LONDON: Faced with mounting criticism over its handling of the humanitarian emergency in Gaza amid Israel’s assault on the Palestinian enclave and obstruction of aid deliveries, the UN has sought to step up its assistance.
However, short of forcing Israel to accept an immediate and lasting ceasefire agreement with the Palestinian militant group Hamas, critics say the UN’s latest moves will fail to ease the suffering of Gaza’s embattled civilian population.
Despite demanding that all parties “facilitate and enable the immediate, safe and unhindered delivery of humanitarian assistance at scale,” the UN Security Council’s resolution of Dec. 22 has been branded woefully inadequate by many in the aid community.
Indeed, obstruction to aid deliveries has only continued, with the UN Relief and Works Agency, which supports Palestinian refugees, suggesting that some 40 percent of Gazans are now at risk of famine.
Muhannad Ayyash, a professor of sociology at Mount Royal University in Calgary, Canada, believes that as long as the US allows Israel to continue its military operation in Gaza, any kind of international pressure appears “meaningless.”
He told Arab News: “Israel is operating regardless of what the international community says because the US is fully supporting it.
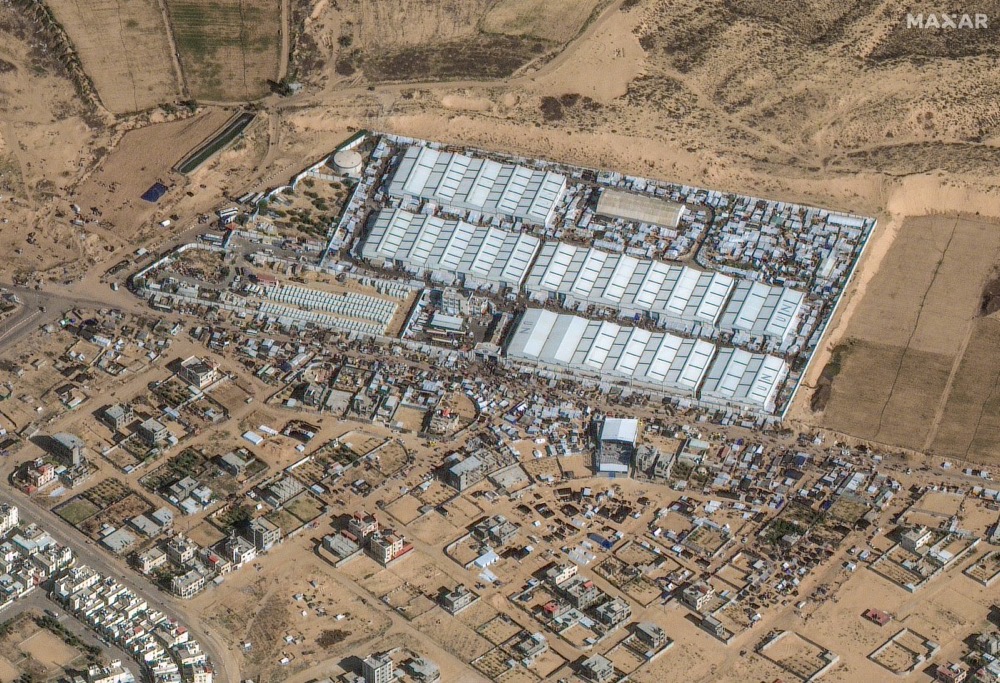

A UN aid center and a camp in Rafah, southern Gaza Strip. (MAXAR/AFP)
“Israel and the US are basically dismissing everyone and moving full throttle ahead in this genocide of Palestine.
“This was never a problem to be resolved with ‘more aid.’ This trickle of aid is part of the US discourse of simply trying to distract from the only real solution.”
For Ayyash and others, that “real solution” remains the enforcement of an immediate and lasting ceasefire, with UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres saying it is the only way to end the “nightmare.”
Israel mounted its assault on Gaza following the unprecedented Hamas attack of Oct. 7, which saw Palestinian fighters cross the border into Israel, killing 1,200 people — most of them civilians — and kidnapping some 240.
FASTFACTS
• The UN Security Council’s resolution of Dec. 22 has been branded woefully inadequate by the aid community.
• Some 40 percent of Gazans are now at risk of famine, according to the UN Relief and Works Agency.
