TOKYO: Vietnam approved plans on Wednesday for a multi-billion-dollar railway with China, boosting links between the two communist countries.
Around the region, China has been financing railways under its Belt and Road Initiative, which funds infrastructure projects globally, but has come under fire with a number of plans stalled or mired in controversy.
Here are some of the key instalments in Asia’s China-backed railway network:
PAKISTAN
In Pakistan, a railway linking southwestern Gwadar Port with China’s northwestern Xinjiang province has long been on the cards but has yet to materialize.
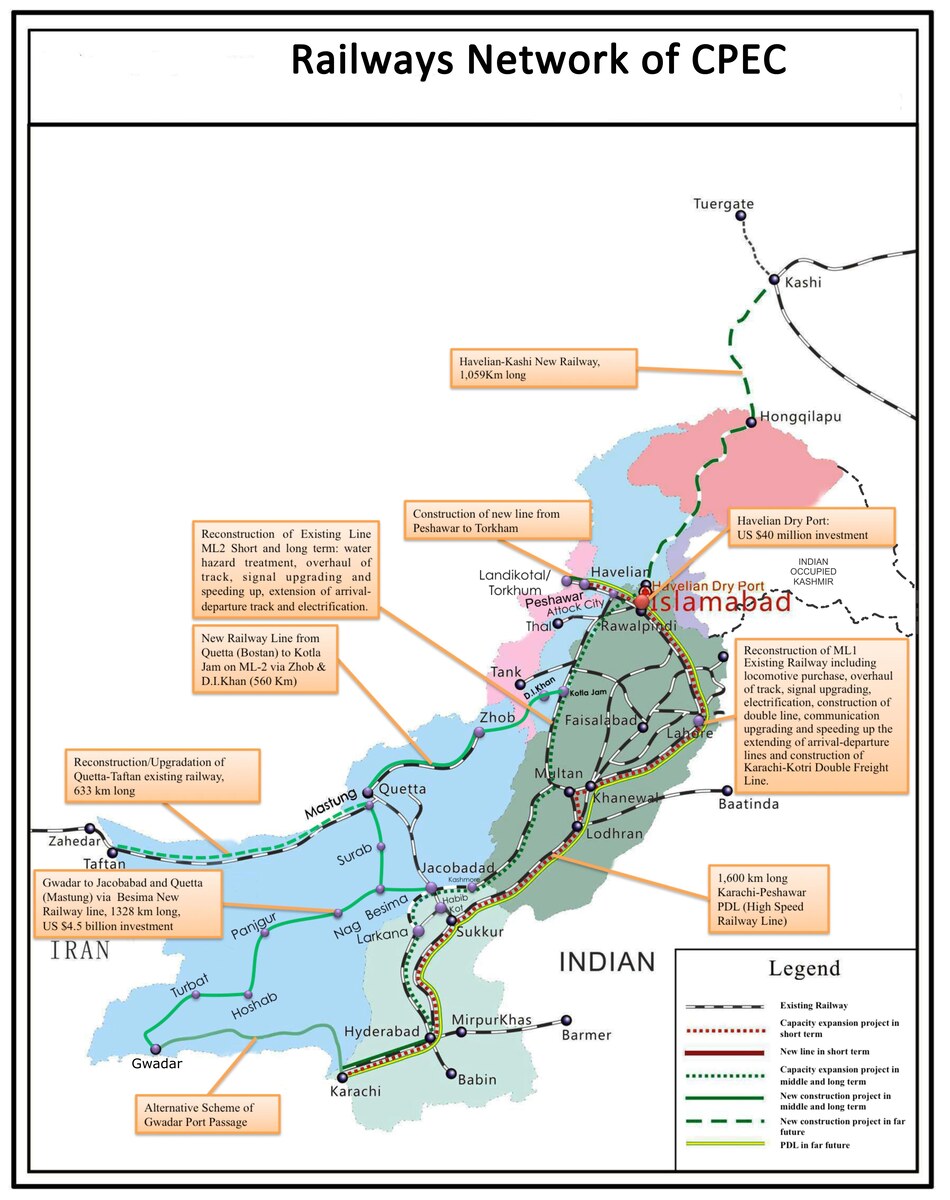
This official route map, posted on the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor website, presents a monographic study on transport planning for CPEC’s Railway Network, covering the period from 2014 to 2030. (Photo courtesy: CPEC)
If the project moves ahead, a 2023 Chinese study estimated an eyewatering price tag of $58 billion.
