out and moves on the sea surface with wind and current while undergoing a number of chemical and physical changes. These processes are collectively termed weathering and determine the fate of the oil.
Some of these processes, such as natural dispersion of the oil into the water, lead to the removal of the oil from the sea surface, and facilitate its natural breakdown in the marine environment.

The oil spill had catastrophic environmental consequences. (Shutterstock image)
“Others, particularly the formation of water-in-oil emulsions, cause the oil to become more persistent, and remain at sea or on the shoreline for prolonged periods of time,” the group says on its website. “The speed and relative importance of the processes depend on factors such as the quantity spilled, the oil’s initial physical and chemical characteristics, weather and sea conditions, and whether the oil remains at sea or is washed ashore.”
Nicolas Tamic, deputy manager at Cedre, a group of international experts in accidental water pollution, said it is now a waiting game. “Some (oil) may biodegradate and some not. The first thing to do is to collect and analyze the oil involved. Without this necessary data, it is impossible to predict the behavior of the oil at sea … Sunrays may modify the shape of the slicks. Instead of staying a sole slick, it is going to disintegrate into smaller parts.
“Moreover, a phenomenon called emulsification is going to happen. Water comes ‘into’ oil, and it is going to be heavier. The consequence is that its viscosity will change.”
Only then, said Tamic, will the exact results on the surrounding environment and marine life become clear.