NEW YORK: Libya’s efforts to heal after 10 years of war will require not only a national reconciliation, but also an international reconciliation between the Libyan people and the global community.
That is the view of Taher Elsonni, Libya’s permanent representative to the UN, who on Monday reiterated his country’s demand for an end to external interference and the withdrawal of all foreign forces and mercenaries.
“Enough is enough,” he said during an exclusive interview with Arab News. “Libyans are tired of 10 years of chaos.
“As much as we talk about national reconciliation, there should also be international reconciliation. As much as we talk about confidence building, there should be confidence building between the international community and Libyans — and that starts with the simultaneous withdrawal of all foreign fighters and mercenaries, and support for the will of Libyans when they go through the electoral process.”
Libyans have been killed and their country ravaged by thousands of foreign fighters recruited by the rival forces in the country. As long as Libya’s “free will” is held hostage by these armed groups and their foreign sponsors, Elsonni said, conflicts will continue to rage in the country at a time when the proliferation of such proxy wars is causing instability across the region.
The rebels who killed Chadian President Idriss Deby in April, for example, were based in Libya, where they amassed money, accessed advanced weaponry and gained battlefield experience as guns-for-hire.
“The challenge with mercenaries is that no one acknowledges their presence,” said Elsonni.
The UN-brokered Libyan ceasefire agreement in October 2020 included a call for all 20,000 mercenaries and foreign fighters to withdraw from the country within three months. But when the UN Security Council discussed ways of repatriating them, observers noted that some council members were fueling the problem.
For example, Russia’s support for the Libyan National Army includes mercenaries from Russian private security company Wagner Group. Turkey, meanwhile, provided transport for thousands of Syrians to fight in Tripoli, paid them salaries and offered promises of Turkish citizenship. Other mercenaries operating in Libya hail from South Africa, the US, the UK, Australia and about 30 additional countries.
Meanwhile, Libyans attempt to navigate this sinister foreign presence as they walk an already tricky path toward national reconciliation, and attempt to consolidate the many small victories achieved in the past year as part of the political process.
These achievements — which paved the way for a ceasefire and the formation of an interim unity government tasked with shepherding the nation toward parliamentary and presidential elections scheduled for December — would not have been possible without both Libyans and foreign powers reaching the conclusion that no one could win the war through military might, according to Elsonni.
“Everything was tried, and in the end everyone was convinced that there can be no military solution,” he said.
He conceded that all countries in the region are entitled to be concerned about preserving their security and national interests, but added: “You don’t need to intervene and interfere the way you did in order to have a stabilized region (and) boost the economy.
“Libya is a hub between Africa and Europe, East and West. Libyans are known for their modesty. I can no longer say Libya is a rich country, but it does have the means and the resources to come back, and with Libya stabilized we can find win-win deals that will satisfy everyone’s national interests as much as possible.
“So, let’s work together, put the past behind us and start a new phase. And let’s not provide an excuse for terrorism and extremism, which feeds on this chaos and perpetuates the conflict.”
The road to the national elections planned for December has been paved with as much fear as hope among Libyans.
Although the new Presidency Council managed to unify civilian executive bodies, the military remains fractured. Some fear that winners with weapons might start another war.
In the absence of a clear constitutional framework setting out the responsibilities of a new president, “who can guarantee that Libyans will not find themselves in the grip of yet another dictator?” asked Elsonni.
“There is a group of people that don’t want to lose the power they have today, so they are maneuvering and finding excuses for the elections not to happen,” he added.
“There are also those who fear losing power by having a high-level executive office, in the form of a president, that might lead to them losing popularity. Some want only parliamentary elections, and think a safer option is to have a steady state and give more time to the constitutional framework to be developed.
“And, finally, you have Libyans on the ground who are fed up with all the attempts of the past and want Libya as a state to have separation of power.
“The challenge in this last one is to have an ‘inclusive’ president, not one who has revenge in mind, because those who have ambitions to be president are all affiliated to a certain group, and so that is scaring people.”
