LONDON: The campaign of attacks by Yemen’s Houthi fighters on shipping in the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden continues, despite renewed US and UK strikes on their positions, leading to fears about the long-term security of these strategically important waterways.
The persistence of the attacks has turned the spotlight on the Iran-backed militia as it appears to be gaining strength, in terms of weaponry and fighters, and confidence in its ability to cause global trade disruptions.
Speaking at the Munich Security Conference last week, Rashad Al-Alimi, chair of the Presidential Leadership Council of the UN-backed Yemeni government, said the Houthis had irrevocably altered the region’s geopolitical contours.

The persistence of the attacks has turned the spotlight on the Iran-backed militia. (AP)
“The Red Sea will continue to be a source of tension, ready to explode at any political turn, as long as the Houthis control coastal regions,” he added.
“To end Houthi piracy, we must address its origin and source. This can only be accomplished by restoring state institutions, ending the coup, and applying maximum pressure on Iran.”
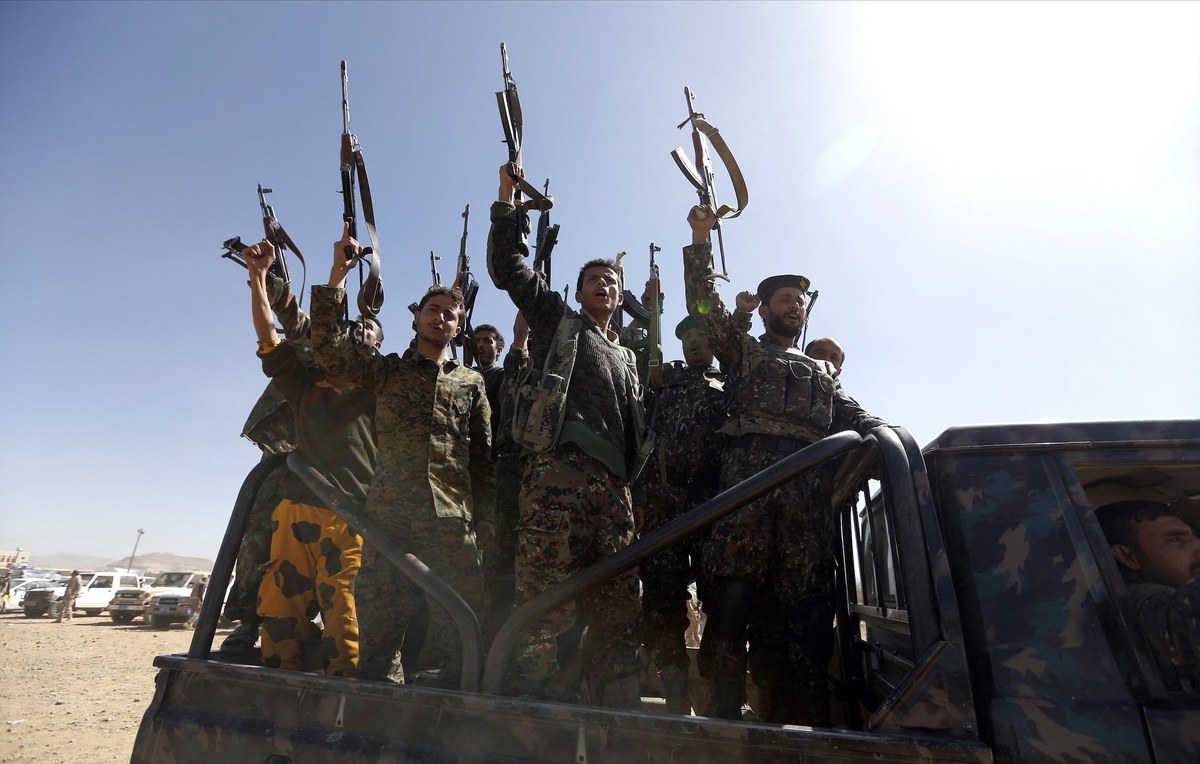
The Houthi militia is part of the “axis of resistance,” a loose network of Iran-backed proxy militias throughout the region that includes the Palestinian militant group Hamas, Hezbollah in Lebanon, and several Shiite groups in Iraq.
