BEIRUT: Wassim Mansouri, the first vice governor of Banque du Liban, Lebanon’s central bank, assumed the responsibilities of former governor Riad Salameh on Monday, ushering in a period of cautious optimism and sparking hopes of a belated return to fiscal responsibility.
Amid the worst financial crisis in the country’s history, made worse by years of asset stripping by the nation’s political elite, Mansouri faces the daunting task of restoring the credibility of the long-abused central bank.
“It is necessary to put an end to the policy of government borrowing from the central bank and limit the process to matters of emergency only, and for a limited period of time, provided that it is legalized,” Mansouri said on his first day in office.
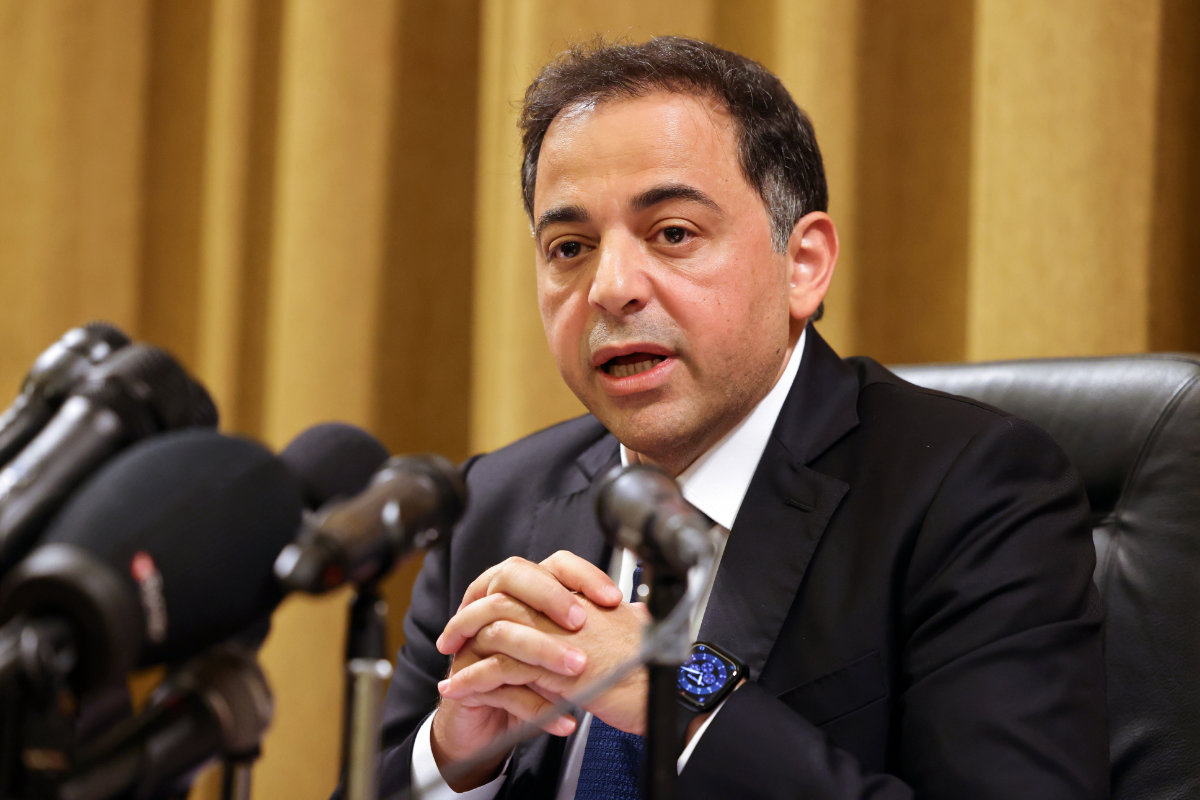

Wassim Manssouri, Lebanon's acting central bank governor, speaks during a press conference at the bank's headquarters in Beirut on July 31, 2023. (AFP)
This was his attempt to establish new rules for monetary dealings between the government and the central bank, to bring fiscal policy back in line with Lebanon’s Code of Money and Credit, which was established in 1963.
