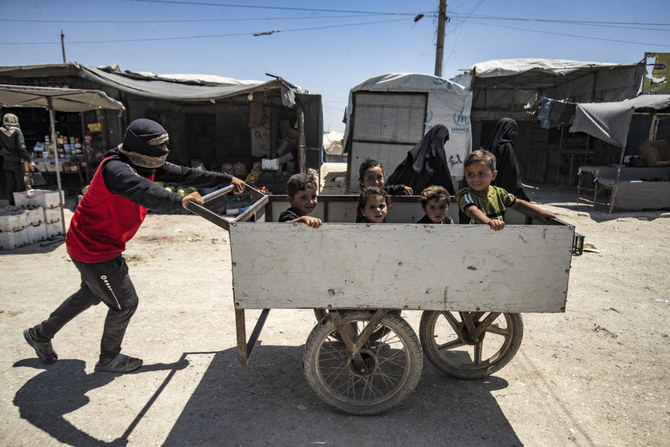
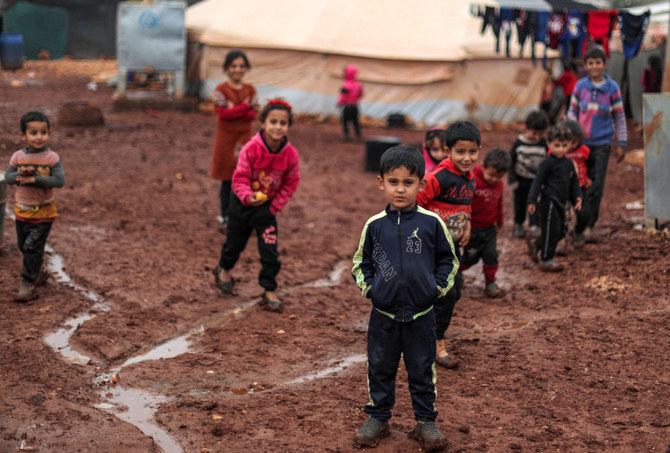
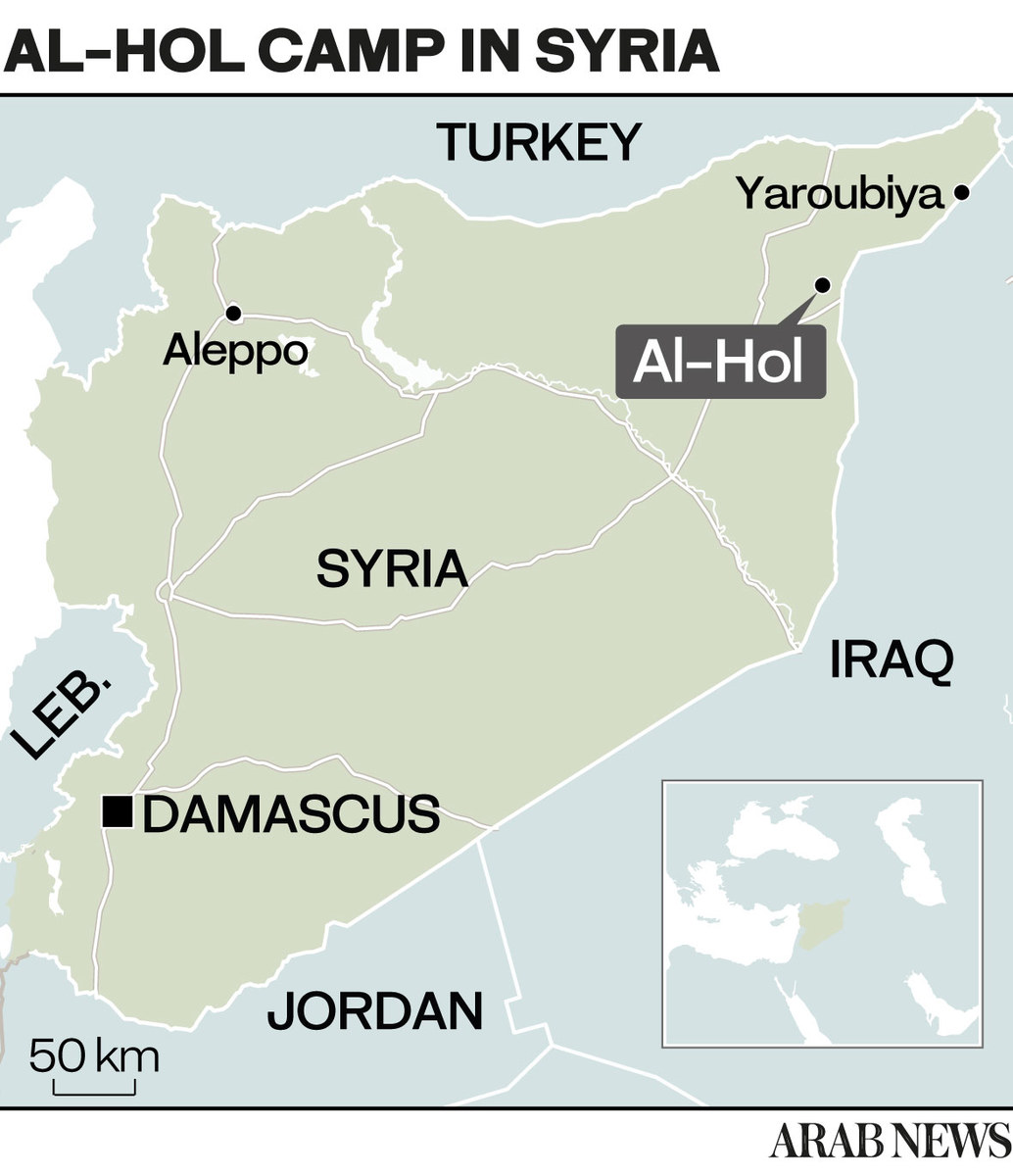
IRBIL, Iraq: Women and children held in Al-Hol, a sprawling camp of some 57,000 people in northeast Syria, endure squalid conditions and almost daily violence, meted out by its many hard-line inmates who still cling to the extremist ideology of Daesh.
Violence is endemic inside the camp, where there have been at least 130 murders since March 2019, according to Save the Children. In 2021 alone, an average of two people per week were killed, often with impunity and in plain sight of children.
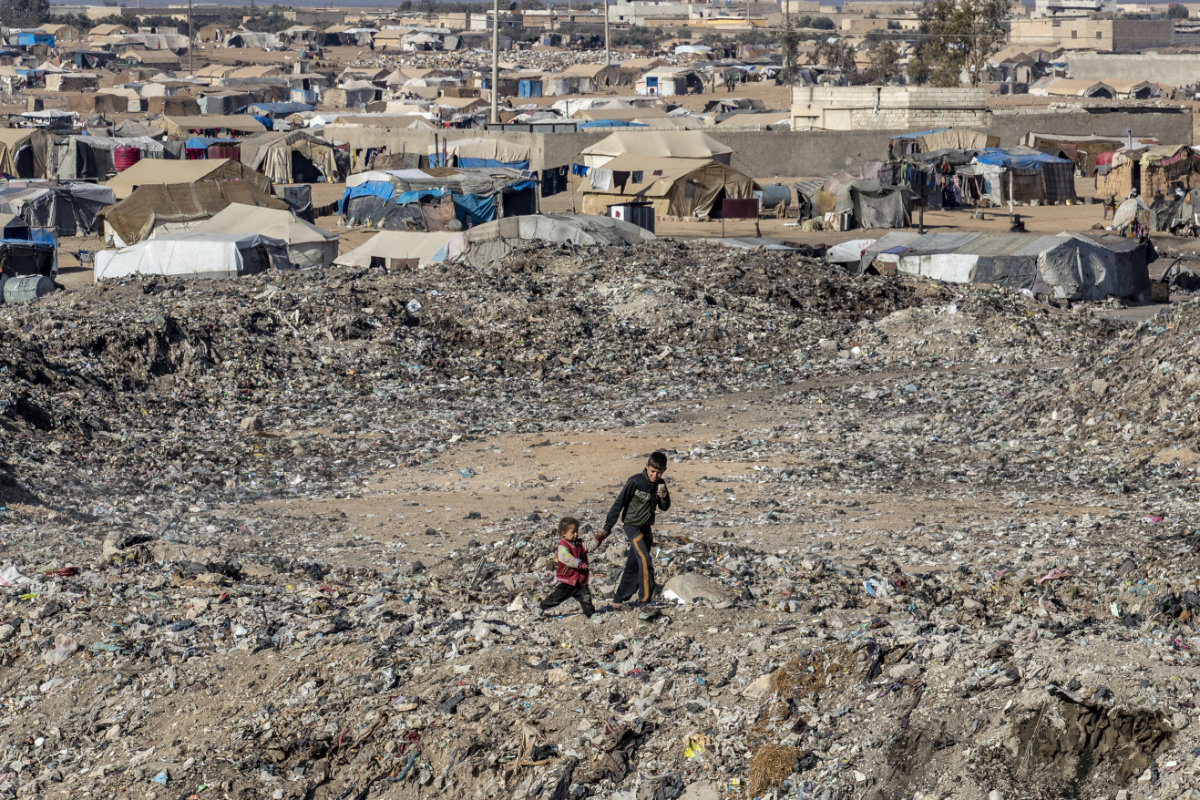