All of the fears people have are valid, said Elsonni.
“But what are the alternatives that we have today?” he asked. “If I name all the obstacles that we face today, one would conclude that the risk of the elections not happening is high.”
Even if they do go ahead, he said, challenges will remain — but they at least offer the hope for change and a better future.
“Anyone who thinks elections will solve all of Libya’s problems is naive,” he said. “But we have had a sick patient for the past 10 years and we have been using the same medicine.
“Now we have the option of a new medicine in the form of elections. We are not sure how that will unfold — it’s a 50/50 risk. But a certain level of legitimate representation will get the ball rolling.”
Meanwhile, Elsonni said, national reconciliation remains “the foundation for any permanent peace in Libya.”
From the establishment of a High Commission for Reconciliation to the release, albeit symbolic, of some prisoners, there have been steps taken in the right direction.
Elsonni stressed the importance of “transitional justice” as a means toward lasting reconciliation and true healing of the nation.
“For there to be a comprehensive national reconciliation, truth needs to be revealed, and apologies issued,” he said.
Although he admitted that the responsibility for reconciliation ultimately lies primarily with the Libyan people themselves, Al-Sonni questioned the lack of useful international support for the efforts.
The ambassador, who was a UN staffer for 17 years and so is familiar with the organization’s methodologies, criticized the UN for adopting a “top-down approach” to Libya, which he said has undermined the role of civil society.
“If you follow all the dialogue that took place, they were all technical discussions that tackled military, political and economical challenges, but there was no national reconciliation track,” he said.
“There is also a lack of understanding of the Libyan context by the international community. For Libya to become a success story, we need to adopt a bottom-top approach, work on civil society and try to get the best of the tribal structure that links Libyans together.
“Some have tried to use our tribal structure as a way to fuel the war. But having tribes is not a bad thing. In fact, it is a golden key, I call it, which can lead us to peace if we use it correctly.”
Inclusivity is another important aspect to the process. Elsonni took part in the Sukhairat dialogue in 2015, and was one of the signatories to the final agreement for the formation of a national unity government.
“Not all parties who really had power on the ground were represented,” he said. “Many were completely excluded, such as the ex-regime loyalists.”
He warned that such “exclusion in any post-conflict reconciliation is one of the biggest mistakes you could make. It is a fatal error.”
Exclusion can also happen in the form of centralized governance, Elsonni said, which can, for example, cause people living outside of Tripoli, where much of the wealth is concentrated, to feel excluded.
Despite all these challenges, however, Elsonni is pinning his hopes on the next generation of Libyan youth.
“The only people who will solve this are our young people,” he said. “They are vocal and much more aware than their elders. The problem is that they still lack coordination and leadership.”
Elsonni also addressed allegations of flagrant abuses of human rights in Libyan detention centers. While he expressed regret over the fact that his country has become a place where “innocent people die,” he denied any accusation of systemic torture. Once again he pleaded with the international community to “help us make Libya stable and these issues will be resolved.”
He added: “We’re totally against such violations and we’re working hard to fix the system and protect the most vulnerable. But there is a difference between a government that doesn’t care and one that really tries, and sees this as a priority, but is spread thin with all the other different challenges and has resource problems.
“The problem is the hypocrisy of the West, and their unwillingness to devise a comprehensive solution for the migrant crisis. You cannot blame a country in conflict for what happens within it when it comes to migrants. Migrants who come to Libya aim to continue to Europe. Nobody wants to live in the hellfire of conflict, that goes without saying.”
Condemning the “double standards” of the international community, he said: “They ask us to accommodate those migrants when they know our resources are stretched thin. They ask us to shut down detention centers but they won’t tell us what to do with migrants who enter illegally, or those who are arrested at sea and pushed back to Libya.
“If you really care about migrants, then agree on a quota also and take in some of them.
