DUBAI/LONDON: Tomato paste is not the most obvious economic indicator, but in Iran, where it is a staple that some people have started panic-buying, it says a lot about the impact of renewed US sanctions.
While Iran makes its own paste from an abundant crop of locally grown tomatoes, sanctions reimposed by US President Donald Trump since August have played havoc with supply.
A 70 percent slide in the rial this year has prompted a scramble for foreign currency that has made exports much more valuable in local terms than selling produce at home.
Some shops are limiting purchases of tomato paste, which is used in many Persian dishes, and some lines have sold out as people buy up existing stock.
The government has responded by banning tomato exports, one of a raft of interventions to try to limit economic instability that has fueled public protests and criticism of the government this year.
But the tomato policy is not working. An industry representative said tomatoes were being smuggled abroad.
“We have heard that trucks full of tomatoes are still leaving the country, especially to Iraq,” Mohammad Mir-Razavi, head of the Syndicate of Canning Industry, said by telephone.
“They put boxes of greenhouse tomatoes on top and hide normal tomatoes at the bottom,” he said, referring to an exemption for hot-house grown tomatoes that left a loophole.
It is one of many ways in which the sanctions are hurting ordinary Iranians while benefiting those with access to hard currency.
Washington reintroduced steps against Iran’s currency trade, metals and auto sectors in August after the US withdrawal from a deal that lifted sanctions in return for limits on Iran’s nuclear program. Trump said the deal was not strict enough.
With US curbs on Iran’s oil exports set to come into force next month, some Iranians fear their country is entering an economic slump that may prove worse than the period from 2012 to 2015, when it last faced major sanctions.
“There is an emerging consensus that the economy will go through a period of austerity similar to that recorded during the Iran-Iraq war,” said Mehrdad Emadi, an Iranian economist who heads energy risk analysis at London’s Betamatrix consultancy.
Jumps in prices are occurring in a range of goods — particularly imports such as mobile telephones and other consumer electronics, but also some staples. A bottle of milk, 15,000 rials last year, now sells for 36,000.
An 800-gram (28-ounce) can of tomato paste was selling in Tehran stores for around 60,000 rials in March; it is now 180,000 rials, or $1.24 at the unofficial rate, prompting a scramble by households to stock up. The price of tomatoes has increased more than five-fold compared to last year.
Signs on the shelves of some stores limit each customer to two cans. Iranian online shopping site Digikala lists the top nine tomato paste items as out of stock, and the rest as “coming soon.” In supermarkets in Najaf in neighboring Iraq, meanwhile, supplies of Iranian tomato paste are plentiful.
Adding to the pressure is a fourfold rise in the price of cans, Mir-Razavi said. Traders importing material to make cans sought to buy dollars at a little-used official rate of 42,000 rials; authorities asked them to use a more expensive rate. The issue has delayed shipments of material to factories.
The government is mounting a campaign against price-gouging, periodically ordering shopkeepers to sell at lower prices. But some shopkeepers respond by not selling at all, believing prices will eventually rise again as the sanctions bite.
Iran, a big oil producer with a diverse economy, has shown its farming, manufacturing and distribution sectors can ride out long periods of war and sanctions.
The Tehran Stock Exchange index has soared 83 percent this year as shares of exporting companies have rocketed. Urban real estate prices have also risen as Iranians plow their savings into property rather than keeping them in depreciating rials.
The rial’s plunge, which in the unofficial market has taken it to around 145,000 against the dollar from 42,890 at the end of 2017, according to currency tracking website bonbast.com, may even have strengthened the financial system in one way.
Banks and pension funds have been struggling with massive debts. Emadi said the rial’s slide, to as low as 190,000 in late September, had given the government huge windfall profits on its dollar holdings; authorities appear to have injected some of those profits into insolvent banks to shore them up, he said.
But while official data for the last few months has not yet been released, Emadi said he believed the economy was already in a recession that could deepen in coming months.
The International Monetary Fund predicted this week that the economy would shrink 1.5 percent this year and 3.6 percent in 2019, before recovering slowly.
That would make the slump less deep than the recession of 2012, when the economy shrank over 7 percent, and not nearly as damaging as the Iran-Iraq war of 1980-1988, when it shrank by about a quarter.
