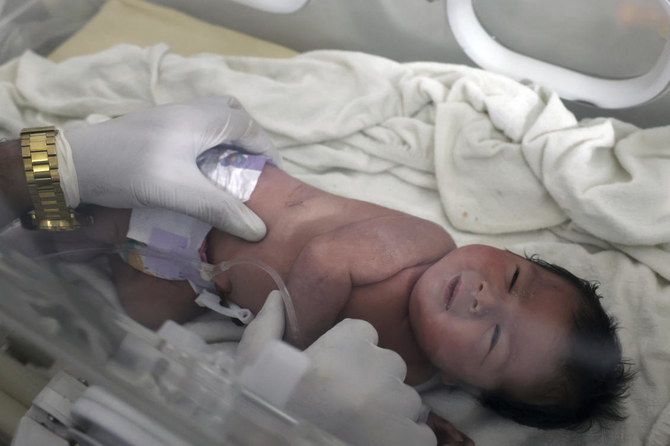
JINDERIS, Syria: Residents digging through a collapsed building in a northwest Syrian town discovered a crying infant whose mother appears to have given birth to her while buried underneath the rubble from this week’s devastating earthquake, relatives and a doctor said Tuesday.
The newborn girl’s umbilical cord was still connected to her mother, Afraa Abu Hadiya, who was dead, they said. The baby was the only member of her family to survive from the building collapse Monday in the small town of Jinderis, next to the Turkish border, Ramadan Sleiman, a relative, told The Associated Press.
Monday’s pre-dawn 7.8 magnitude earthquake, followed by multiple aftershocks, caused widespread destruction across southern Turkiye and northern Syria. Thousands have been killed, with the toll mounting as more bodies are discovered. But dramatic rescues have also occurred. Elsewhere in Jinderis, a young girl was found alive, buried in concrete under the wreckage of her home.
The newborn baby was rescued Monday afternoon, more than 10 hours after the quake struck. After rescuers dug her out, a female neighbor cut the cord, and she and others rushed with the baby to a children’s hospital in the nearby town of Afrin, where she has been kept on an incubator, said the doctor treating the baby, Dr. Hani Maarouf.
Video of the rescue circulating on social media shows the moments after the baby was removed from the rubble, as a man lifts her up, her umbilical cord still dangling, and rushes away as another man throws him a blanket to wrap her in.
The baby’s body temperature had fallen to 35 degrees Celsius (95 degrees Fahrenheit) and she had bruises, including a large one on her back, but she is in stable condition, he said.
Abu Hadiya must have been conscious during the birth and must have died soon after, Maarouf said. He estimated the baby was born several hours before being found, given the amount her temperature had dropped. If the girl had been born just before the quake, she wouldn’t have survived so many hours in the cold, he said.
“Had the girl been left for an hour more, she would have died,” he said.
When the earthquake hit before dawn on Monday, Abu Hadiya, her husband and four children apparently tried to rush out of their apartment building, but the structure collapsed on them. Their bodies were found near the building’s entrance, said Sleiman, who arrived at the scene just after the newborn was discovered.
“She was found in front of her mother’s legs,” he said. “After the dust and rocks were removed the girl was found alive.”
Maarouf said the baby weighed 3.175 kilograms (7 pounds), an average weight for a newborn, and so was carried nearly to term. “Our only concern is the bruise on her back, and we have to see whether there is any problem with her spinal cord,” he said, saying she has been moving her legs and arms normally.
Jinderis, located in the rebel-held enclave of northwest Syria, was hard hit in the quake, with dozens of buildings that collapsed.
Abu Hadiya and her family were among the millions of Syrians who fled to the rebel-held territory from other parts of the country. They were originally from the village of Khsham in eastern Deir Ezzor province, but left in 2014 after the Daesh group captured their village, said a relative who identified himself as Saleh Al-Badran.
In 2018, the family moved to Jinderis after the Turkish-backed Syrian National Army, an umbrella for several insurgent groups, captured the town from US-backed Kurdish led fighters, Sleiman said.
On Tuesday, Abu Hadiya and the girl’s father Abdullah Turki Mleihan, along with their four other children were laid to rest in a cemetery on the outskirts of Jinderis.
