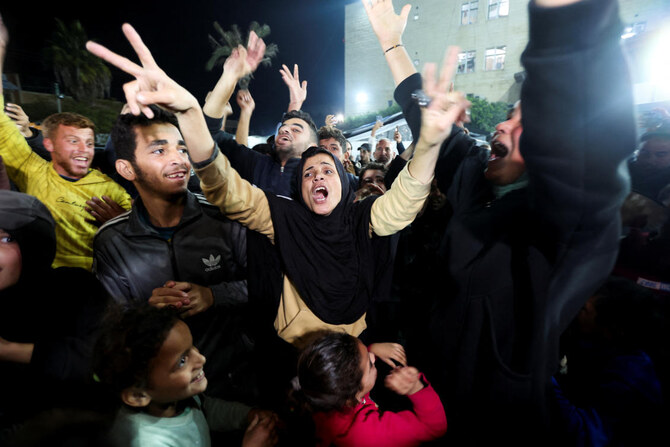Israel and Hamas agreed to a ceasefire deal on Wednesday pausing a devastating 15-month war in Gaza and raising the possibility of winding down an Israeli military operation that has killed more than 46,000 Palestinians.
The deal, coming after weeks of painstaking negotiations in the Doha, promises the release in phases of dozens of hostages held by Hamas since it led an attack on Israel in October 2023 that killed at least 1,200 people.
International response to the deal, which is yet to be confirmed by Israel, overwhelmingly welcomed the agreement.
US President Joe Biden
"I can announce a ceasefire and a hostage deal has been reached between Israel and Hamas," Biden said at the White House.
"Fighting in Gaza will stop, and soon the hostages return home to their families."
US President-elect Donald Trump
"We have a deal for the hostages in the Middle East. They will be released shortly. Thank you!" he said in a post on his Truth Social platform.
"With this deal in place, my National Security team, through the efforts of Special Envoy to the Middle East, Steve Witkoff, will continue to work closely with Israel and our Allies to make sure Gaza NEVER again becomes a terrorist safe haven," Trump said in a second post.
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres
"The United Nations stands ready to support the implementation of this deal and scale up the delivery of sustained humanitarian relief to the countless Palestinians who continue to suffer," he told reporters.
Turkish Foreign Minister Hakan Fidan
He told reporters in Ankara the ceasefire deal was an important step for regional stability. Fidan also said Turkish efforts for a two-state solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict would continue.
Qatar's Prime Minister Sheikh Mohammed Bin Abdulrahman Al Thani
The prime minister called for calm in the Gaza Strip between now and Jan. 19 when the ceasefire deal takes effect.
Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi
He welcomed the Gaza ceasefire deal, according to a post on X, and stressed the importance of a fast delivery of humanitarian aid to Gaza.
Saudi Arabia's Ministry of Foreign Affairs
In a statement, the Kingdom stressed the need for adherence to the deal, an end to Israel’s aggression against Gaza, and the complete withdrawal of Israeli forces from the territory and all other occupied Palestinian and Arab lands. It also highlighted the importance of building on the agreement by addressing the underlying reasons for the conflict and enabling the Palestinian people to secure their rights, the foremost of which is the establishment of an independent Palestinian state based on 1967 borders, with East Jerusalem as its capital.
Saudi Arabia expressed hope that the ceasefire deal would mark a permanent end to a brutal Israeli war.
UAE's Minister of Foreign Affairs Sheikh Abdullah bin Zayed
Sheikh Abdullah "stressed the need for both parties to abide by the agreements and commitments reached in order to end the suffering of Palestinian prisoners and Israeli detainees." He called for "the urgent and sustainable delivery of humanitarian aid to those in need and to allow its flow by all means and without obstacles to end the critical humanitarian conditions facing civilians for more than 15 months."
Ursula Von Der Leyen, President of the European Commission
"I warmly welcome the ceasefire and hostage release agreement in Gaza. Hostages will be reunited with their loved ones and humanitarian aid can reach civilians in Gaza. This brings hope to an entire region, where people have endured immense suffering for far too long. Both parties must fully implement this agreement, as a stepping stone toward lasting stability in the region and a diplomatic resolution of the conflict,” she said.
British Prime Minister Keir Starmer
"After months of devastating bloodshed and countless lives lost, this is the long-overdue news that the Israeli and Palestinian people have desperately been waiting for," Starmer said in an emailed statement.
"For the innocent Palestinians whose homes turned into a warzone overnight and the many who have lost their lives, this ceasefire must allow for a huge surge in humanitarian aid, which is so desperately needed to end the suffering in Gaza. "And then our attention must turn to how we secure a permanently better future for the Israeli and Palestinian people - grounded in a two-state solution that will guarantee security and stability for Israel, alongside a sovereign and viable Palestine state."
Alexander De Croo, Belgium's Prime Minister
“After too many months of conflict, we feel tremendous relief for the hostages, for their families and for the people of Gaza.
Let’s hope this ceasefire will put an end to the fighting and mark the beginning of a sustained peace. Belgium stands ready to help.”
German Foreign Secretary Annalena Baerbock
"In these hours there is hope that the hostages will finally be released and the deaths in Gaza will come to an end. Everyone who bears responsibility should now ensure that this opportunity is seized."
Norwegian Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Stoere
"The Palestinian institutions must be strengthened and prepared to assume full control and responsibility, including in Gaza. Both Israel and Palestine must receive credible security guarantees, and the solution must be anchored regionally."
*With AP and Reuters