Since then, Israeli forces have laid siege to the Gaza Strip, controlled by Hamas since 2007, with the stated aim of destroying the group’s leadership and freeing the hostages.
However, in the process, more than 22,500 Gazans have been killed, according to the Hamas-run Health Ministry.
Furthermore, the suspected Israeli killing of Hamas deputy head Saleh Arouri and two commanders from its Al-Qassam Brigades in a blast in Beirut on Jan. 2 has added to fears that the Gaza war could morph into a wider regional conflict.
The destruction of homes and infrastructure in Gaza has displaced almost 2 million people and left the population vulnerable to disease, starvation and being killed in the crossfire, leading to a growing chorus of international condemnation.
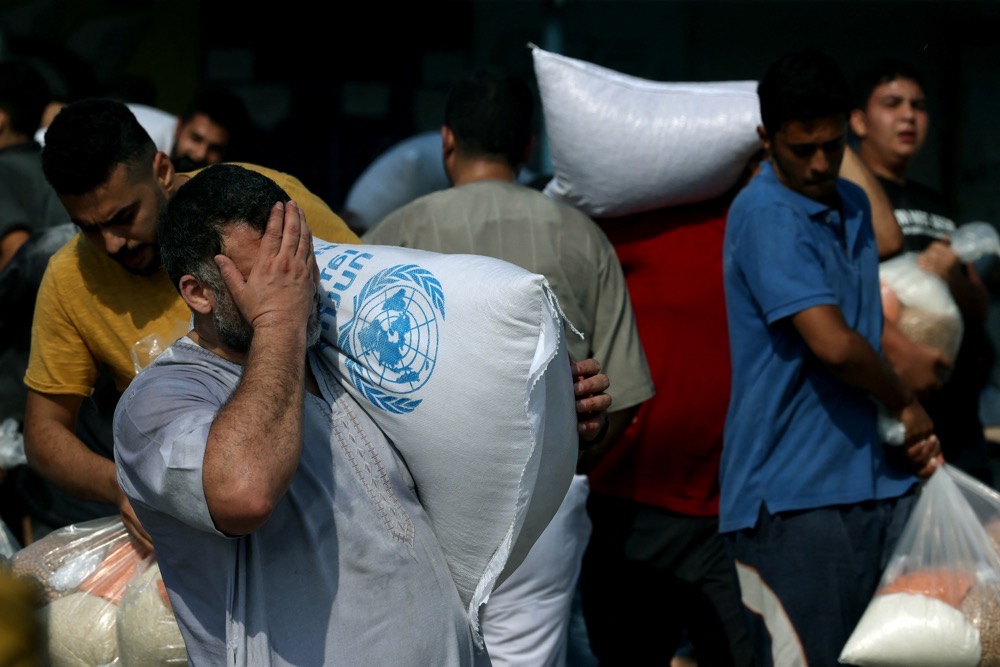

UN Security Council’s resolution of Dec. 22 has been branded woefully inadequate by many in the aid community. (AFP)
There is now a growing consensus that the UNSC’s Dec. 22 resolution, adopted with 13 votes in favor and the US and Russia abstaining, has failed to achieve its central aim of facilitating the flow of aid.
Thomas White, director of UNRWA affairs in Gaza, said Israeli troops have fired on aid convoys.
Medecins Sans Frontieres, one of the aid agencies working in Gaza, said the resolution has fallen “painfully short.”
Avril Benior, executive director of MSF-USA, said: “This resolution has been watered down to the point that its impact on the lives of civilians in Gaza will be nearly meaningless.”
The Dec. 22 resolution tasked the UN secretary-general with appointing a senior humanitarian and reconstruction coordinator with responsibility for “facilitating, coordinating, monitoring, and verifying” in Gaza.
It also called for the “expeditious” establishment of a UN mechanism to accelerate aid consignments to Gaza through states that are not party to the conflict; to expedite, streamline and accelerate assistance; and to continue helping to ensure that aid reaches its civilian destination.
Posting recently on X, Martin Griffiths, the UN’s undersecretary-general for humanitarian affairs and emergency relief coordinator, described the challenges of moving aid into Gaza.
He said restrictions imposed by the Israel Defense Force have resulted in a growing list of rejected items, with aid trucks contending with “three layers of inspection before even entering” crossings designed for pedestrians, not trucks.
Scott Paul, senior humanitarian policy adviser at Oxfam America, said even if aid flows improve, there is “no point” delivering assistance if the infrastructure required to use it is being destroyed.