“The countries that are being most forceful with Libya on this issue are the same ones that are shutting their doors to migrants. One such country literally took in four or five migrants out of the thousands that are trying to cross.
“The problem is bigger: it is EU competition between countries, and we know it. You want to blame us? Blame yourself first.”
‘Leave us alone to heal,’ Libya’s UN envoy tells foreign powers
https://arab.news/67ss5
‘Leave us alone to heal,’ Libya’s UN envoy tells foreign powers
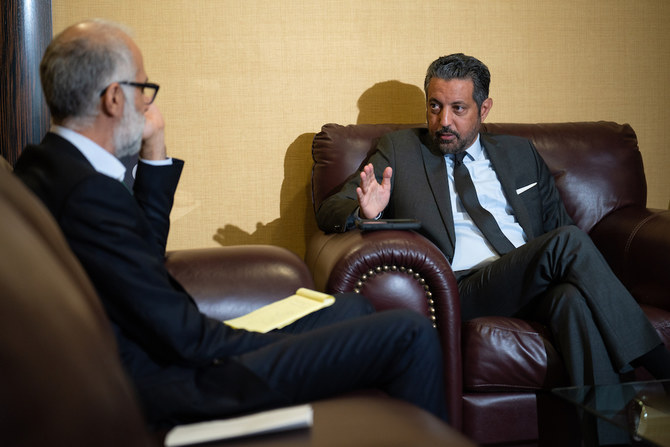

- In an exclusive interview with Arab News, Taher Elsonni highlights the challenges facing Libya and how foreign powers are making them worse
- In addition to national reconciliation there is a need for international reconciliation between the international community and Libyans, he said.
As airplane makers struggle to meet demand, Morocco wants to become a manufacturing hub
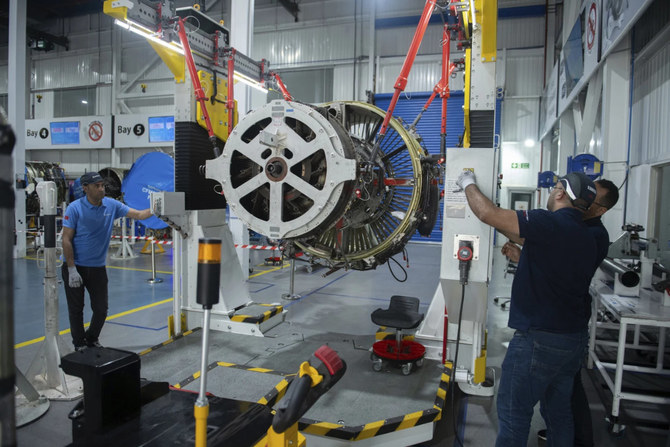

- The North African kingdom is among a list of countries vying for contracts with plane makers looking to speed up production to meet demand
- Many companies eye Morocco as a source for comparatively cheap labor and workers with an expanding pool of skilled workers
CASABLANCA, Morocco: Moroccan officials want to turn the country into an aviation hub, luring investors aiming to spread out their supply chains to more nations with available and affordable workers.
The North African kingdom is among a longer list of countries vying for contracts with big manufacturers looking to speed up production and deliver more planes to meet demand. Companies like Boeing and Airbus — as well as the manufacturers that build their components — are outsourcing design, production and maintenance to countries from Mexico to Thailand.
In Morocco, efforts to grow the country’s $2 billion-a-year aerospace industry are part of a years-long push to transform the largely agrarian economy through subsidizing manufacturers of planes, trains and automobiles. Officials hope it dovetails with efforts to grow Moroccan airlines, including the state-owned Royal Air Maroc.
“The needs are huge and we are in a very good position,” said Hamid Abbou, the airline’s CEO. “Most of the big suppliers in Europe are struggling to get people to work in this industry. We don’t have that issue.”