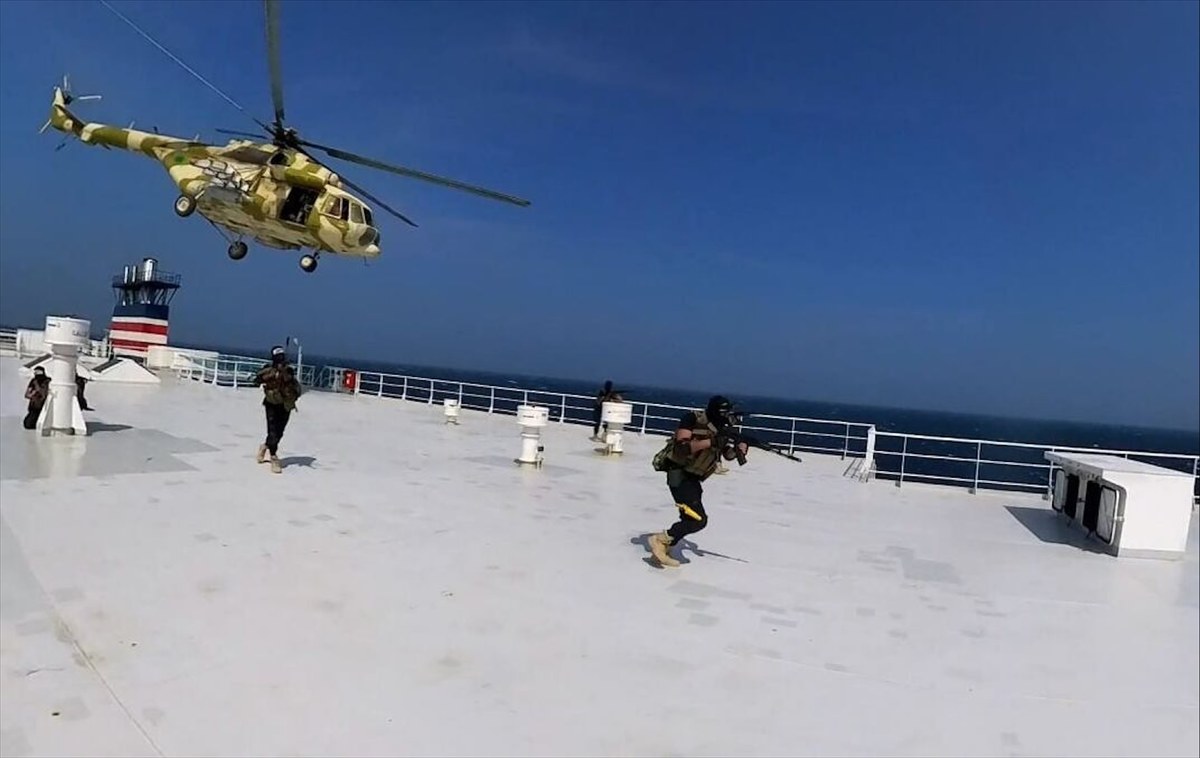
When the Houthis began attacking commercial shipping in November, they claimed they were only targeting vessels with links to Israel in an attempt to pressure the Israeli government to end its military operation against Hamas in Gaza.
However, Houthi drones, missiles and acts of piracy have been launched against several ships with no ties to Israel. In fact, in recent weeks Yemeni ships, and even vessels belonging to Houthi-allied Iran, have come under attack.