Mansouri aims to secure legal and legislative cover for his conditions, from both the executive and legislative authorities, to continue financing the government while exempting himself from the possibility of any subsequent responsibility.
He called for the implementation of fiscal reforms within six months, which should include approval of the budget for 2023-24, the adoption of capital controls, a restructuring of banks, and enforcement of financial discipline.
Financial markets reacted positively to the news of Salameh’s departure after a checkered 30-year stint. The value of the US dollar fell against the Lebanese pound, dropping from 99,000 to 88,500 in the week before he stepped down.
“
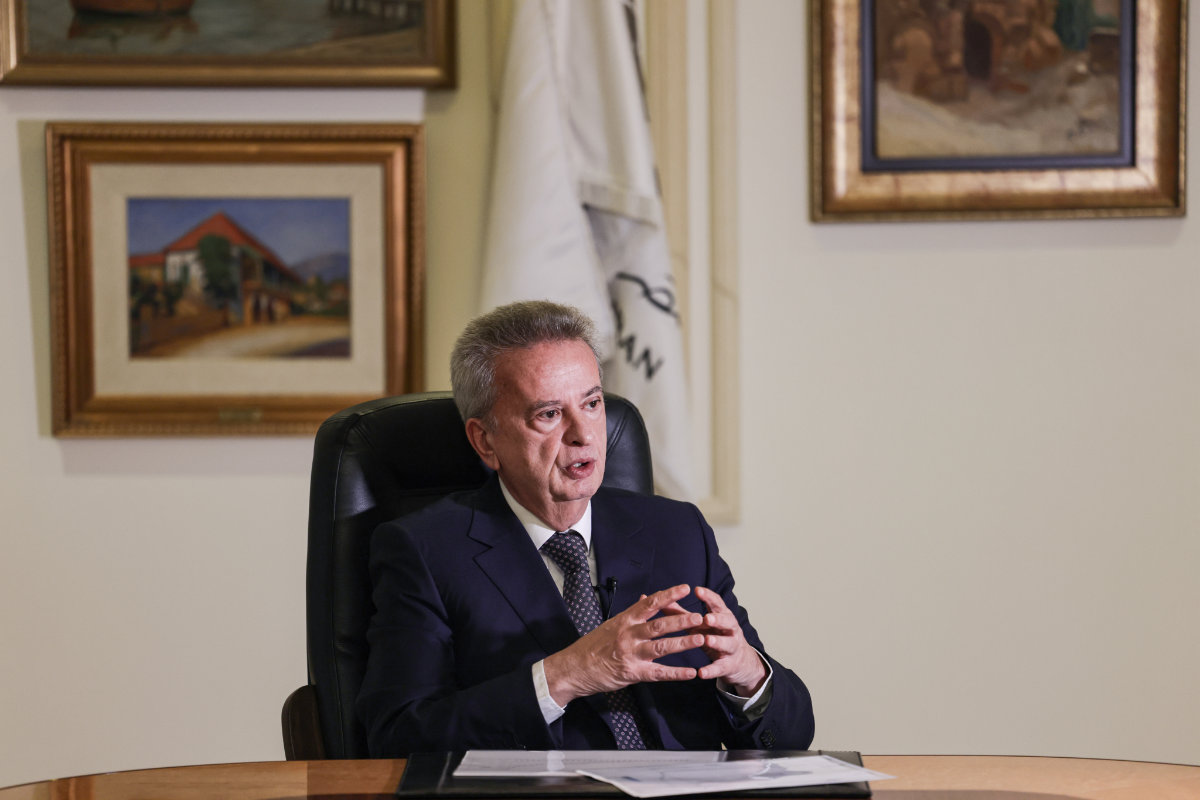

Lebanon's failed former central bank governor Riad Salameh. (AFP file photo)
It feels like a breath of fresh air has just blown from a hole that has opened suddenly in a thick, impenetrable wall that was built between the central bank and literally the whole world,” George Kanaan, CEO of the Arab Bankers Association, told Arab News.
“Suddenly we are told that he is willing to provide statistics, he is willing to work with the government, he is willing to inform the parliament, he is willing to discuss things, he wants matters legalized under proper legislation to allow him to work.
