ISLAMABAD: At the Islamabad Museum, history no longer sits quietly behind glass.
In September 2025, the museum introduced Pakistan’s first Digital Immersive Gallery, an experiment in how ancient civilizations can be narrated in the age of artificial intelligence, 3D projection and virtual environments. Developed in collaboration with the Korea Heritage Agency, Pakistan’s Department of Archaeology and the National Heritage and Culture Division, the gallery marks a shift from object-centered displays to experience-based storytelling.
Rather than beginning with labels and timelines, the gallery opens with movement, sound and light. Visitors are invited to step into a reconstructed visual world shaped around Gandhara, one of South Asia’s most influential yet often under-explained civilizations that developed across what is now northwestern Pakistan and parts of eastern Afghanistan and later played a foundational role in the spread of Buddhism beyond the subcontinent.
“We have shown here in our Immersive Gallery how Buddhism flourished here, how it was introduced, how it declined and how it shifted to China, Korea and Japan from here,” Dr. Abdul Ghafoor, Deputy Director at the Department of Archaeology and Museums, told Arab News.
“In order to make it, the content developed by Korea has fully used AI and IT,” he continued. “AI and IT are common in Korea and other developed countries, but we have done it for the first time in Pakistan.”
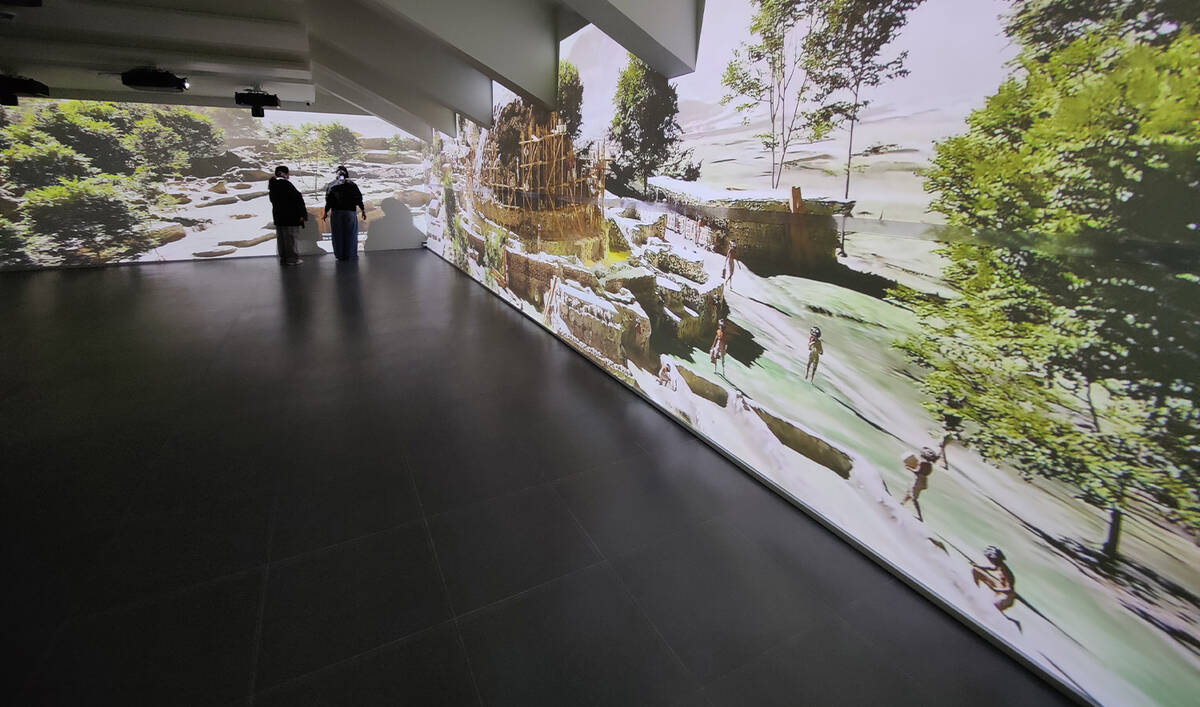

A picture taken on December 30, 2025, shows women watching Gandhara history at the Digital Immersive Gallery in Islamabad, Pakistan. (AN photo)
Gandhara flourished between the first century BCE and the fifth century CE in this region, which served as a cultural crossroads, shaped by Greek, Central Asian, Persian and South Asian influences.
It was here that artists first began depicting the Buddha in human form, a visual language that later traveled along trade routes to Central Asia, China, Korea and Japan. This transmission of ideas, beliefs and artistic styles forms the core narrative of the immersive gallery.
“Inside the gallery, visitors are drawn into a world of interactive experiences, heritage documentaries they can zoom in and out of, Gandhara artifacts explored up close and photo zones where they can capture themselves against Pakistan’s most iconic sites,” Muhammad Azeem, Project Director at the Department of Archaeology and Museums, said.