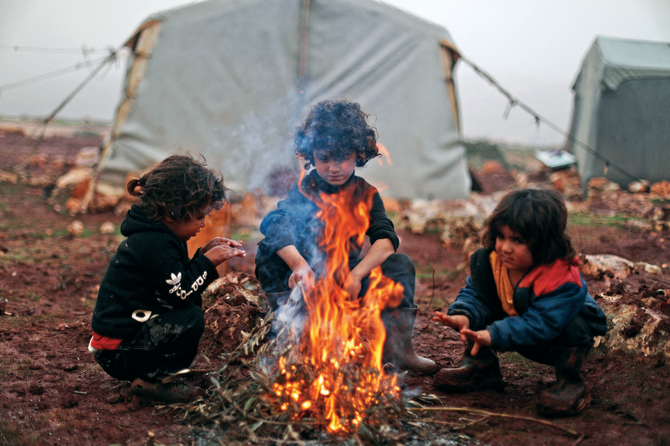
Owing to the often extreme climate and the lack of facilities, respiratory tract infections and malnutrition are rife in camps for IDPs in Syria. (AFP)
The overwhelming majority of these attacks took place in Al-Hol’s main camp, which is home to Syrian and Iraqi nationals. Al-Hol annex, which has also seen its share of insecurity, houses women and children from at least 60 other countries.
“We provide services, but, at the end of the day, it is still a camp and is, therefore, inadequate as a housing project,” Dr. Alan Dahir, an official from the Kurdish Red Crescent, which manages the site, told Arab News.