The IMF also forecast the average inflation rate would jump to a peak above 34 percent next year, briefly returning to its level in 2013.
How much the current recession resembles past periods of economic pain for Iran will depend on the extent to which Washington can use the sanctions to push other countries into cutting oil and non-oil trade with the Islamic Republic.
US officials have said the sanctions will be tougher than the steps in 2012-2015. They aim to reduce Iranian oil exports more sharply, and to disrupt exports to Iran from trading hubs such as Dubai more aggressively.
“I think the return of the sanctions has had a devastating effect on their economy and I think it’s going to get worse,” Trump’s national security adviser John Bolton told Reuters in late August.
Tomato squeeze: US sanctions begin to hurt Iran’s economy
Tomato squeeze: US sanctions begin to hurt Iran’s economy

- With US curbs on Iran’s oil exports set to come into force next month, some Iranians fear their country is entering an economic slump that may prove worse than the period from 2012 to 2015
‘Where can we go?’ say Rafah residents as Israel demands evacuation

- Areas designated for evacuation currently shelter some 250,000 people
- Israel’s retaliatory offensive, aimed at destroying Hamas, has killed at least 34,683 people in Gaza, mostly women and children
Rafah: Palestinian civilians in the southern Gazan city of Rafah voiced despair on Monday as Israel dropped fliers urging them to evacuate for their own “safety” ahead of a “limited” military operation.
Israel’s army said it was instructing Palestinian families in eastern Rafah to flee in preparation for an expected ground assault on the city which abuts Gaza’s border with Egypt.
Residents of Rafah described emerging outside after a terrifying night in which around a dozen air strikes were carried out on Rafah, to find fliers falling from the sky telling them to “evacuate immediately.”
“The army is working with intensive power against the terrorist forces near you,” read a flier circulated in eastern Rafah.
“For your safety, the IDF (Israeli military) tells you to evacuate immediately toward the expanded humanitarian zone of Al-Mawasi,” it said, with a map indicating the location to the north of Rafah.
Osama Al-Kahlout, of the Palestinian Red Crescent Society in Gaza, told AFP that the areas designated for evacuation currently shelter some 250,000 people, many of whom have already been displaced from other areas in the Gaza Strip.
“The evacuation process has begun on the ground, but in a limited manner,” he said.
An Israeli militark spokesman, when asked how many people should move, said: “The estimate is around 100,000 people.”
About 1.2 million people are currently sheltering in Rafah, according to the World Health Organization, most having fled there during the seven-month war between Israel and Hamas Palestinian militants.
Amid pouring rain, some of those sheltering in Rafah said they had begun packing up their things from the densely packed tents and preparing to leave even before Israel’s directive arrived.
“Whatever happens, my tent is ready,” a resident told AFP.
But others said the area they were being told to flee to was already overcrowded, and they did not trust that it would be safe.
Abdul Rahman Abu Jazar, 36, said he and 12 family members were in the designated evacuation area.
Jazar and his family did not know what to do, he said, because the “humanitarian zone” they were told to head for “does not have enough room for us to make tents because they are (already) full of displaced people.”
“Where can we go? We do not know,” he told AFP.
“There are also no hospitals and it is far from any services many need,” he said, adding that one of his family members relied on dialysis at the Al-Najar hospital, in the area of Rafah instructed to evacuate.
“How will we deal with her after that? Should we watch her die without being able to do anything?“
An Israeli military spokesman told reporters that the evacuation “is part of our plans to dismantle Hamas ... we had a violent reminder of their presence and their operational abilities in Rafah yesterday.”
On Sunday, four Israeli soldiers were killed and others wounded, the army said, when a barrage of rockets was fired toward the Kerem Shalom border crossing between Israel and Gaza.
The army said the rockets were fired from an area adjacent to Rafah.
International aid organizations have voiced alarm at the expected invasion of Rafah.
“From the humanitarian perspective, no credible humanitarian plan for an attack on Rafah exists,” said Bushra Khalidi, advocacy director for Oxfam in the Palestinian territories.
She said she could “not fathom that Rafah will happen,” asking where displaced Palestinians will go “when most of their surroundings have been reduced to death and rubble?“
Gaza’s bloodiest-ever war broke out following Hamas’s unprecedented October 7 attack on Israel which resulted in the deaths of more than 1,170 people, mostly civilians, according to an AFP tally of Israeli official figures.
