RIYADH: The Saudi Ministry of Energy, in cooperation with other governmental agencies, announced on Sunday that it had completed all legislative and technical aspects to regulate the electric vehicle charging market, according to the Saudi Press Agency.
The team includes the Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs, the Ministry of Transport and Logistics, the Ministry of Commerce, the Saudi Electricity Co. and the King Abdullah Petroleum Studies and Research Center, among others.
The move will enhance job creation in the Kingdom and contribute to its green initiative to reach net-zero carbon by 2060.
The regulating team will monitor and follow up on the activity to ensure that investors comply with the infrastructure requirements for EV charging stations, SPA reported.
The imports of EV charging equipment were permitted in 2020, said Saad Alkasabi, governor of Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization.
Sustainability to the core
As part of the Riyadh Sustainability Strategy, the Royal Commission of Riyadh launched an initiative last year to ensure that 30 percent of all vehicles in the capital would be powered by electricity by 2030.
Fahd Al-Rasheed, the CEO of the Royal Commission for Riyadh City, told Arab News earlier that they intend to be a global steward of environmental preservation and a global economic powerhouse driven by resource conservation.
Highlighting the Kingdom’s green economy plan, he said last year that the private sector had a vital role in achieving these goals, and it would create 360,000 green jobs and raise $40 billion in investments.
The plan sought to reduce emissions and increase the share of renewables to 50 percent by 2030.
Charging the EV infrastructure
Electromin, a wholly owned e-mobility turnkey solutions provider under Petromin, in May announced the rollout of electric vehicle charging points across the Kingdom.
In an earlier interview with Arab News, Kalyana Sivagnanam, the group CEO of Petromin, said that the network includes 100 locations across the Kingdom powered by a customer-centric mobile application.
Sivagnanam said that the company would set up most of its charging stations in Riyadh, Jeddah and Dammam and eventually branch out across the country.
Electromin’s charging network will offer a complete spectrum of services from AC chargers to DC fast and ultra-fast chargers, catering to all customer segments.
According to a statement, the chargers installed in phase one will be compatible with all vehicles approved by the Saudi standards organization using AC Type 2 connectors.