INDONESIA
Indonesia launched Southeast Asia’s first high-speed railway in October 2023, after years of delays. The $7 billion China-backed project links the capital Jakarta to the city of Bandung in 45 minutes — slashing the journey by about two hours.
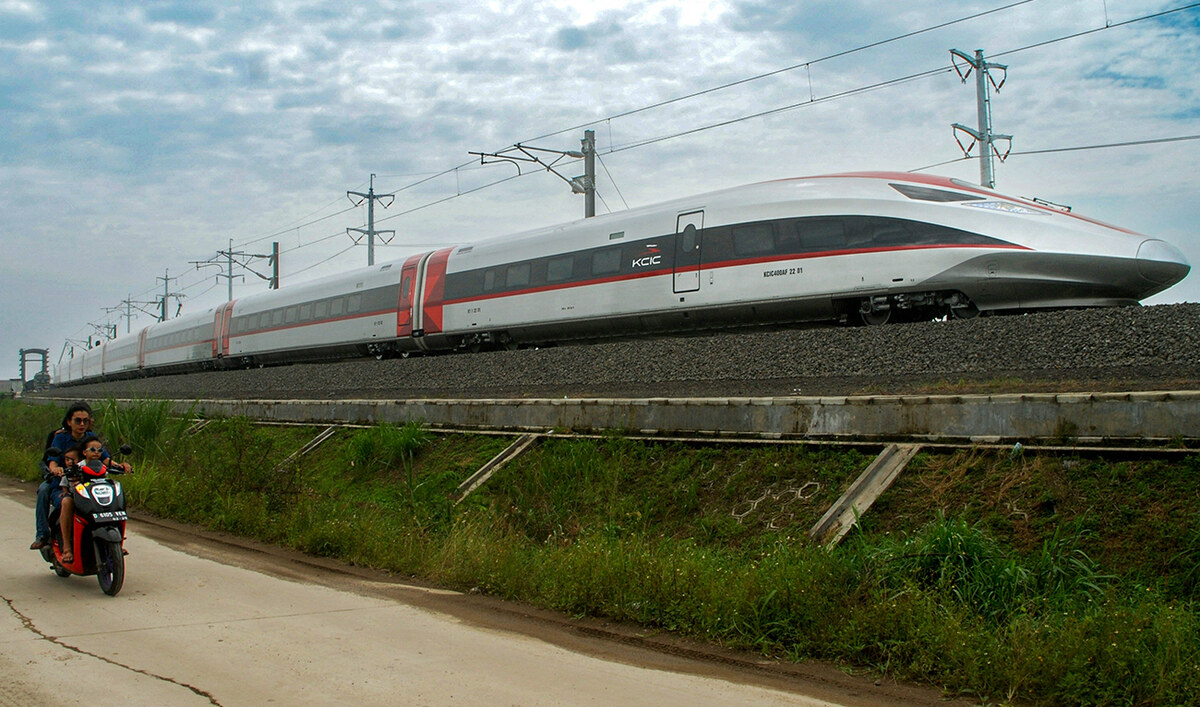

A hi-speed train built in cooperation between Indonesia and China moves along its dedicated track, prior to a dynamic test, in Tegalluar on November 9, 2022. (AFP/File)
Built by a joint venture of four Indonesian state companies and Beijing’s China Railway International Co, it was initially set to cost less than $5 billion and be completed by 2019. But construction challenges and the pandemic led to delays and surging expenses.
Indonesia’s then-president Joko Widodo nevertheless hailed its opening as a symbol of modernization.