Militants also seized some 250 hostages, with Israel estimating that 128 of them remain in Gaza, including 35 whom the military says are dead.
Israel’s retaliatory offensive, aimed at destroying Hamas, has killed at least 34,683 people in Gaza, mostly women and children, according to the Hamas-run territory’s health ministry.
US weapon system identified in Israeli-Lebanon strike may breach international law

- Guardian investigation with Human Rights Watch identifies Boeing-made Joint Direction Attack Munition fragments at site where aid workers were killed
- US bans export of such systems to foreign militaries where ‘credible information’ of human rights breaches exists
LONDON: An Israeli airstrike in Lebanon that killed seven aid workers in March may have been conducted with a US-supplied weapon system, according to an investigation by The Guardian.
The incident claimed the lives of seven paramedics aged 18-25, all volunteers, at an ambulance center in Al-Habariyeh in southern Lebanon on March 27.
It came five days before an Israeli strike in Gaza killed seven aid workers working for World Central Kitchen.
Debris found at the scene in Al-Habariyeh was identified by The Guardian, an independent expert and Human Rights Watch as having belonged to a 500-pound Israeli MPR bomb and a Boeing-made Joint Direction Attack Munition, a system attached to explosives to turn them from “dumb bombs” into GPS-guided weapons.
HRW’s Lebanon researcher Ramzi Kaiss told The Guardian: “Israel’s assurances that it is using US weapons lawfully are not credible. As Israel’s conduct in Gaza and Lebanon continues to violate international law, the Biden administration should immediately suspend arms sales to Israel.”
The US government is legally unable to help or arm foreign militaries where “credible information” of human rights abuses exists, under the terms of the 1997 Leahy law.
A spokesperson for the US National Security Council told The Guardian: “The US is constantly working to ensure defense articles provided by the US are being used consistent with applicable domestic and international law. If findings show violations, we take action.”
But Josh Paul, a non-resident fellow with Democracy for the Arab World Now and a former State Department employee, said: “The State Department has approved several of these (weapons) transfers on a 48-hour turnaround. There is no policy concern on any munitions to Israel other than white phosphorus and cluster bombs.”
He added that JDAMs have been “key items” regularly requested by Israel since the start of the Gaza war.
Secretary of State Antony Blinken will deliver a report on Wednesday to Congress on Israel’s use of American weapons and whether they may have been involved in violations of this or other laws.
Maryland Sen. Chris Van Hollen told The Guardian that the findings from Al-Habariyeh are “deeply concerning and must be fully investigated by the Biden administration, and their findings should certainly be included in the NSM-20 report that is due to be submitted to the Congress on May 8.”
The airstrike on the ambulance center in Al-Habariyeh came without warning before 1 a.m. on March 27. No fighting had been reported in the area.
The victims had been at the center for the night shift, and were named as twin brothers Hussein and Ahmad Al-Shaar, aged 18; Abdulrahman Al-Shaar, 19; Mohammad Hamoud, 21; Mohammad Al-Farouk Aatwi, 23; Abdullah Aatwi, 24; and Baraa Abu Kaiss, 24.
The Israeli military claimed that the strike, which leveled the two-storey building, killed a “prominent terrorist belonging to Jamaa Islamiya,” an armed Lebanese political group with ties to Hezbollah. It did not identify the person by name.
A Jamaa Islamiya spokesman acknowledged that some of the ambulance volunteers were members of the group, but denied that they were part of its armed wing.
Samer Hardan, head of the local Civil Defense center who was among the first responders, told The Guardian: “We examined every centimetre looking for parts of bodies and their possessions. We saw nothing military-related. We knew (the victims) personally, so we could identify their remains.”
Since Oct. 7, 16 medical workers have been killed by Israeli airstrikes in Lebanon, and a further 380 people have died including 72 civilians. Eleven Israeli soldiers and eight civilians have also been killed.
Kassem Al-Shaar, father of Ahmad and Hussein, said he had warned his sons not to volunteer.
“I told them that it was dangerous to do this type of work, but they said that they accepted the risk. I don’t know what Israel was thinking — these were young people excited to help others,” he said.