The Israeli government has consistently rejected claims that it has targeted aid convoys and civilian infrastructure in Gaza.
Government spokesperson Eylon Levy has even accused UNRWA on X of “covering up for Hamas and deflecting blame onto Israel.”
In recent weeks, Israeli authorities accused the UN of not doing enough to process humanitarian aid into Gaza, and charged that the world body is responsible for supplies not reaching the enclave fast enough.
“We have expanded our capabilities to conduct inspections for the aid delivered into Gaza. Kerem Shalom (border crossing) is to be opened, so the number of inspections will double. But the aid keeps waiting at the entrance of Rafah,” the Coordination of Government Activities in the Territories wrote on X. “The UN must do better — the aid is there, and the people need it.”
By contrast, Ayyash said Israel has very deliberately obstructed the flow of aid, and has demolished civilian infrastructure as a means of permanently displacing the Palestinian population.
“Israel turned off the aid tap on Oct. 9 when it announced the ‘total siege’ of Gaza,” he told Arab News. “More than this, it has carried out this deliberate plan to destroy all life-sustaining infrastructure.
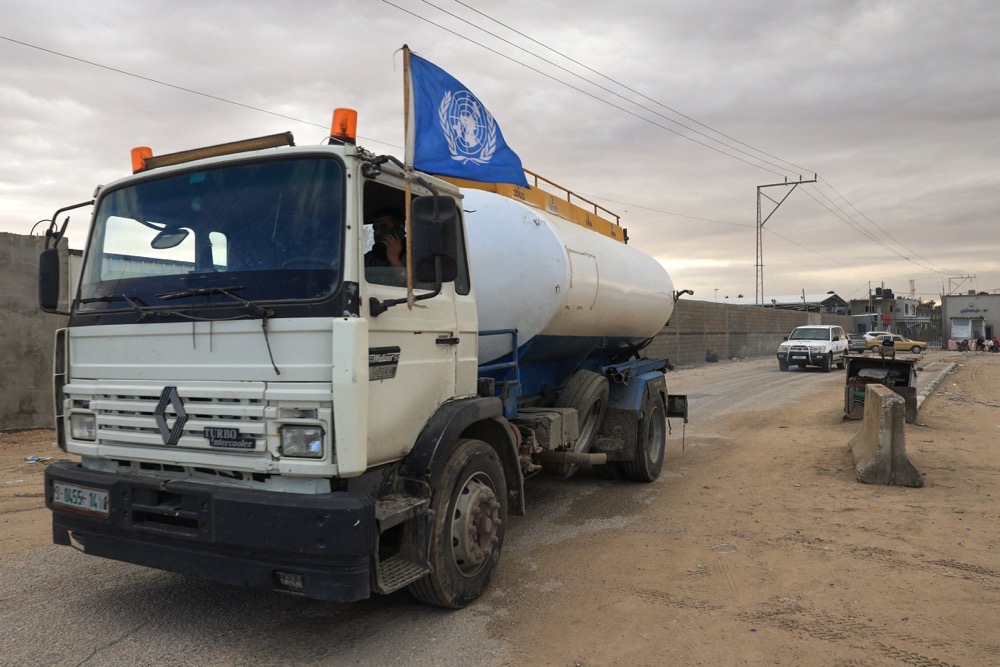

A truck carrying fuel decorated with a UN flag crosses into Rafah in the southern Gaza Strip. (AFP)
“It has bombed everything in Gaza, including its bakeries, markets, hospitals, water and sanitation infrastructure, fishing boats, farmlands, residential areas and so on.
“People are starving, thirsty, freezing when it’s cold, and suffering from illnesses, diseases and serious injuries without access to proper medical care or any medical care at all.”
Although some believe that Israel feels it can disregard international pressure thanks to the diplomatic cover and largesse provided by the US, others suspect that Israel is now also acting in open defiance of the US, which has urged Israel to respect the rules of engagement.
Indeed, after the perceived security failures that allowed the Oct. 7 attack to take place, the far-right government of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu is unlikely to survive beyond the end of the war.
Netanyahu’s only option for political survival may hinge upon positioning himself as the only man strong enough to stand up to the US.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Yossi Mekelberg, professor of international relations and associate fellow of the Middle East and North Africa Programme at international affairs think tank Chatham House, has questioned assertions of Israeli disregard for international censure, saying Netanyahu’s willingness to submit to US pressure is dependent to some extent on the way the message is delivered.