“Most children are orphans. While I don’t think they have been forgotten, including the foreign women, their respective countries are yet to come forward and claim them.”
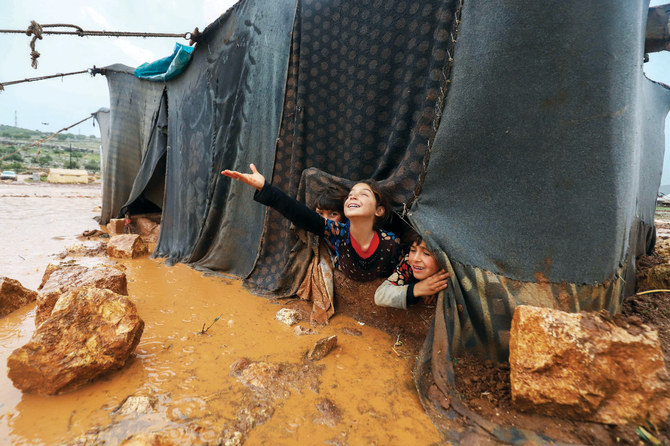
Imene Trabelsi, a spokesperson for the International Committee of the Red Cross, which provides basic assistance in Al-Hol, said that living conditions are far below international standards in terms of access to food, water, healthcare and education.
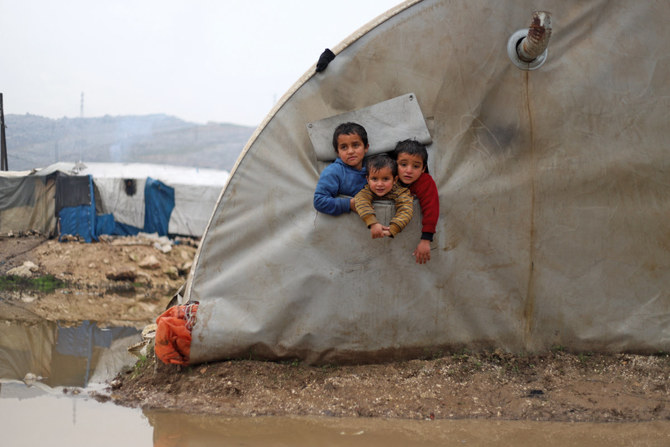
“There are children who have tragically spent their entire short lives in camps like Al-Hol, having been born and dying there without ever leaving the perimeter,” Trabelsi told Arab News.