“(This is) nothing like the old times. This is a great new beginning. The question, though, is what needs to follow immediately? The answer is a series of reforms, starting with legislative reforms. And then we can begin to see how the crisis will eventually come to an end.
“However, there is a reason why they have been blocked, as the political class in Lebanon does not see that they are necessary, or they believe that, if implemented, the reforms will harm them. And in that case the spring will be short lived.”
Indeed, there is no guarantee that Mansouri will succeed. There is no proposed law that would allow the central bank to lend money to the state in a way that provides legislative cover. And there is no indication of the possibility of a parliamentary session to pass such draft legislation.
Caretaker Prime Minister Najib Mikati has not presented a draft law that would allow the government to borrow foreign currencies from the bank. According to local media reports, he hesitated to do so “due to its unlawfulness,” putting the ball in parliament’s court.
The policy of lending by the central bank to the state has been a fundamental cause of the depletion of monetary reserves and the collapse of Lebanon’s once-flourishing banking and financial sectors, compounded by the government’s failure to implement reforms and curb waste and corruption.
The government is currently seeking a loan of up to $1.2 billion over six months to cover the salaries of public sector, military and security personnel, the cost of essential imports, and interventions in the market when necessary.
Can Mansouri succeed where Salameh failed? The government is in prolonged caretaker mode and the parliament remains deeply divided, making it difficult to pass any legislation that might prove controversial. Meanwhile, the central bank’s reserves, according to financial references, now stand at only between $9 billion and $10 billion.
Parliament is split into factions, including the Lebanese Forces, the Lebanese Kataeb, reformist MPs, and some independent MPs, who refuse to pass laws in the absence of a president. The president’s office has been vacant since Michel Aoun’s term ended in October last year as the parliament cannot agree on a successor. They will therefore likely boycott the legislative session if it is scheduled.