Despite hopes among its cheerleaders, the air travel industry faces headwinds. When demand rebounded after much air traffic stopped during the pandemic, manufacturers faced challenges building enough planes to meet demand from airlines. For Boeing, delays caused by supply chain issues were compounded by high-profile emergencies and deadly crashes that further curtailed deliveries.
From eastern Europe to southeast Asia, new levels of demand have forced manufacturers to seek out new locations to build and repair parts.
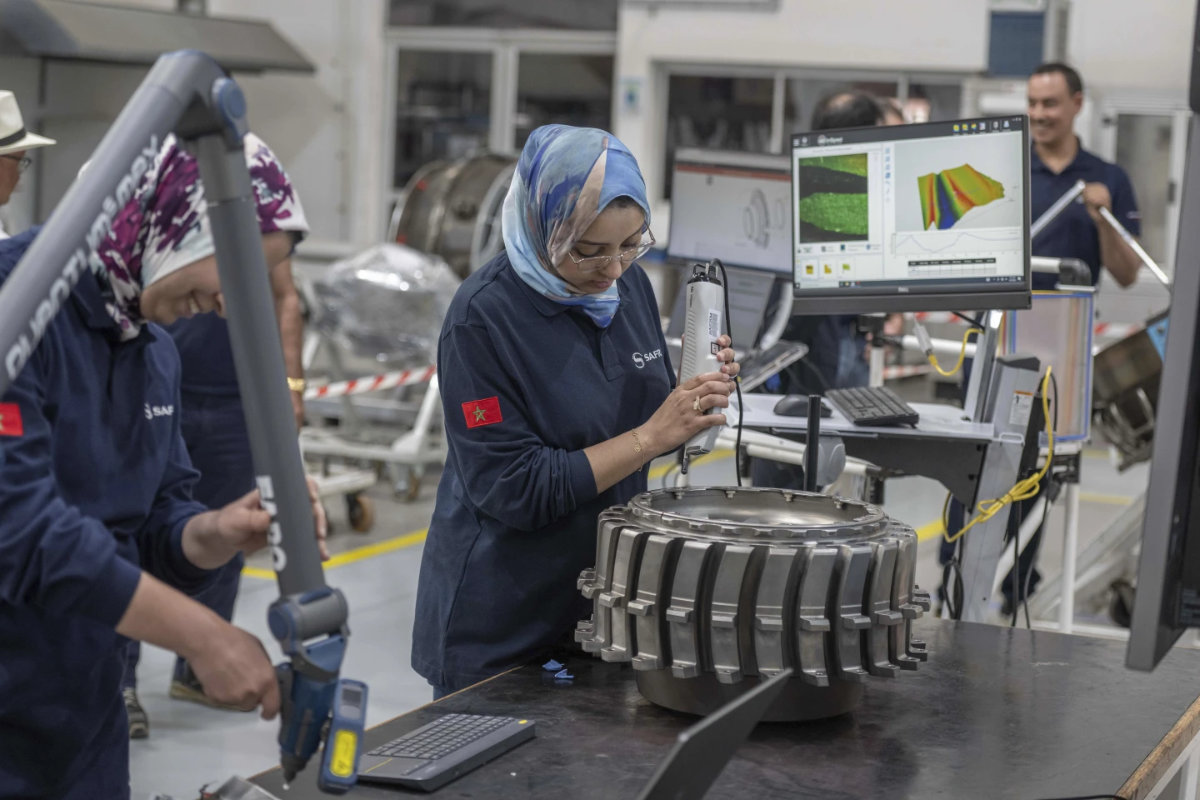
Safran Aircraft Engines, a French manufacturer, sends engines for Boeing 737s and Airbus 320s to a repair plant outside of Casablanca every six to eight years and then sends them back to airlines from countries including Brazil, Saudi Arabia, the United Kingdom and Ireland.
The company is among 130 in the sector active in Morocco, where parts ranging from wings to fuselages are produced in an industry that employs 42% women — a proportion that industry lobbyists say is larger than its European and North American manufacturing industry counterparts.