“Tens of thousands of other children are spending their early years — so important for their development — in such conditions, in the full knowledge and view of the international community and their own states of origin.”
In February last year, a fire tore through part of the camp, leaving at least eight people dead and many seriously injured, including more than a dozen children. Owing to the often extreme climate and the lack of facilities, respiratory tract infections and malnutrition are rife.
“The children are endlessly exposed to dangers and their rights often ignored. The world cannot continue to look away while children draw their first and last breaths in camps or grow up stateless and in limbo,” said Trabelsi.
FASTFACTS
In February 2021, a fire tore through part of Al-Hol camp, leaving at least eight people dead and many seriously injured.
Western governments have been reluctant to take back their citizens, fearing the political blowback.
“This is one of the biggest and most complex child protection emergencies of our time and it is high time to find the political will to act before more lives are lost.”
Al-Hol has been housing people displaced by conflicts that have shaken the region down the years. But its population suddenly soared in March 2019 following the defeat of Daesh in the group’s last territorial holdout of Baghouz in the eastern province of Deir ez-Zor.
Thousands of women and children, many of them the families of captured or killed militants, were trucked from Baghouz to Al-Hol in neighboring Hasakah, where most have since remained under guard by US-backed Syrian Democratic Forces.
“I hadn’t eaten for what seemed like weeks at the time. We were left to literally eat grass,” said Ayman, a young Yazidi who was forced to fight in Daesh’s ranks in Baghouz after being abducted as a child.
“We had nothing. I do not know how I survived. I ended up at Al-Hol and was later rescued thanks to the local efforts of those looking for Yazidi survivors.”
When Daesh militants stormed into the Yazidi ancestral homelands of Sinjar in northwestern Iraq in the summer of 2014, thousands of women and children were abducted and forcibly converted to the group’s warped interpretation of Islam.
By the time the group was territorially defeated in early 2019, many of these former captives were too frightened to identify themselves as Yazidi or too indoctrinated to part ways with their former captors inside Al-Hol.
“I count myself lucky,” Ayman told Arab News. “Some of my friends and women I know refused to be rescued. They had been so brainwashed and traumatized they chose to remain in the camp under the radar. I do not know what has become of them now.”
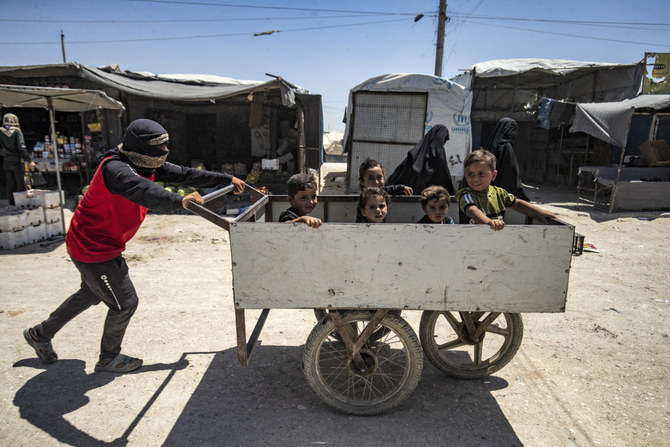

Living conditions are far below international standards in terms of access to food, water, healthcare and education, according to ICRC officials. (AFP)
Aid agencies have long called on governments to support the safe, voluntary and dignified return of Syrian and Iraqi families from Al-Hol to their communities, and for the repatriation of children of foreign fighters and their mothers back to their home countries.
“I’ve been pursuing this issue since 2018, and have managed to bring about 40 people back to their home countries. Most were children,” Peter Galbraith, a former US diplomat and longtime advocate of the Kurdish people, told Arab News.
Western governments have been reluctant to take back their citizens, fearing the political blowback, expense, and indeed the security risks should authorities fail to successfully prosecute suspected Islamist radicals.
“Part of the problem is that the UN and other NGOs are saying countries should take back their citizens, but the reality is no one is really doing that,” said Galbraith. “It doesn’t help to keep shouting about something and not working it out.
“For some countries like the UK, Canada and France, they find keeping their citizens in northeast Syria less complicated and less expensive. Bringing them home and putting them through a trial, sentencing, then sending them to jail would cost thousands of dollars, instead of keeping them in the camp for a couple hundred dollars.”
As a result, thousands of children who wound up in the camp through no fault of their own have been effectively abandoned by Western governments, left vulnerable to violence, sickness and radicalization.