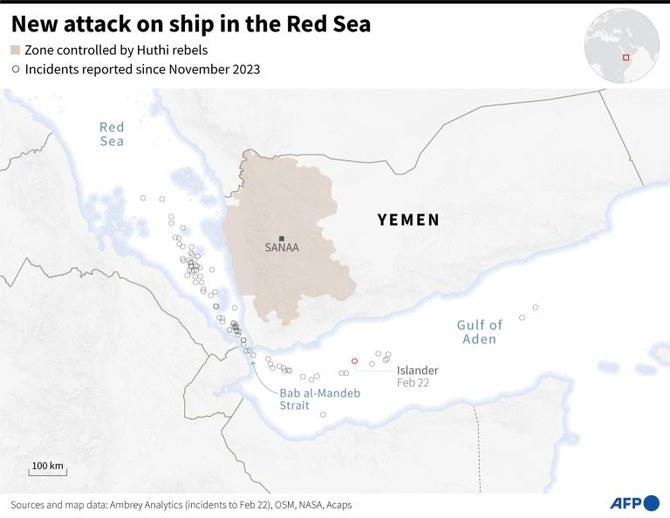
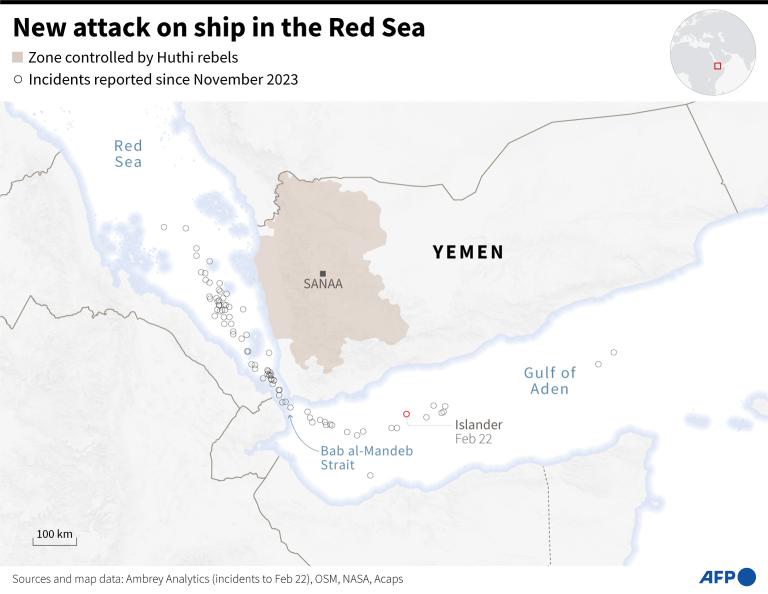
According to a tally by the Associated Press news agency, the Houthis have carried out at least 57 attacks on commercial and military ships in the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden since Nov. 19. US Central Command has even identified the use of a Houthi-operated submarine drone.
In response to these attacks, many of the world’s biggest freight companies have redirected their vessels from the Suez Canal route to the Mediterranean, thereby avoiding the Red Sea, and instead are using much longer and more expensive routes via the Cape of Good Hope.

The Houthis have carried out at least 57 attacks on commercial and military ships in the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden since Nov. 19. (AFP)
Simon Evenett, founder of nonprofit organization the St. Gallen Endowment for Prosperity Through Trade, said that while shipping costs have risen, they are still “well below” their pandemic-era peaks. He also noted that some freight companies had simply continued to traverse the waterways of the Red Sea despite the risk of attack.
“The New York Fed’s index of Global Supply Chain Pressure has barely moved,” Evenett told Arab News. “Important as it is, just 11 percent of global trade flows through the Red Sea. This isn’t enough to disrupt the world economy.
“What’s harder to assess is whether yet more upheaval in trade routes further undermines policymakers’ and corporate trust in long-distance sourcing. A further nudge towards national and regional sourcing can be expected.”
To prevent disruption to trade, protect mariners and uphold the right to freedom of navigation, the US-led patrol mission, Operation Prosperity Guardian, was established in December. When the Houthi attacks persisted, the US and UK launched strikes against militia targets in Yemen.
In a joint statement on Feb. 24, the US and the UK said their military forces struck 18 Houthi sites across eight locations in Yemen, including underground weapons and missile storage facilities, air defense systems, radars and a helicopter.

The Houthi militia is part of the “axis of resistance,” a loose network of Iran-backed proxy militias throughout the region. (AFP)
The operation was the fourth time the US and UK had carried out joint attacks against the Houthis since Jan. 12. The US has also carried out almost daily operations against Houthi targets, including incoming missiles, rockets and drones targeting vessels.
