CAIRO: On Oct. 6, 1981, Islamist extremists gunned down Egyptian President Anwar Sadat as he reviewed troops at a military parade in Cairo to celebrate the country’s 1973 war against Israel. Sadat’s bullet-riddled body was rushed to the Maadi Military Hospital, where he was pronounced dead at 2:40 p.m. due to “intense nervous shock and internal bleeding in the chest cavity.”
Two years earlier, Sadat had become the first Arab leader to make peace with Israel — a decision that angered many Egyptians and led to violent demonstrations against him. But the assassination of Sadat did not derail the peace process, which continued without him, with Egypt formally establishing diplomatic relations with Israel in 1982.
In an exclusive interview ahead of the 40th anniversary of the assassination, Gamal El-Sadat, son of Anwar Sadat and chairman of Etisalat Misr, spoke with Arab News about his father’s political legacy, the values he learned from his father, and his memory of that fateful day.
“I was traveling in the US at that time with a couple of my friends,” Gamal El-Sadat said, referring to his location on Oct. 6, 1981. “I had just arrived in Florida. It was a fishing trip that never happened. It was the only time that I had missed the parade.”
Back in Cairo, a group of officers wearing army uniforms and led by Khaled Al-Islambouli, a lieutenant in the Egyptian army, stopped in front of the parade’s reviewing stand. They then fired shots and threw grenades into a crowd of Egyptian government officials.
Anwar Sadat, who was shot four times, died two hours later as 10 other people were also killed in the attack.
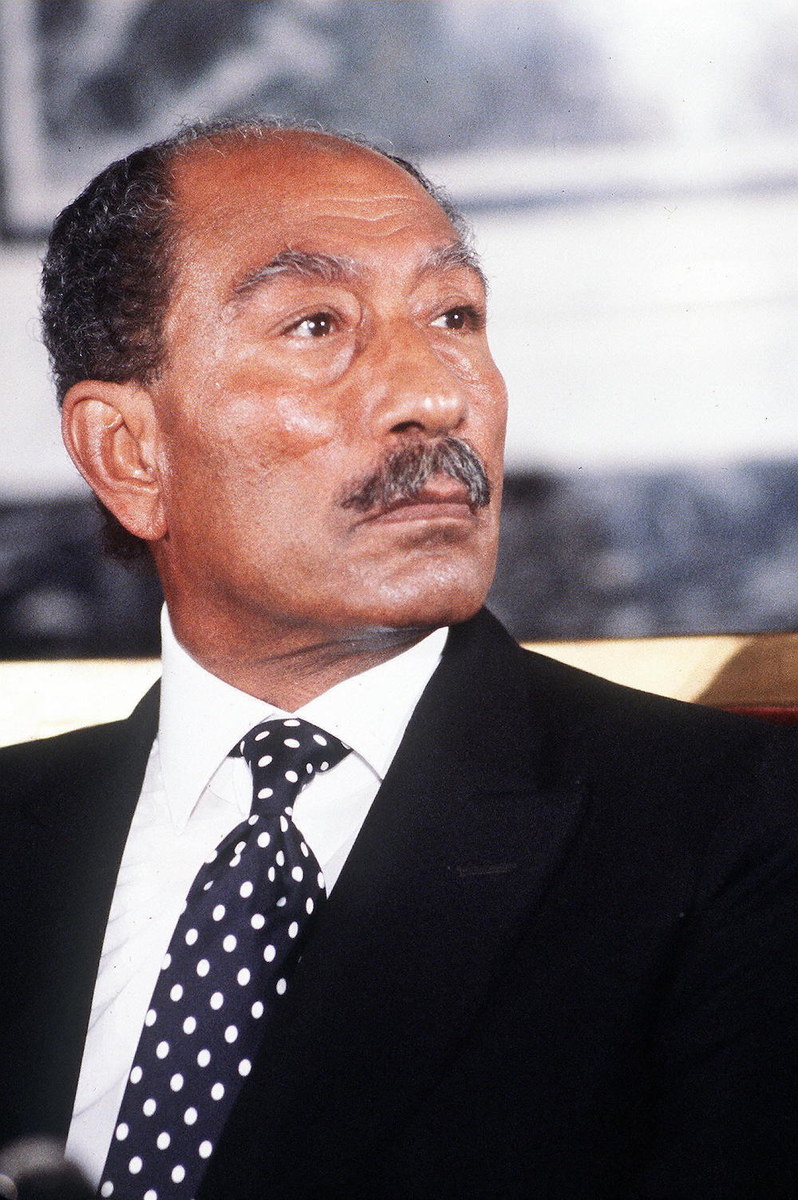

Egyptian President Anwar Sadat shown in a photo taken February 11, 1981 during a private visit to Paris. (AFP/File Photo)
“In the morning, I woke up to a call from the resort manager telling me that there was a shooting in the parade and my father was hurt,” Gamal El-Sadat said.