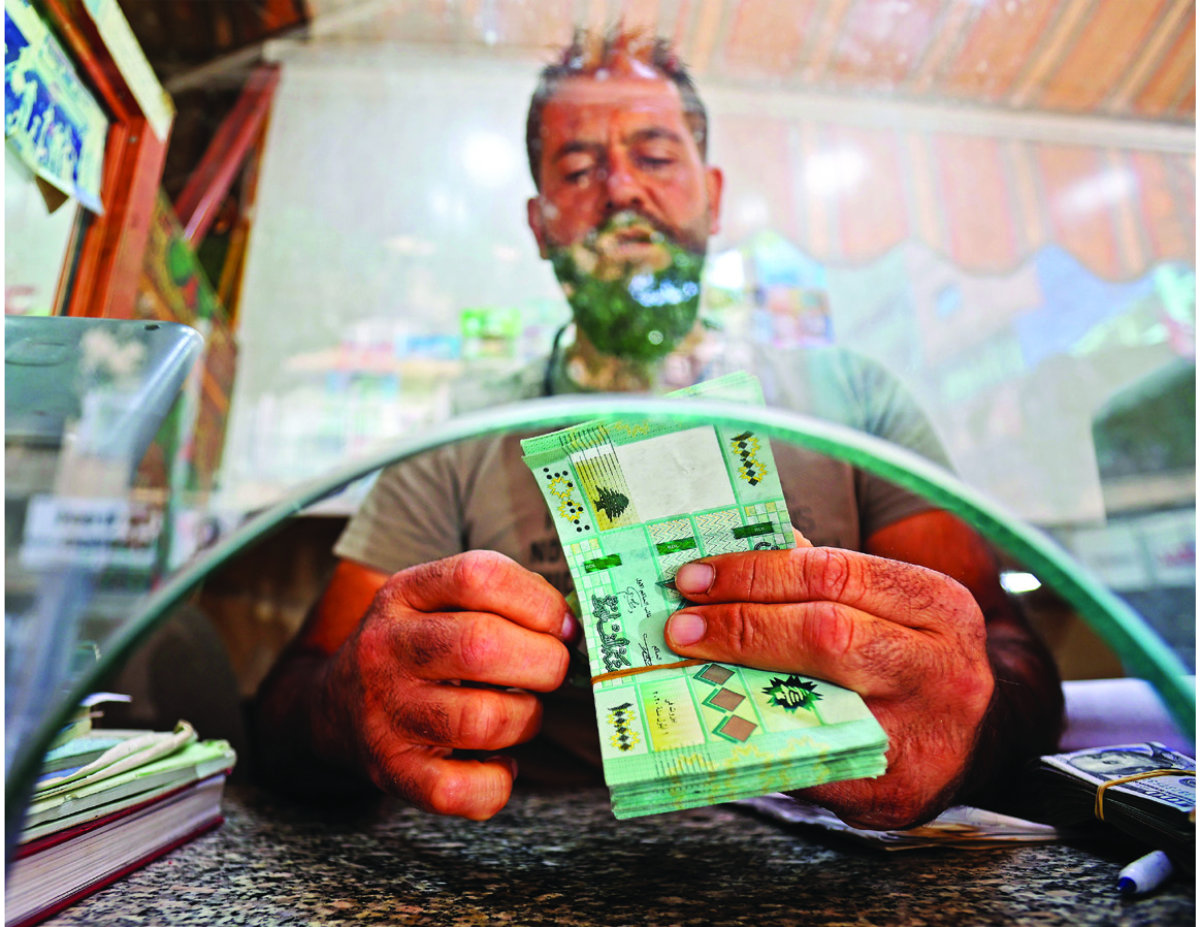

The Lebanese pound has plumbed new depths against the US dollar. (AFP file photo)
Some factions, such as the Free Patriotic Movement, have set conditions for attending sessions, while others, notably the Amal movement and Hezbollah, have shown little enthusiasm for them at all.
Asked whether Mansouri will be able to enact change, given this state of political paralysis, Kanaan noted that the new governor does have allies who want him to succeed.
“He is not alone,” Kanaan said. “There are a lot of people who support him. On his own he cannot do it. On his own, he and the other vice governors will probably be forced to leave if they insist on the reforms.
“I think there are other parties in Lebanon, but not necessarily political bodies, that want the reforms done. Certainly, the whole word outside of Lebanon is crying out for those reforms. Everybody wants those reforms.
“Lebanon right now is witnessing a flow of liquidity and a positive economic atmosphere, which is pointing in an upward direction, and that releases pressure for reforms. Everybody would say, if things are going okay, why do we need reforms since things will eventually go in the right direction without the need of those reforms. And this would be unfortunate.”
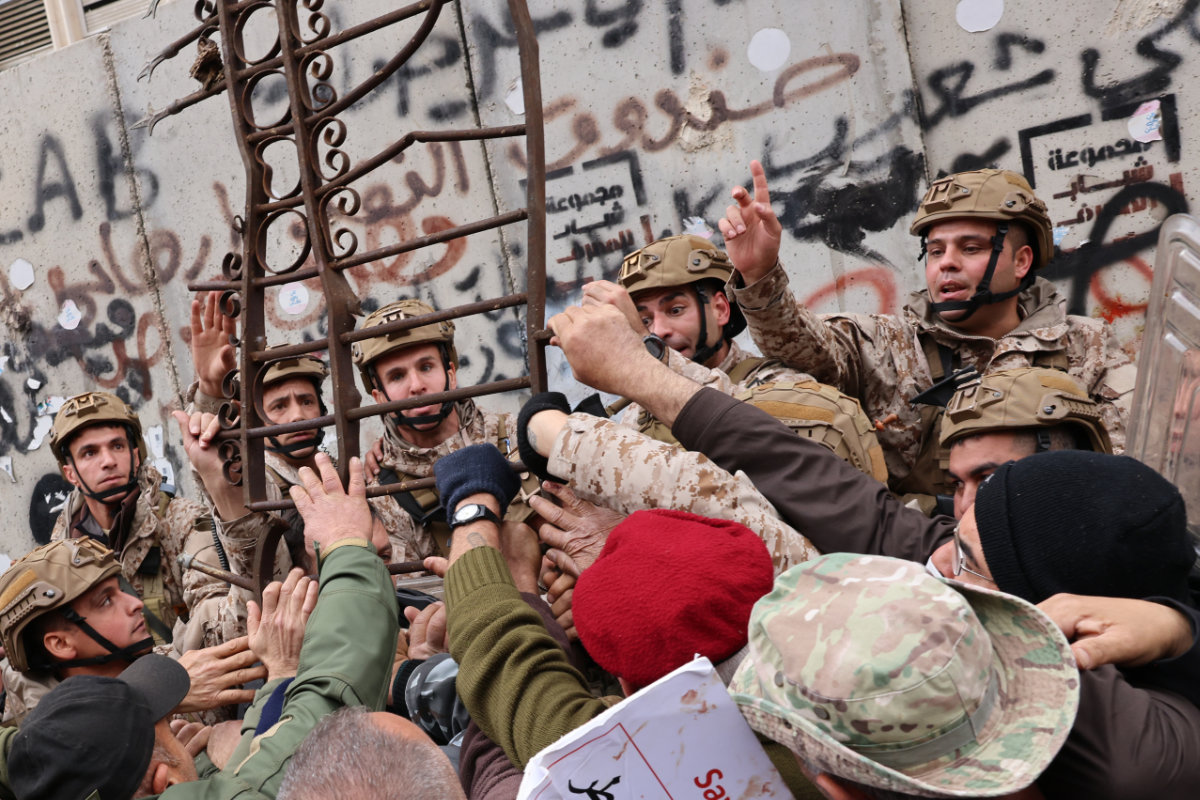

Retired servicemen clash with soldiers outside Lebanon's central bank during a demonstration demanding inflation-adjustments to their pensions, in Beirut on March 30, 2023. (AFP)
Mansouri has been cautious during his first few days in office and has refrained from making any further statements to the media, leaving time for “action,” as members of his entourage put it. But this means it is hard to predict what the ultimate outcome will be.
Fadi Khalaf, the secretary-general of the Association of Banks in Lebanon, told Arab News: “It is too early to comment on the policy that the central bank’s deputy governor intends to pursue. We are currently in a monitoring and waiting phase.”
Regarding the legacy of Salameh, whose term as governor was renewed four times between the era of the late President Elias Hrawi and that of Aoun, there is no denying he enjoyed the support of most political factions.