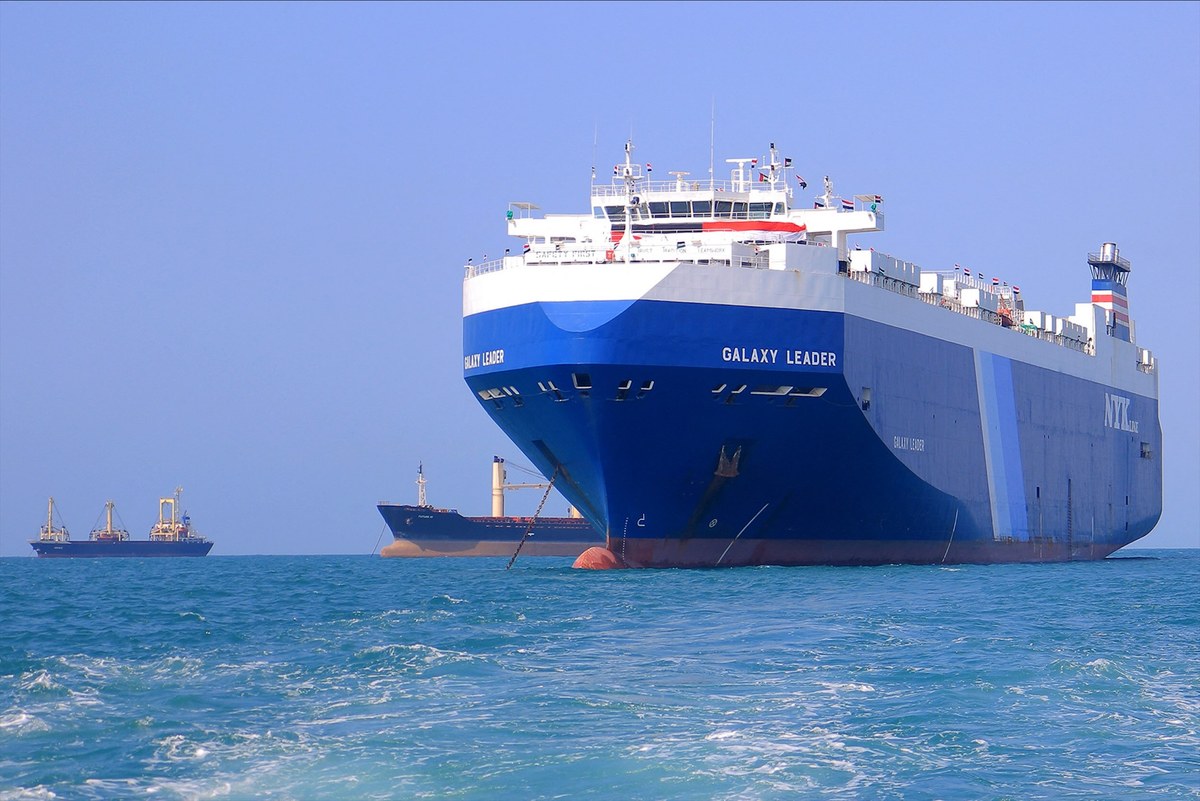
These Western strikes have done little to stem the tide of attacks, however. On Feb. 19, the Houthis mounted one of their most damaging assaults yet, on the Belize-flagged Rubymar, carrying cargo from the UAE to Bulgaria, forcing its crew to abandon ship.
Indeed, far from curtailing the activities of the Houthis, their popularity in Yemen appears to have grown since the shipping attacks began, with thousands of recruits reportedly joining their ranks.
If its intent was to force a swift Houthi climbdown, the Western military response has so far borne little fruit. The Houthis seem only too keen to up the ante, with their leader Abdul Malik Al-Houthi stating “we will also attack with submarine weapons.”
However, in a message posted recently on social media platform X, the militia said: “What the world is impatiently waiting for is not the militarization of the Red Sea, but rather an urgent and comprehensive declaration of ceasefire in Gaza, for humanitarian reasons that are clear to anyone.
“There is no danger to international or European navigation so long as there are no aggressive operations, and thus, there is no need to militarize the Red Sea.”