“It has to be explicit and credible in the sense that it makes clear that this is what Washington demands,” Mekelberg told Arab News.
Similarly, Amer Al-Sabaileh, a Jordanian university professor and geopolitical expert, believes there are several factors that Israel’s government and military leaders would be considering when it comes to balancing calls from the international community with their own needs.
Of “paramount” importance, he said, are Israel’s ongoing security considerations, noting that “as long as these persist, navigating the delivery of aid becomes intricate.”
Both Mekelberg and Al-Sabaileh also challenged assertions that the UNSC resolution is “meaningless,” with the latter saying it marks a “crucial step.”
Al-Sabaileh added: “It undoubtedly establishes a platform to activate humanitarian aid efforts under international oversight.
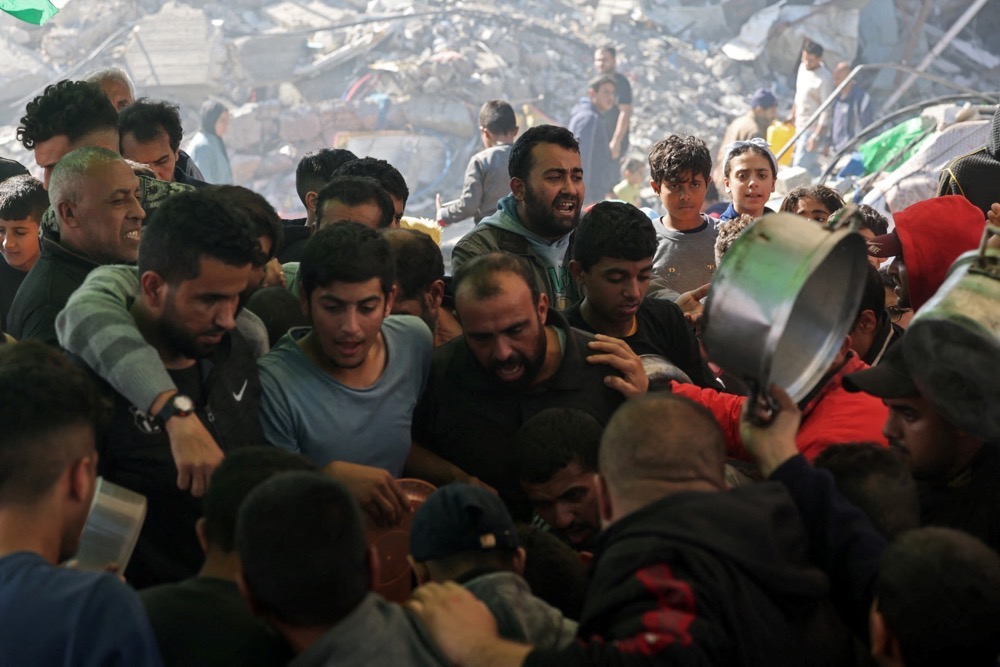

Consensus is growing that the UNSC’s Dec. 22 resolution has failed to achieve its central aim. (AFP)
“But definitely, the current situation in Gaza presents a significant challenge for the delivery of humanitarian aid.
“Ongoing Israeli operations targeting Hamas, its leaders, and remnants of its infrastructure maintain Israeli control and decision-making.”
In this “complex political landscape,” the delivery of aid is “highly challenging,” he said, with the IDF in the unenviable position of charting a “delicate balance between military operations and an imperative to ensure aid reaches the civilians who are profoundly suffering.”
He added: “This delineation is crucial for mitigating the impact of the crisis on innocent civilians and addressing the broader challenges facing the region.”
Acknowledging that Israel could “make it as easy or as difficult to let aid in” as it wanted, Mekelberg told Arab News that the UNSC resolution nonetheless “increased the pressure on Israel” despite lacking any enforcement mechanism beyond diplomatic negotiation.
For Ayyash, though, there is only one resolution that would change the situation on the ground.
“The immediate halt to the attack on Gaza and the complete withdrawal of all Israeli forces from the Gaza Strip can resolve the humanitarian disaster,” he said. “Until the attack stops, a sufficient amount of aid won’t enter Gaza.”


















