The Greek-flagged ship Sounion has been on fire since Aug. 23 after an attack by Yemen’s Houthis with no obvious signs of an oil spill, EU Red Sea naval mission Aspides said in a post on X on Monday.
The EU mission published photos dated Sunday showing fire and smoke coming out of the vessel’s main deck.
Houthis, who control Yemen’s most populous regions, said on Thursday that they attacked the Sounion oil tanker in the Red Sea. The Iran-aligned group has been attacking ships in solidarity with Palestinians in the war between Israel and Hamas in Gaza.
Fires were observed on at least five locations on the main deck of the vessel, Aspides said. Additionally, part of the superstructure is on fire too.
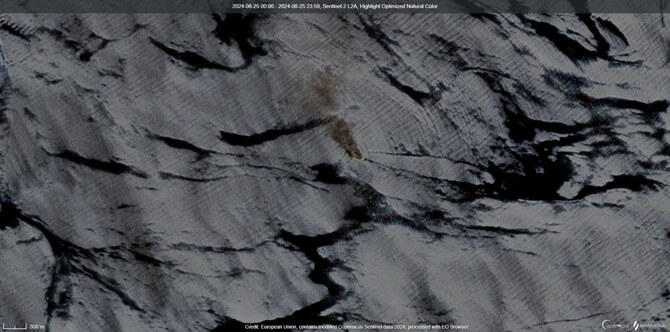
Satellite image captured by European Space Agency’s Copernicus Satellite 2 showed smoke visible at sea in the vicinity where Sounion was last detected.
Reuters was able to locate the image from matching the last location for MV Sounion seen from LSEG ship tracker.
Aspides said on Thursday that the oil tanker carrying 150,000 tons of crude oil poses an environmental hazard.
Greek-flagged ship on fire since August 23 after Houthi attack, EU naval mission says
https://arab.news/zrwhp
Greek-flagged ship on fire since August 23 after Houthi attack, EU naval mission says

- Houthis, who control Yemen’s most populous regions, said on Thursday that they attacked the Sounion in the Red Sea
- The Greek-flagged tanker carries 150,000 tonnes of crude oil which poses an environmental hazard
Russian forces begin pulling out of bases in northeast Syria

- Despite having been on opposite sides of the battle lines during the civil war, the new rulers in Damascus have taken a pragmatic approach to relations with Moscow
QAMISHLI, Syria: Russian forces have begun pulling out of positions in northeast Syria in an area still controlled by the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces after the group lost most of its territory in an offensive by government forces.
Associated Press journalists visited one base next to the Qamishli airport Tuesday and found it guarded by SDF fighters who said the Russians had begun moving their equipment out in recent days.
Inside what had been living quarters for the soldiers was largely empty, with scattered items left behind, including workout equipment, protein powder and some clothing.
Ahmed Ali, an SDF fighter deployed at the facility, said the Russian forces began evacuating their positions around the airport five or six days ago, withdrawing their equipment via a cargo plane.
“We don’t know if its destination was Russia or the Hmeimim air base,” he said, referring to the main Russian base on Syria’s coast. “They still have a presence in Qamishli and have been evacuating bit by bit.”
A UN humanitarian convoy from Damascus reached Qamishli on Tuesday, UN spokesman Stéphane Dujarric said.
“It delivered food, warm clothes and blankets, among other supplies,” he told UN reporters. “More convoys are planned in the coming days.”
Dujarric said the UN is also continuing to distribute food, bread and cash elsewhere including displacement sites.
There has been no official statement from Russia about the withdrawal of its forces from Qamishli.
Russia has built relations with the new central Syrian government in Damascus since former President Bashar Assad was ousted in December 2024 in a rebel offensive led by now-interim President Ahmad Al-Sharaa — despite the fact that Moscow was a close ally of Assad.
Moscow’s scorched-earth intervention in support of Assad a decade ago turned the tide of Syria’s civil war at the time, keeping Assad in his seat. Russia didn’t try to counter the rebel offensive in late 2024 but gave asylum to Assad after he fled the country.
Despite having been on opposite sides of the battle lines during the civil war, the new rulers in Damascus have taken a pragmatic approach to relations with Moscow. Russia has retained a presence at its air and naval bases on the Syrian coast.
Al-Sharaa is expected to visit Moscow on Wednesday and meet with Putin.
Fighting broke out early this month between the SDF and government forces after negotiations over a deal to merge their forces together broke down. A ceasefire is now in place and has been largely holding.
After the expiration of a four-day truce Saturday, the two sides announced the ceasefire had been extended by another 15 days.
Syria’s defense ministry said in a statement that the extension was in support of an operation by US forces to transfer accused Daesh militants who had been held in prisons in northeastern Syria to detention centers in Iraq.