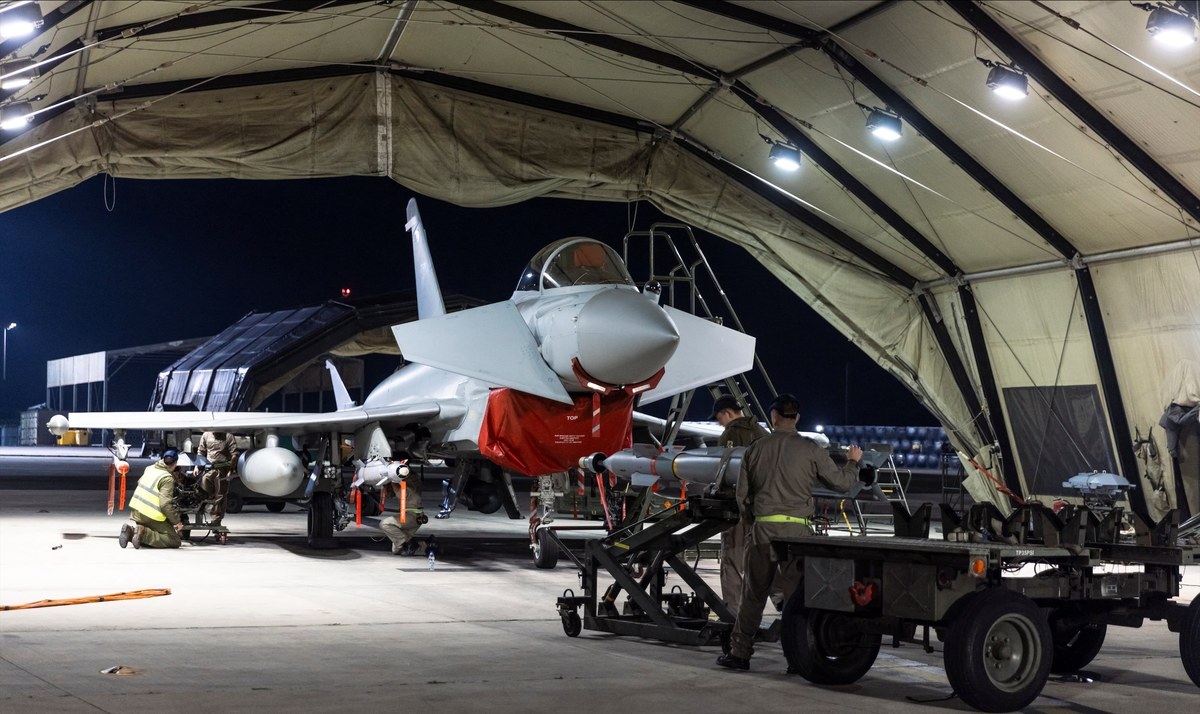

In a joint statement on Feb. 24, the US and the UK said their military forces struck 18 Houthi sites across eight locations in Yemen. (Getty Images/AFP)
Not everyone is convinced that securing a ceasefire in Gaza will end the Houthi attacks on shipping. Like Al-Alimi, those with such concerns want the international community to take the worst-case scenario more seriously and take preventive action now.
Raiman Al-Hamdani, a researcher at social enterprise organization Ark, agreed that attacks are likely to continue after the war, but in the form of piracy in a “push to monetize their presence” in the seas off the coast of Yemen.
“This could mean attacking commercial vessels in the future, albeit not to the extent that we are seeing today,” he told Arab News, adding that the Houthis could begin demanding taxes from vessels passing through Bab Al-Mandab Strait in return for not striking them.
Farea Al-Muslimi, a research fellow at Chatham House, likewise believes the Houthis have hit upon an opportunity to raise revenues from passing vessels.
“They will, of course, try to make deals and there are already countries that are looking for waivers,” Al-Muslimi told Arab News.
“But there are several problems with this, one of which is that were they to escalate the crisis in the Red Sea, it would not be safe for anyone.
“As you can see, they have already attacked ships linked to Yemen and vessels belonging to their own ally, Iran, so any escalation of this will not be a clean battle.”
Some countries, including regional states, have called for a more measured response to the attacks, rather than military action that might inflame tensions in the region.
The Egyptian Foreign Ministry recently expressed “deep concern over the escalation of military operations in the Red Sea and the airstrikes that were directed at a number of sites in Yemen.” It called for a “united international and regional effort to reduce tension and instability in the region, including navigation security.”