LAOS
Laos unveiled its $6 billion Chinese-built railroad in 2021, bringing hopes of an economic boost despite backlash after thousands of farmers had to be evicted to make way for construction.
The 414-kilometer (260-mile) route connects the Chinese city of Kunming to Laotian capital Vientiane, with plans for the high-speed line to ultimately reach Singapore.
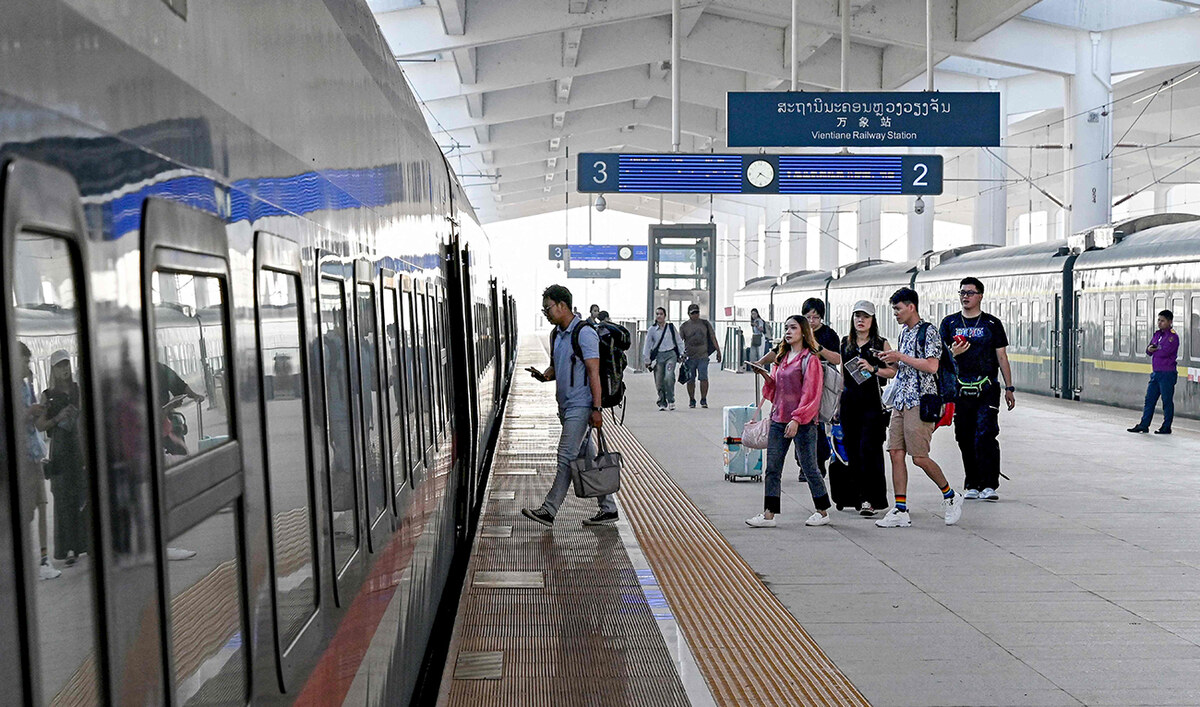

This photo taken on October 12, 2024 shows passengers boarding a high-speed train in the railway station in Laos' capital Vientiane. (AFP/File)
Infrastructure-poor Laos, a reclusive communist country of about 7.4 million people, previously had only four kilometers of railway tracks.
It was hoped that the railway would boost the Southeast Asian country’s ailing tourism industry, which struggled to rebound from the pandemic.
But experts also raised concerns over whether cash-strapped Laos — where public debt made up 116 percent of GDP in 2023 — would ever be able to pay back Beijing.
THAILAND
After long delays, Thailand is pressing ahead with a Chinese-backed high-speed line set to partially open in 2028. The $5.4 billion project aims to expand the connection to Kunming, running to Bangkok via Laos by 2032.
Thailand already has nearly 5,000 kilometers (3,000 miles) of railway but the sluggish, run-down network has long driven people to favor road travel — despite extremely high accident rates.