“I tried to call Cairo, with no luck, then turned the news on. The bulletin said that Anwar Sadat was hurt in his arm, but he was in stable condition. I kept trying to call Cairo until I reached my mother (Jehan Sadat) who told me directly ‘your father has passed away.’”
Jehan Sadat was sitting in the stands at the military parade, just a few meters away from her husband when the deadly attack unfolded.
Gamal El-Sadat remembers very clearly the events that took place immediately after his return to Cairo. His father’s autopsy had not been conducted yet. There was a theory at the time that Anwar Sadat’s murder might have been an inside job.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Gamal El-Sadat recalled arriving directly at the Sadat family home but something cropped up. “I received a call from the prime minister at the time, Dr. Fouad Mohideen, who told me that ‘we would like to have an autopsy done because there is a bullet that is lodged somewhere. We just need to verify because there is a theory that some of my father’s own bodyguards might have assassinated him.’”
Gamal El-Sadat said he would like to be present for the autopsy.
“The autopsy concluded that when the shooting started, my father stood up and he took bullets in his arm and thigh. Those were not fatal,” he said.
“However, another bullet from an AK-74 assault rifle that was fired from one of the parade’s trucks had ricocheted off the counter in front of my father, took an upward trajectory to enter his chest. The bullet went through his heart and got stuck in his neck.
“This finding laid to rest all suspicions about my father’s murder being an inside job. Members of his security detail used to carry sidearms only.”
Less than two years before his killing, in an unprecedented move for an Arab leader, Anwar Sadat traveled to seek a permanent peace settlement with Israel after decades of conflict.
Sadat’s meeting with Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin and address to Israel's parliament were met with outrage in most of the Arab world. The global reaction was different: Sadat and Begin were jointly awarded the 1978 Nobel Prize for peace.
Gamal El-Sadat said: “Before going to Jerusalem, my father went to Syria when he met President (Hafez) Assad to invite the Syrian leader to join him. President Assad was a dear friend of my father but he said ‘No, I will not come with you.’ So, my father told him, ‘Please, I ask you to give me your permission to speak on your behalf. If I fail, it will be me who failed. If I succeed, then we will both succeed.’ But Assad told him ‘No, I will not give you permission to do that as well.’ So, my father left and was very unhappy because it was an offer that had no downsides for Syria at the time.”
Gamal El-Sadat continued: “My father believed that the military had finished its role; there was no way we were going to go any further with the military. It had to be political. It had to be diplomacy. … He had no other choice. (He could not be) the man who looked out for his own fame and kept saying ‘I will throw (the Israelis) into the sea’ and got the support of all the countries, yet not do anything in the end, because nobody was going to throw (the Israelis) into the sea because their safety was guaranteed by the US and the Soviet Union.”
Despite criticism from Egypt’s regional allies, Sadat continued to pursue peace with Begin, and in September 1978 the two leaders met again in the US, where they negotiated an agreement with President Jimmy Carter at Camp David, Maryland.
The Camp David Accords, the first peace agreement between the state of Israel and one of its Arab neighbors, laid the groundwork for diplomatic and commercial relations.
The peace efforts were greeted with suspicion and hostility across the Arab world. In addition to being subjected to political, economic, and diplomatic sanctions, Egypt was also suspended from the Arab League and the body’s headquarters was temporarily moved from Cairo to the Tunisian capital, Tunis.
Today, besides Egypt, five other Arab countries — Jordan, the UAE, Bahrain, Sudan, and Morocco — have established full diplomatic relations with Israel.

Sadat was portrayed as "The Hero of the Crossing" following the 1973 war with Israel, which gave him a huge bump in status and popularity. (Getty Images)
“When my father came to office as president after Gamal Abdel Nasser, he made several proposals for peace with Israel, but they were never met with any seriousness,” Gamal El-Sadat said.
“They were completely disregarded, and he came to understand that the world only listens to power. It was the October war that demonstrated that Egypt would not keep silent regarding Israel’s occupation of its territory.”
Gamal El-Sadat rejects the notion, however, that Egypt did not emerge victorious in the 1973 war.
“The Israelis crossed over to the western side of the Suez Canal, yes,” he said. “They tried to take Suez but could not take Suez, which was a civilian city. And they could not go any further west. The Egyptian reserves blocked the west.”
Gamal El-Sadat continued: “My father understood the (necessity of the) peace deal earlier. He knew that wars were not going to solve the issue. He wanted other Arab countries to join Egypt in the Camp David Accord, and history has shown his vision to be right. Now Arab countries have begun to build strong relations with Israel as they have started to understand that the only solution is politics and dialogue.”
Gamal El-Sadat cited the generosity shown by Anwar Sadat to the dying shah of Iran as proof of the principles his father lived by. Their friendship dated back to the 1970s when Mohamed Reza Pahlavi stood by Egypt during the 1973 war with Israel and sent medical aid and doctors.