Though many companies eye Morocco as a source for comparatively cheap labor, the industry and government have worked to train skilled workers at IMA, an institute for aeronautics professions in Casablanca.
At an event celebrating Safran’s 25-year partnership with Royal Air Maroc, Safran CEO Jean-Paul Alary said he hoped Morocco’s aviation industry would continue to expand, particularly as industrywide demand increases and companies face labor shortages in Europe.
“It’s the access to well-qualified talent that’s been well-trained,” Alary said of Morocco. “They are the key players for achieving our goals.”
Another former US State Department official alleges Israeli military gets ‘special treatment’ on abuses

- “In my experience, Israel gets special treatment that no other country gets,” says Charles O. Blaha, former director of a State Department security and human rights office
- Late last year, Josh Paul resigned as a director overseeing arms transfers to other countries’ militaries in October in protest of the US rushing arms to Israel amid its war in Gaza
WASHINGTON: A former senior US official who until recently helped oversee human-rights compliance by foreign militaries receiving American military assistance said Wednesday that he repeatedly observed Israel receiving “special treatment” from US officials when it came to scrutiny of allegations of Israeli military abuses of Palestinian civilians.
The allegation comes as the Biden administration faces intense pressure over its ally’s treatment of Palestinian civilians during Israel’s war against Hamas in Gaza. And it matters because of who said it: Charles O. Blaha.
Before leaving the post in August, he was a director of a State Department security and human rights office closely involved in helping ensure that foreign militaries receiving American military aid follow US and international humanitarian and human rights laws.
Blaha said his departure from the State Department after decades of service was not related to the US-Israeli security relationship. He is the second senior State official involved in that relationship to assert that when it comes to Israel, the US is reluctant to enforce laws required of foreign militaries receiving American aid.
“In my experience, Israel gets special treatment that no other country gets,” Blaha said. “And there is undue deference, in many cases, given” to Israeli officials’ side of things when the US asks questions about allegations of Israeli wrongdoing against Palestinians, he added.
He spoke to reporters at an event where he and other members of an unofficial, self-formed panel of former senior US civilian and military officials released a report pointing to civilian deaths in specific airstrikes in Gaza. They said there was “compelling and credible” evidence that Israeli forces had acted illegally.
Blaha’s comments echoed those of another State Department official and panel member, Josh Paul. Paul resigned as a director overseeing arms transfers to other countries’ militaries in October in protest of the US rushing arms to Israel amid its war in Gaza.
Asked about the allegations from the two, a State Department spokesman, Vedant Patel, said “there is no double standard, and there is no special treatment.”
Israeli officials did not immediately respond to a request for comment. Israel consistently says it follows all laws in its use of US military aid, investigates allegations against its security forces and holds offenders accountable.
Israel historically is the United States’ biggest recipient of military aid, and Biden on Wednesday signed legislation for an additional $26 billion in wartime assistance. But Biden has come under growing pressure over that support as Palestinian deaths mount.
The latest Israel-Hamas war began on Oct. 7, when Hamas and Islamic Jihad, two militant groups backed by Iran, carried out a cross-border attack that killed 1,200 people in Israel. Israel responded with an offensive in Gaza that has caused widespread devastation and killed more than 34,000 people, according to local health officials.
In coming days, the administration says it will announce its official findings from reviews it did into allegations of especially serious human rights abuses by specific Israeli military units. Those units would be barred from receiving US military aid if the US review confirms those allegations.
Separately, the Biden administration also is expected to disclose by May 8 whether it has verified assurances from Israel that the country is not using US military aid in a way that violates international or human rights law. Both Israel’s written assurance and the US verification were mandated by a new presidential national security memo that Biden issued in February.
The February agreement was negotiated between the Biden administration and members of his own Democratic Party, who had been pushing for the US to begin conditioning military aid to Israel on improving treatment of Palestinian civilians.