“The children end up paying for the faults of their parents,” said Galbraith. “Every man and woman who decided to join Daesh had agency in one way or another. The kids brought or born here had no choice. They are now condemned to a life in prison.
“They are also at risk of child marriage and being brought up by the hard-line extremist women who run the camps. An American orphan we rescued was being raised by a Somali extremist woman when we found him.
“Children risk ending up in the hands of ruthless smugglers, human traffickers, who would do anything for a buck. Some Yazidi women, after all their ordeals with Daesh, ended up being trafficked into prostitution by these smugglers.
“Kids must be removed and put in villages or foster care.”
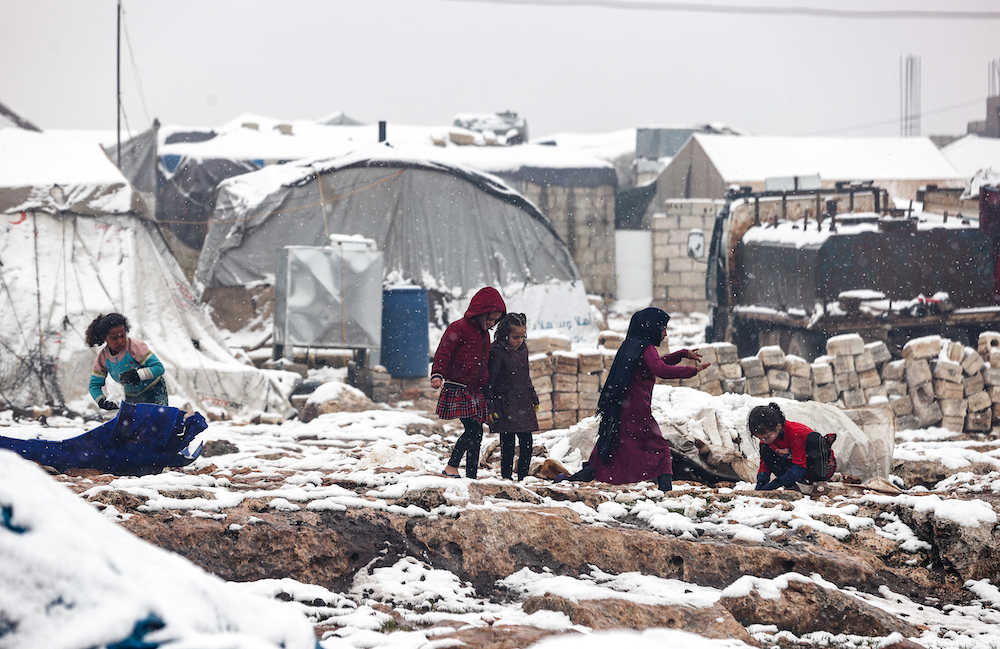

Children of internally displaced Syrians, here seen playing in the snow at a camp by the border with Turkey, suffer from exposure to extreme weather conditions. (AFP)
Far from expediting repatriation schemes, Western governments have instead sought to outsource the problem to SDF-controlled jails, the crude justice system of neighboring Iraq, or the cash-strapped Kurdish-run authorities and aid agencies operating Al-Hol.
The dangers posed by outsourcing the problem were amply demonstrated in January this year when Daesh remnants launched a massive and highly sophisticated attack on a prison in Hasakah where thousands of its former combatants were being held under SDF guard.
Some reports suggest that 374 militants were killed during the attack, along with 77 prison staff, 40 members of the SDF and four civilians. About 400 inmates remain unaccounted for, indicating that a significant number escaped.
The incident was only the latest in a spate of attacks and attempted escapes at camps and prisons throughout the region that suggest Daesh could be making a resurgence in an area where they had been considered a spent force.
Meanwhile, the children in Al-Hol are now fast becoming adults, radicalized by their mothers and peers, and resentful of their ill-treatment. Unless their plight is urgently addressed, and their psychological needs properly met, aid groups warn of extreme and lasting damage.
“Children cannot continue to live in such distressing conditions,” Sonia Khush, Save the Children’s Syria response director, said in a recent statement.
“The level of violence they experience in Al-Hol on a daily basis is appalling. Insecurity in the camp needs to be effectively addressed without adding more stress and fear to these children’s lives, and they urgently need access to more psychosocial support to cope with their experiences.
“But the only lasting solution for this situation is to support children and their families to be able to safely and voluntarily leave the camp.
“This is no place for children to grow up.”


