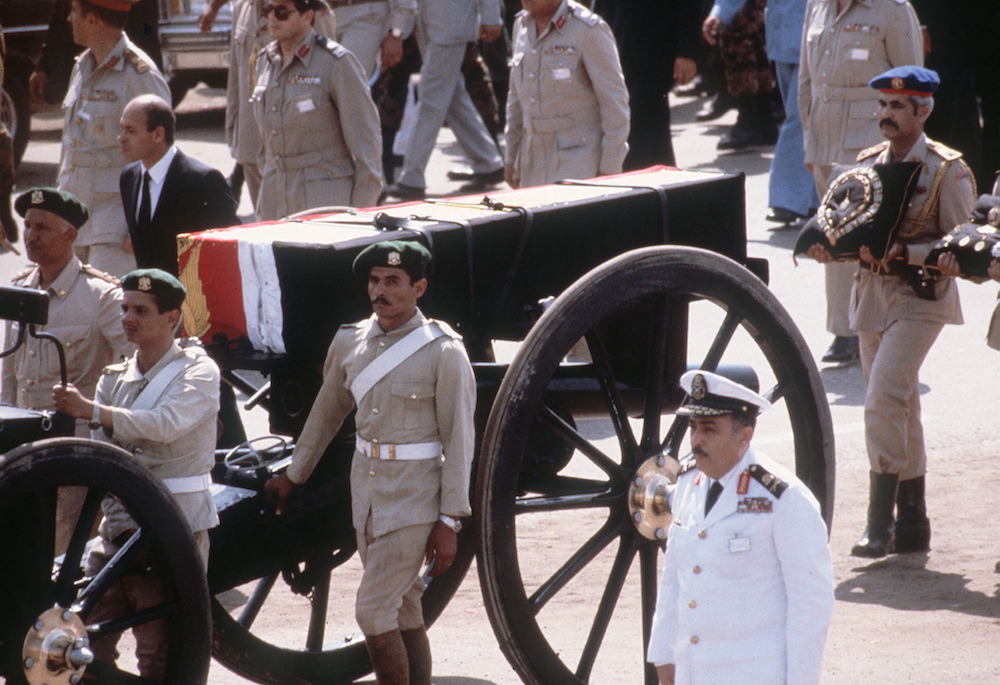

The coffin of late Egyptian President Anwar al-Sadat is transported on a gun carriage during his funeral 10 October 1981 in Cairo. (AFP/File Photo)
After being overthrown by the Islamic Revolution in 1979, the ailing shah moved between Morocco, the Bahamas, Mexico, the US, and Panama. He then took refuge in Egypt on March 24, 1980, after being received by President Sadat.
Gamal El-Sadat said: “My father did not want to make an enemy of anyone or hurt anyone’s feelings. But he could not deny (the fact) that this man stood by Egypt — not by my father, but by Egypt in its time of need.”
For Gamal El-Sadat, Anwar Sadat was of course not just a president of Egypt whose place in history is recognized and secure. He also remembers his father as a kind and simple person.
“I am biased because I am his son, but I believe this statement is true,” Gamal El-Sadat said. “Anwar Sadat was a man in touch with reality. He had lived a hard life and understood what it was to be poor. He appreciated life and understood that life has so many aspects other than money and politics.”
Indeed, Anwar Sadat’s personal history simply reflected the tortuous history of Egypt itself in the 20th century. He was born into a peasant family in the Nile Delta. He joined the Egyptian army, took the side of the Axis powers during World War II, and participated in activism against the British, who imprisoned him.
Anwar Sadat was a senior member of the Free Officers who overthrew King Farouk in the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, and a close confidant of Nasser, under whom he served as vice president twice and whom he eventually succeeded as president in 1970.
“My father was a religious person and very humble,” Gamal El-Sadat told Arab News. “He taught me and my siblings to love our country, and always respect people regardless of their position or station. He used to pray with poor people to show me that we are all alike.”
Until her death from cancer at the age of 88 in July, Jehan Sadat spent much of her life dedicated to promoting social justice and female empowerment in Egypt. Long before she became a global public figure, Jehan helped lead a campaign to reform Egypt’s status law which would go on to grant women new rights to divorce their husbands and retain custody of their children.
She was frequently photographed alongside her husband on official visits abroad and in more intimate settings, at home with their family.
Jehan Sadat would go on to earn a master’s and doctorate degree in comparative literature and, in her later years, took on lecturing posts in Cairo and the US.
“Jehan Sadat was a public figure during Sadat’s time and afterward,” Gamal El-Sadat said. “She was really a strong lady. After my father passed away, she would not sit back and stay at home. She continued her career and got a Ph.D. in Arabic literature, traveled to the US, and started teaching as a visiting professor.
“She used to promote women’s rights in our part of the world. She kept doing so until very recent years when she decided to spend more time with her family.”
Jehan Sadat was just 46 when Anwar Sadat was assassinated. She spent the rest of her life trying to preserve his legacy of peace through her travels and lectures around the world.















