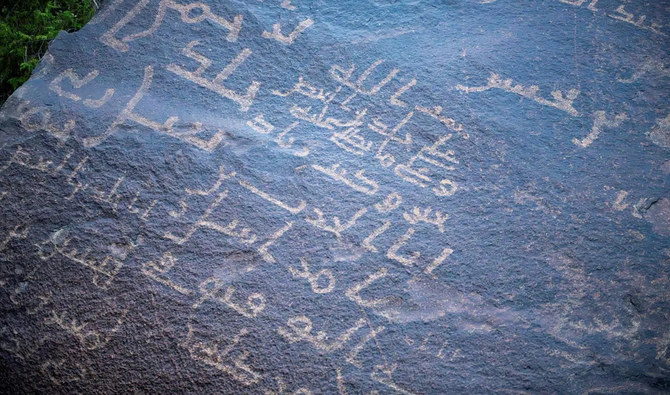RIYADH: The “Book Plateau,” in the heart of Saudi Arabia’s Baha region, is drawing visitors from far and wide. Nestled in Baljurashi, the inscribed rock epitomizes the rich cultural tapestry of the area.
Located at the confluence of two streams at the foot of Wadi Khara, this archaeological wonder has been likened to the pages of an open book and earned its name from the old inscriptions adorning its surface, the Saudi Press Agency reported.
The carvings are believed to date back some 1,400 years. The site boasts early Islamic inscriptions without diacritical marks, some of which bear the names of the Prophet’s companions and their followers.
There is another rock formation nearby which resembles a palm, bearing different inscriptions. Five graves can be found at the top of Mihras Mountain, two of which are noticeably elevated. While their exact history and occupants remain unknown, it is believed they belong to people who once inhabited the area.
Abdulrahman Al-Ghamdi, director general of the Heritage Authority in Baha, told the SPA that the authority had included the site in the National Antiquities Register following a survey in 2005. The inscriptions, which are etched onto granite rock faces, stand as silent witnesses to the area’s historic importance.
Baha’s summer season is attracting local and international visitors to its heritage villages and historic and archaeological sites.
These attractions have become crucial economic drivers, shaping the national tourism vision in line with the Kingdom’s ambitious goals.
They also showcase the region’s historic legacy for present and future generations.