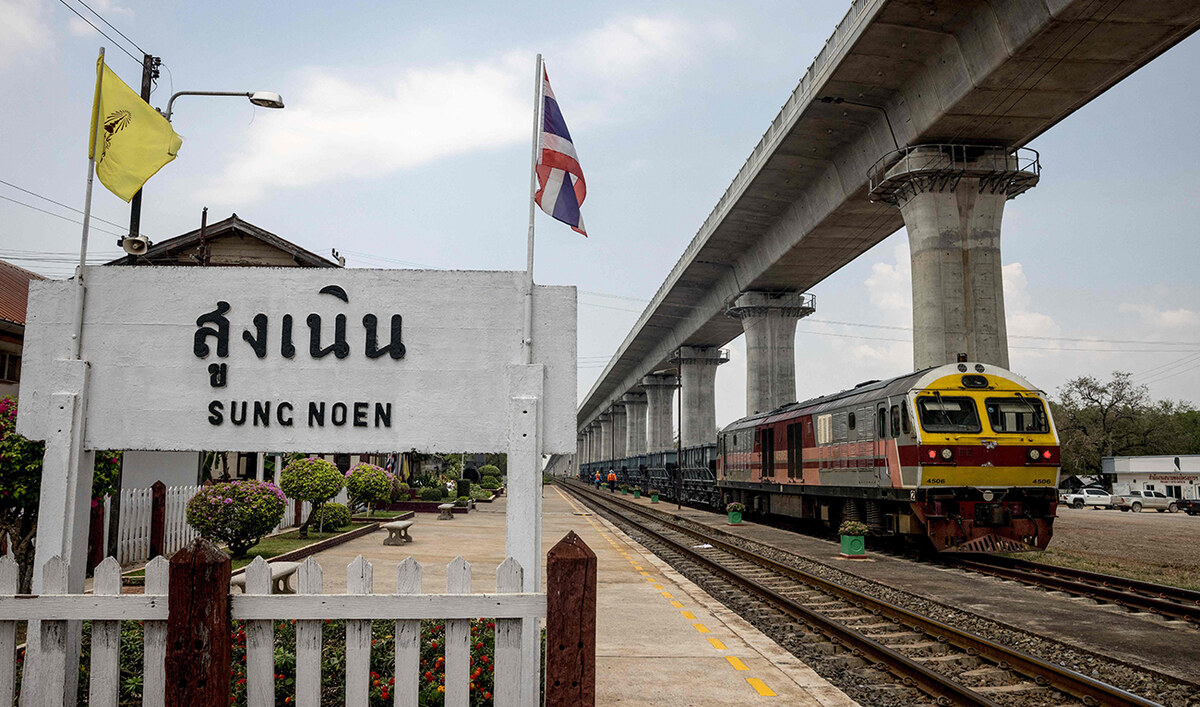

In this photo taken on March 29, 2023 a train sits below an elevated track, still under construction as part of the Thai-Chinese Bangkok-Nong Khai high-speed railway project at Sung Noen Station in Nakhon Ratchasima province. (AFP/File)
When the new railroad is fully complete, Chinese-made trains will run from Bangkok to Nong Khai, on the border with Laos, at up to 250 km/h.
Unlike Laos, Thailand signed a deal to cover project expenditures itself and has pitched it as a way to boost the economy through trade with China.
KYRGYZSTAN
Kyrgyz President Sadyr Japarov inaugurated construction in December of a railway linking China, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan, with hopes it will serve as a supply route to Europe.