Despite his constant objections to policies adopted by the ruling political elite, he continued to cover the Lebanese state’s deficits and operating expenses.
One of the biggest expenses borne by the central bank was the cost of electricity generation, which ran as high as $2 billion annually. The money was handed over in the form of treasury advances that went to the Ministry of Energy, without ever being paid back to the bank.

A woman stands with a sign during a protest by the Depositors Solidarity Union group protesting against the Lebanese Central Bank's monetary policies outside the bank's headquarters in Beirut on June 23, 2023. (AFP)
This prompted Salameh to halt the process in 2020. The electricity sector continues to be the biggest burden on the bank’s mandatory reserve, as well as on the already empty state treasury.
Although the conflict and crisis in neighboring Syria created tough economic challenges for Lebanon, Salameh’s financial legerdemain shielded the country from many of the repercussions, until the financial crisis of 2019 struck.
This brought about the unraveling of the banking sector and the deterioration of the dollar-exchange rate, in a crisis that grew worse when former Prime Minister Hassan Diab’s government defaulted on Lebanon’s foreign debt in 2020.
One banking expert, who spoke to Arab News on condition of anonymity, believes that borrowing “will continue, whether directly or in accordance with the law,” largely continuing Salameh’s legacy.
“(The central bank’s) dollars will go to the state’s expenditure items, but what is required is improvement of the state’s finances and rationalization of spending of dollars,” the expert said.
Mansouri’s window of opportunity for implementing meaningful change is small.
“Not very long — I would say it is a matter of weeks,” said Kanaan.
“In a few weeks’ time, he either makes a step in the right direction, accompanied by all sorts of other reforms, and then we are making real headway in the right direction. Or he leaves. That’s the second alternative. Or he buckles and performs his duties just like Riad was doing before him.”


