The second phase will include additional AC chargers and DC chargers up to 360 kilowatts, effectively allowing users to add up to 100 kilometers in four minutes.
Swiss EV infrastructure major ABB E-mobility has been instrumental in driving the Saudi EV infrastructure by providing Electromin with EV chargers for installation at 100 petrol stations across the Kingdom.
The e-mobility company is the world leader in EV charging solutions and the partner of choice for some of the world’s biggest EV manufacturers. After receiving approvals from the Saudi standards organization, the company has been installing a network of chargers across the country.
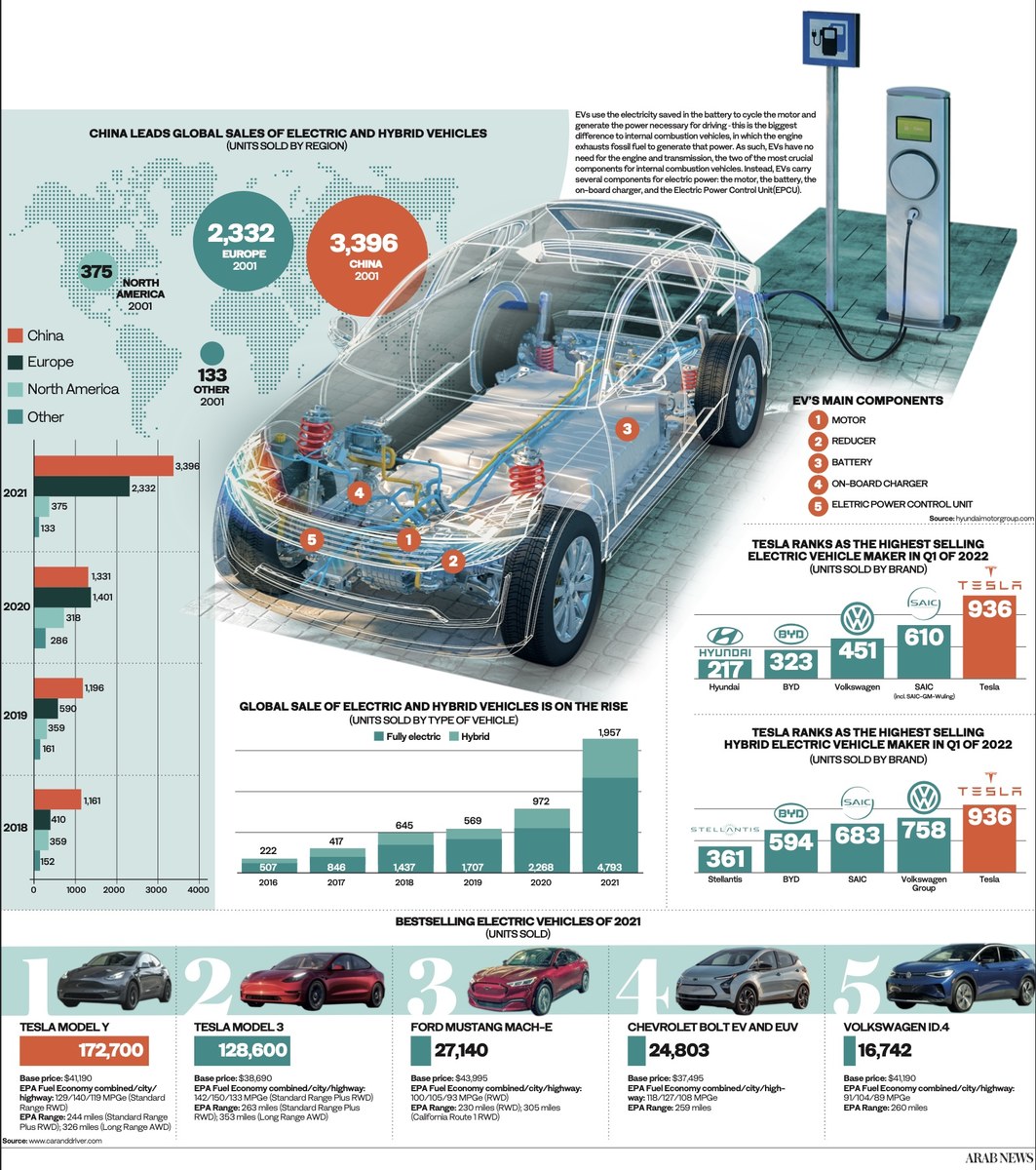
According to an ABB E-mobility press note, EV sales in the country will expand, with 1.3 million electric vehicles expected to be delivered in the next eight years. So, there is an urgent need to establish an EV ecosystem in the region that provides a one-stop e-mobility solution for EVs while monitoring and maintaining the network of charging stations in a flexible and efficient manner.
“Today, we are significantly expanding our e-mobility footprint and sustainability goals in the country. This partnership is momentous and supports the key objectives of ABB in Saudi Arabia – it shows our alignment and commitment to supporting the Kingdom’s Vision 2030,” said Fadi Alshaikh, E-mobility lead for ABB in the Kingdom, in the press note.
Moreover, to make the fuel-to-electric transition convenient for customers, Electromin has also devised an app to show all charging locations within the selected Petromin Express and Petromin AutoCare outlets. It will allow customers to check the charger’s status and fully control their charging sessions. The app will also facilitate payments and bookings.
Empowering EV manufacturing
The Kingdom is also leading the EV wave by encouraging the US-based Lucid Motors to establish its first EV factory in the region with an annual capacity of 150,000 zero-emission units.
The deal is estimated to provide Lucid Motors financing and incentives of up to $3.4 billion over the next 15 years to build and operate the manufacturing facility in the Kingdom.
Peter Rawlinson, CEO of Lucid Motors, had told Arab News in an earlier interview that the company has an alignment of mindset with the Kingdom’s Vision 2030 which could extend beyond cars. His objective was to build a supply chain infrastructure that benefits the economy of the Kingdom.
The production will start next year, and a complete assembly will be ready by 2025. To be located in King Abdullah Economic City, the factory is the EV manufacturer’s first production facility outside the US.



