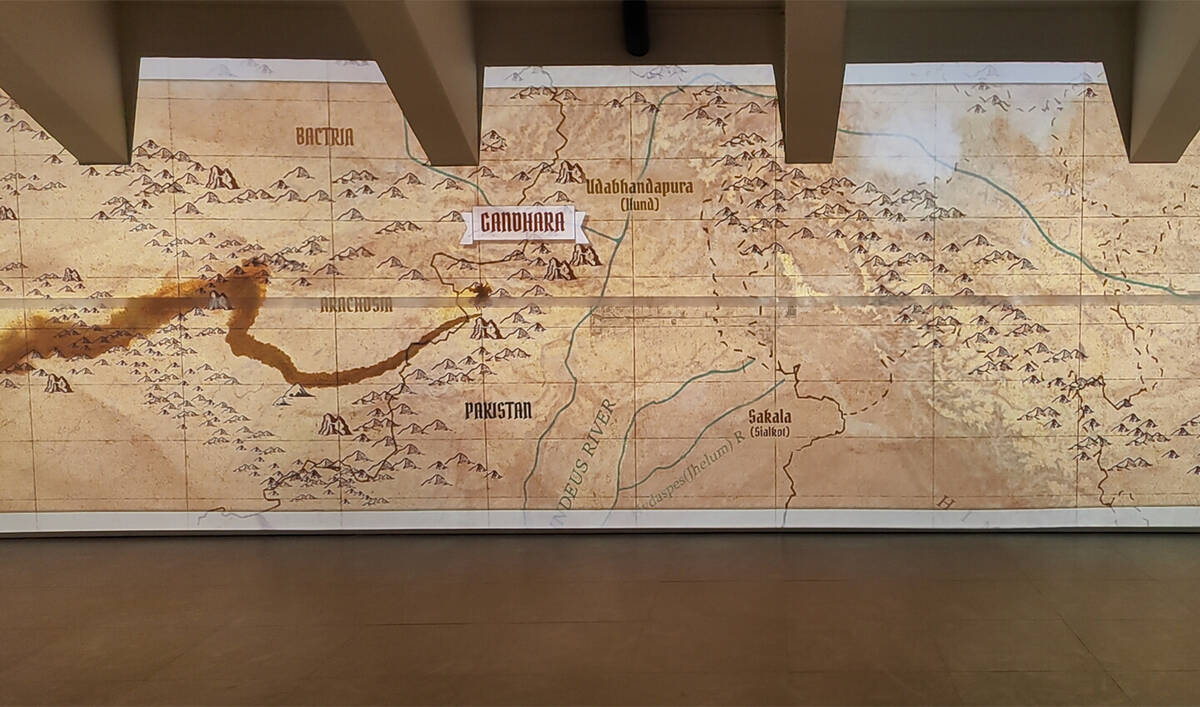
A picture taken on December 30, 2025, shows map of Gandhara civilization at the Digital Immersive Gallery in Islamabad, Pakistan. (AN photo)
While Gandhara anchors the gallery, the experience expands outward to place it within a longer and wider historical arc. One section is dedicated to Pakistan’s six UNESCO World Heritage Sites, offering visitors a compressed journey across centuries and regions.
“The main hall takes it further with a fully immersive 3D journey,” Azeem added. “Each seven-minute segment transports audiences to treasures like Mohenjo-Daro, Makli Necropolis, Lahore’s Shalimar Gardens and Sheesh Mahal, and the historic landscapes of Taxila and Takht-i-Bahi, making the past feel vivid, unforgettable and alive.”
For many visitors, the gallery’s appeal lies in how it lowers the barrier to understanding. Instead of long explanatory panels, history is introduced through visuals, motion and guided narrative.
“I saw different historical sites on big screens which was very exciting for me,” Fatima Nawaz, a government employee, said. “After that, I watched a complete documentary in the gallery, which was about 20 minutes long, and in which different historical sites related to Gandhara were highlighted.”
“Overall, it was a very good experience,” she added.

A picture taken on December 30, 2025, shows visitors watching Gandhara history at the Digital Immersive Gallery in Islamabad, Pakistan. (AN photo)
Researchers see the initiative as part of a broader global shift in how museums function.
“My topic is Cultural Heritage Museum, and with this research, I am studying and visiting museums,” Abdul Khaliq, an M.Phil. student at Quaid-e-Azam University, said. “One thing I have not seen in Pakistan before is the shift toward virtual reality.”
He added that it was a good step while calling the immersive gallery “very educational and gives us a lot to learn.”
For the officials involved in the project, the gallery is a starting point rather than a finished model.
“The response we have received from the public in Islamabad makes me feel that this should be done in all the museums, in all four provinces of Pakistan,” Dr. Ghafoor, the senior archaeology department official, said. “This is because it can make it easier to follow history.”
“I think such immersive galleries should be there in all the museums,” he added.