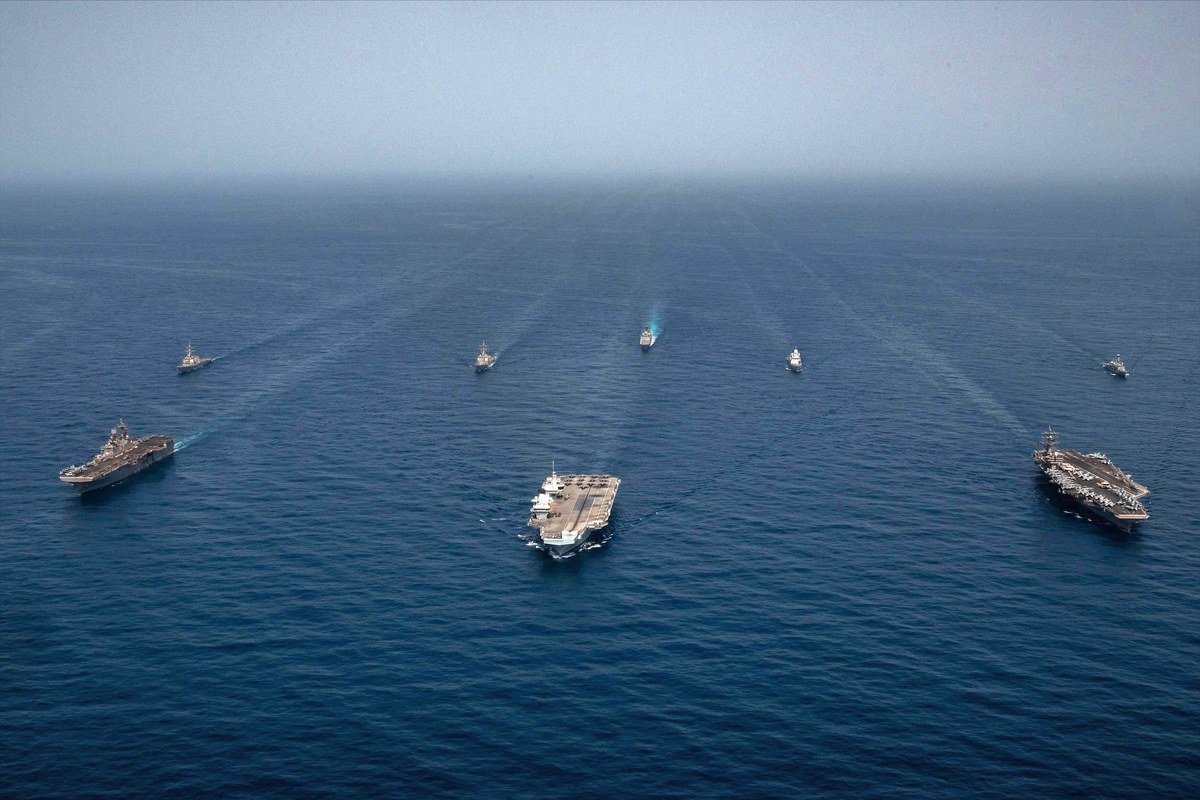

US Central Command has identified the use of a Houthi-operated submarine drone. (AFP)
It added: “The dangerous and escalating developments taking place are a clear indication of what we’ve repeatedly warned against regarding the dangers of expanding the conflict in the region as a result of the continued Israeli attacks in the Gaza Strip.”
Security experts have also said the military response might prove counterproductive, with concerns that it could play into the hands of the Houthis, who have sought to present themselves as defenders of Gaza who are standing up to Israel and its Western allies.
Al-Hamdani believes the attacks on shipping serve several purposes for the Houthis: to help recruit new followers, distract from domestic problems, burnish support among the population, and to strengthen the militia’s negotiating position in the ongoing Yemen peace process.
Al-Muslimi believes the Houthis have “already capitalized on it as much as they could politically,” suggesting the attacks will likely stop when the war in Gaza ends.

The persistence of the attacks has turned the spotlight on the Iran-backed militia. (AP)
However, he said the regional calculus has changed as a result of the Houthi onslaught and the broader context in the region since the Oct. 7 attacks by Hamas on southern Israel that sparked the conflict in Gaza, increasing the chances the Middle East could be plunged into a wider war.
“Nothing in the Middle East will be the same after Oct. 7, and this includes how the world views Yemen, how the world views the Red Sea,” said Al-Muslimi.
“That applies to everything and everywhere. That is how much of an influence it has had. That is how much it has spilled over.”