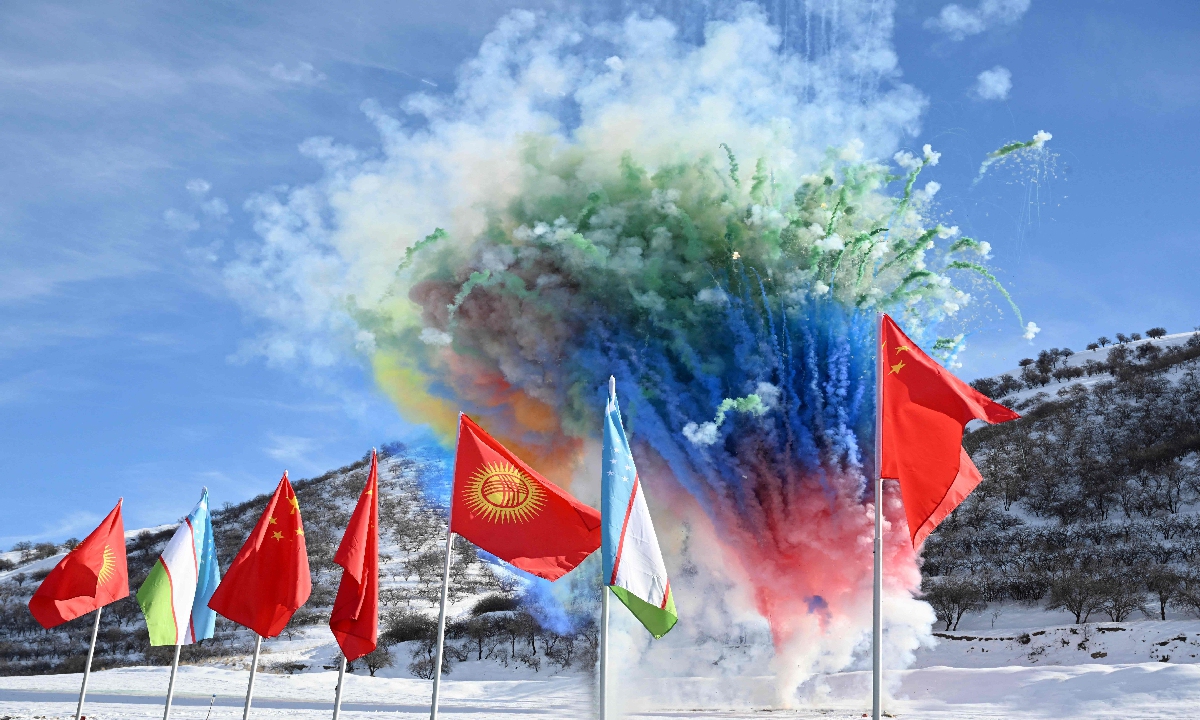

In this handout picture taken and released by the Kyrgyz presidential press office on December 27, 2024, fireworks explode behind state flags during the commencement ceremony of the China-Kyrgyzstan-Uzbekistan railway project in the settlement of Tash-Kitchu. (Photo courtesy: VCG/File)
“This route will ensure supply of goods from China to Kyrgyzstan and then onto Central Asia” and nearby countries “including Turkiye” and “even to the European Union,” he said.
The project, which Kyrgyz authorities estimate could cost up to $8 billion, includes construction through mountains and in areas of permafrost, where the ground never fully thaws.
VIETNAM
Vietnam this week approved an $8-billion railroad running from its largest northern port city to China. The line will operate through some of Vietnam’s key manufacturing hubs, home to Samsung, Foxconn and Pegatron factories, many of which rely on components from China.

Railway workers guide a train at a railway crossing in Hanoi on February 18, 2025. (AFP/File)
Another yet-to-be-approved line to China would connect Hanoi to Lang Son province, traveling through more areas packed with manufacturing facilities.
MALAYSIA
Malaysia has revived construction of a nearly $17 billion railroad to carry passengers and freight between shipping ports on its east and west coasts. The China-backed, 665-kilometer project was originally launched in 2011 under ex-leader Najib Razak, but shelved due to a dispute about payments.
After blowing past several deadlines and budgets, it now looks set to be operational by 2027.
MYANMAR
In coup-hit Myanmar, talks on building a railway from Mandalay to China’s Yunnan province appear to have stalled.
And in the Philippines, plans for China to fund three railways flopped after Manila backed out of talks in 2023 as the South China Sea dispute heated up.