“My sons wanted to do humanitarian work, and look what happened to them. Israel wouldn’t dare to do what they did if it wasn’t for the US standing behind them.”
Aid groups issue urgent appeal for Yemen funds

- UN agencies warned that 18.2 million people in need of help after nine years of war
Dubai: Nearly 200 aid groups appealed on Monday for funds to bridge a $2.3 billion shortfall in assistance for war-torn Yemen, warning of potentially “catastrophic consequences” for the Arabian Peninsula’s poorest country.
A joint statement from 188 humanitarian organizations, including several UN agencies, warned that 18.2 million people — more than half the population — were in need of help after nine years of war.
Their appeal came a day before a meeting of high-ranking EU officials in Brussels to discuss the aid program for Yemen, which is suffering one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises.
“Inaction would have catastrophic consequences for the lives of Yemeni women, children and men,” the statement said, calling Tuesday’s meeting a “critical moment.”
“The humanitarian community appeals to donors to urgently address existing funding gaps, and provide sustainable support to enhance resilience and reduce aid dependency.”
Yemen has been gripped by conflict since the Iran-backed Houthis overran the capital Sanaa in 2014, triggering the Saudi-led military intervention in support of the government the following year.
Hundreds of thousands have died in the fighting or from indirect causes such as a lack of food, the United Nations says.
Hostilities slowed considerably in April 2022, when a six-month, UN-brokered ceasefire came into effect, and they have remained at a low level since.
But only $435 million of the $2.7 billion called for in Yemen’s 2024 Humanitarian Response Plan requirement has been raised, the aid groups said, warning of threats including food insecurity, cholera and unexploded ordnance.
“Underfunding poses a challenge to the continuity of humanitarian programming, causing delays, reductions and suspensions of lifesaving assistance programs,” it said.
“These challenges directly affect the lives of millions who depend on humanitarian assistance and protection services for survival.”
UN atomic watchdog chief Rafael Grossi arrives in Iran: media
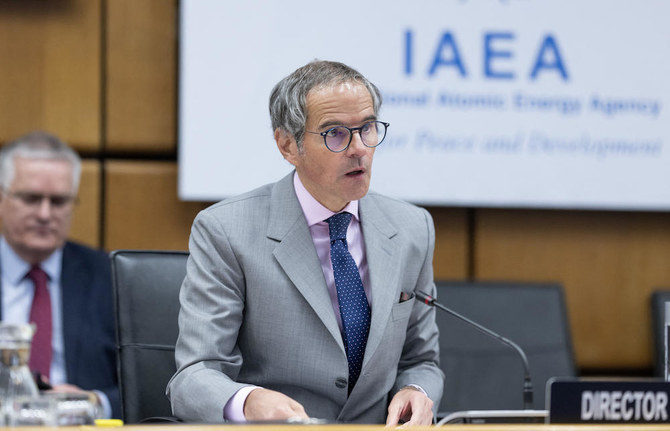

- Visit comes at a time of heightened regional tensions and with IAEA criticizing Iran for lack of cooperation on inspections and other outstanding issues
TEHRAN: UN atomic watchdog chief Rafael Grossi arrived Monday in Iran, where he is expected to speak at a conference and meet officials for talks on Tehran’s nuclear program.
“The Director General of the International Atomic Energy Agency arrived in Tehran on Monday at noon at the head of a delegation to participate in the nuclear conference and negotiate with top nuclear and political officials of the country,” Tasnim news agency said, with other agencies reporting the same details.
The visit comes at a time of heightened regional tensions and with the IAEA criticizing Iran for lack of cooperation on inspections and other outstanding issues.
Grossi, head of the IAEA, is expected to deliver a speech at Iran’s first International Conference on Nuclear Science and Technology.
The three-day event, which starts on Monday, is being held in Isfahan province, home to the Natanz uranium enrichment plant and where strikes attributed to Israel hit last month.
The IAEA and Iranian officials reported “no damage” to nuclear facilities after the reported attack on Isfahan, widely seen as Israel’s response to Iran’s first-ever direct attack on its arch foe days earlier, which itself was a retaliation for a deadly strike on Tehran’s Damascus consulate.
During his visit, Grossi is expected to meet with Iranian officials including the Islamic republic’s nuclear chief Mohammad Eslami.