Back inside the town, rescue operations were still ongoing in their building hoping to find survivors.
The town saw another dramatic rescue Monday evening, when a toddler was pulled alive from the wreckage of a collapsed building. Video from the White Helmets, the emergency service in the region, shows a rescuer digging through crushed concrete amid twisted metal until the little girl, named Nour, appeared. The girl, still half buried, looks up dazedly as they tell her, “Dad is here, don’t be scared. … Talk to your dad, talk.”
A rescuer cradled her head in his hands and tenderly wiped dust from around her eyes before she was pulled out.
The quake has wreaked new devastation in the opposition-held zone, centered on the Syrian province of Idlib, which was already been battered by years of war and strained by the influx of displaced people from the country’s civil war, which began in 2011.
Monday’s earthquake killed hundreds across the area, and the toll was continually mounting with hundreds believed still lost under the rubble. The quake completely or partially toppled more than 730 buildings and damaged thousands more in the territory, according to the White Helmets, as the area’s civil defense is known.
The White Helmets have years of experience in digging victims out from buildings crushed by bombardment from Russian warplanes or Syrian government forces. An earthquake is a new disaster for them.
“They are both catastrophes — a catastrophe that has been ongoing for 12 years and the criminal has not been held accountable, and this one is a natural catastrophe,” said the deputy head of the White Helmets, Munir Mustafa.
Asked if there was a difference between rescue work in the quake and during the war, he said, “We cannot compare death with death … What we are witnessing today is death on top of death.”
Newborn, toddler saved from rubble in quake-hit Syrian town
https://arab.news/8ebm2
Newborn, toddler saved from rubble in quake-hit Syrian town

- The newborn girl’s umbilical cord was still connected to her mother, Afraa Abu Hadiya, who was dead
- Baby was the only member of her family to survive from the building collapse Monday in the town of Jinderis
’We can’t make ends meet’: civil servants protest in Ankara

- Some 800 civil servants from the Confederation of Public Employees’ Unions joined a march to the labor ministry
- “The increase in rents is almost three times higher than the pay rise we received,” Kocak told demonstrators
ANKARA: Hundreds of angry civil servants marched through Ankara Wednesday demanding a realistic pay rise as they battle poverty amid the soaring prices and double-digit inflation.
Some 800 civil servants from the Confederation of Public Employees’ Unions (KESK) joined a march to the labor ministry in the Turkish capital, carrying banners demanding an immediate pay rise.
“The increase in rents is almost three times higher than the pay rise we received, meaning our salaries are not even enough to cover the rent increases alone,” Ayfer Kocak, KESK’s co-chair, told demonstrators outside the ministry.
“We are experiencing growing poverty and insecurity.”
Turkiye’s annual inflation rate fell to 30.89 percent in December from 44.38 percent a year earlier, official figures showed, but independent economists and unions say real numbers remain much higher.
According to December figures released by the Confederation of Turkish Trade Unions (TURK-IS), the absolute minimum needed to feed a family of four was just over 30,000 liras ($690).
At the same time, Turkiye’s poverty threshold — the sum required to cover the basic needs for a family of that size — had risen to 98,000 liras ($2,270), it said.
Food inflation approached 43 percent annually, it added.
- ‘We can’t make ends meet’ -
“The government is condemning civil servants to live in degrading conditions by relying on misleading data” from the official statistics agency TUIK, Tulay Yildirim, head of a local teachers’ union branch, told AFP.
“We workers’ voices to be heard, saying we can no longer make ends meet and want to receive our fair share of a budget created through taxes paid by all citizens,” she added.
Earlier this month, public sector wages were hiked by 18.6 percent for the next six months, an increase unions said was insufficient.
“There are not only workers here, but also pensioners. The salary increase granted falls below the poverty line,” said Osman Seheri, head of a local branch of the municipal workers’ union.
“We cannot even afford proper clothes to go to work, let alone a suit and tie. With such wages, it is impossible to live in a major city.”
According to the independent Inflation Research Group (ENAG), which challenges the official data, annual inflation in Turkiye reached 56.14 percent in December 2025, with prices rising 2.11 percent in December alone.