On Wednesday Eslami, head of the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran, said he was “sure that these negotiations will further help clear ambiguities, and we will be able to strengthen our relations with the agency.”
Iran in recent years has deactivated IAEA monitoring devices at nuclear facilities and barred inspectors, according to the UN agency.
Grossi last visited Iran in March 2023 and met with top officials including President Ebrahim Raisi.
Iran has suspended its compliance with caps on nuclear activities set by a landmark 2015 deal with major powers after the United States in 2018 unilaterally withdrew from the agreement and reimposed sweeping sanctions.
Tensions between Iran and the IAEA have repeatedly flared since the deal fell apart, while EU-mediated efforts have so far failed both to bring Washington back on board and to get Tehran to again comply with the terms of the accord.
Last year, Iran slowed down the pace of its uranium enrichment, which was seen as a goodwill gesture while informal talks began with the United States.
But the Vienna-based UN nuclear agency said Iran accelerated the production of 60-percent enriched uranium in late 2023.
Enrichment levels of around 90 percent are required for military use.
Tehran has consistently denied any ambition to develop nuclear weapons, insisting that its atomic activities were entirely peaceful.
In February, the IAEA said in a confidential report seen by AFP that Iran’s estimated stockpile of enriched uranium had reached 27 times the limit set out in the 2015 accord.
On Sunday, the Iranian official news agency IRNA said Grossi’s visit provides “an opportunity for the two sides to share their concerns,” especially with regard to the IAEA’s inspectors.
Iran in September withdrew the accreditation of several inspectors, a move described at the time by the UN agency as “extreme and unjustified.”
Tehran, however, said its decision was a consequence of “political abuses” by the United States, France, Germany and Britain.
Eslami said the IAEA has “more than 130 inspectors” working in Iran, insisting Tehran remains committed to cooperating with the nuclear watchdog.
Lebanon’s Hezbollah says fired dozens of rockets at Israeli base

- The Israeli army said its warplanes “struck a Hezbollah military structure... deep inside Lebanon,”
The Iran-backed Hezbollah group said it fired “dozens of Katyusha rockets” at an Israeli base in the occupied Golan Heights on Monday in retaliation for a strike in Lebanon’s east.
Earlier, Lebanese official media said three people had been wounded in an Israeli strike early Monday in the country’s east, with the Israeli army saying it had struck a Hezbollah “military compound.”
Hezbollah fighters launched “dozens of Katyusha rockets” targeting “the headquarters of the Golan Division... at Nafah base,” the group said in a statement, saying it was “in response to the enemy’s attack targeting the Bekaa region.”
Israel and Lebanon’s Hezbollah have exchanged regular cross-border fire since Palestinian militant group Hamas’s unprecedented October 7 attack on southern Israel sparked war in the Gaza Strip.
In recent weeks Hamas-ally Hezbollah has stepped up its attacks on northern Israel, and the Israeli military has struck deeper into Lebanese territory.
“Enemy warplanes launched a strike at around 1:30 am this morning on a factory in Sifri, wounding three civilians and destroying the building,” Lebanon’s official National News Agency said.
Sifri is located in Lebanon’s Bekaa Valley, near the city of Baalbek, around 80 kilometers from the Israel-Lebanon frontier.
The Israeli army said its warplanes “struck a Hezbollah military structure... deep inside Lebanon,” referring to the location as “Safri.”
Last month, a building in Sifri was targeted in an Israeli raid, according to a source close to Hezbollah, while the Israeli army said it had targeted Hezbollah sites in Lebanon’s east.
East Lebanon’s Baalbek area is a Hezbollah stronghold and has been repeatedly struck by Israel in recent weeks.
On Sunday official media in Lebanon said an Israeli strike on a southern village killed four family members, with Hezbollah announcing retaliatory fire by dozens of rockets toward Kiryat Shmona in northern Israel.
The intensifying exchanges have stoked fears of all-out conflict between Israel and Hezbollah, which went to war in 2006.
In Lebanon, at least 390 people have been killed in nearly seven months of cross-border violence, mostly militants but also more than 70 civilians, according to an AFP tally.
Israel says 11 soldiers and nine civilians have been killed on its side of the border.
Tens of thousands of people have been displaced on both sides.