Panel members released their report Wednesday to urge the US to scrutinize specific attacks in Gaza that the former officials argued should lead to a conclusion that Israel was wrong when it confirmed it was complying with the laws. If that determination is made, the US could then suspend military aid.
Wednesday’s unofficial report points to 17 specific strikes on apartments, refugee camps, private homes, journalists and aid workers for which the former US officials and independent experts allege there’s no evidence of the kind of military target present to justify the high civilian death tolls.
They include an Oct. 31 airstrike on a Gaza apartment building that killed 106 civilians, including 54 children. Israeli officials offered no reason for the strike, and a Human Rights Watch probe found no evidence of a military target there, the officials said. Israel has said in many of the instances that it is investigating.
Hamas releases video showing well-known Israeli-American hostage
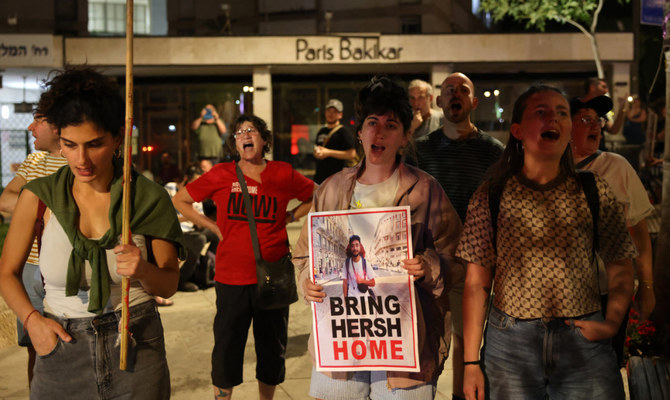
- Goldberg-Polin is one of the most recognized captives. Posters with his image are pinned up across Israel
JERUSALEM: Hamas released a hostage video on Wednesday showing a well-known Israeli-American man who was among scores of people abducted by the militants in the attack that ignited the war in Gaza.
The video was the first sign of life of Hersh Goldberg-Polin since Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack on southern Israel, and its release ignited new protests in Jerusalem calling on the government to do more to secure the captives’ release.
In the video, Goldberg-Polin accused Israel’s government of abandoning the people who are being held hostage by Hamas. He also claimed that some 70 captives have been killed in Israel’s bombing campaign. Goldberg-Polin was clearly speaking under duress, and the claim could not be independently verified. It was not clear when the video was made.
Goldberg-Polin, 23, was at the Tribe of Nova music festival when Hamas launched its attack from nearby Gaza. In the video, Goldberg-Polin is missing part of his left arm.
Witnesses said he lost it when attackers tossed grenades into a shelter where people had taken refuge. He had tied a tourniquet around it before being bundled into the truck by Hamas.
Goldberg-Polin is one of the most recognized captives. Posters with his image are pinned up across Israel. His mother, Rachel Goldberg, has met with world leaders and addressed the United Nations.
Though there was no date on the video, Goldberg-Polin appeared to reference the weeklong Jewish holiday of Passover, which began on Monday.
His parents said they were relieved to see him alive but were concerned about his health and well-being, as well as that of the other hostages.
“We are here today with a plea to all of the leaders of the parties who have been negotiating to date,” said his father, Jon Polin, naming Egypt, Israel, Qatar, the United States and Hamas.
“Be brave, lean in, seize this moment and get a deal done to reunite all of us with our loved ones and end the suffering in this region,” he said.
Hostages’ families have accused Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s government of not doing enough to secure the release of their relatives.
After the Hamas video was made public, hundreds of Israelis gathered outside Netanyahu’s official residence in central Jerusalem on Wednesday, calling on the government to strike a deal to bring home hostages. Many held posters of Goldberg-Polin, and some of the protesters set cardboard boxes on fire.
“We are afraid for his life, so we went to protest and call for the government to do whatever is possible to bring him and everybody else back, as soon as possible,” said one of the marchers, Nimrod Madrer. “Bring them back home,” the crowd chanted.
At the nearby Great Synagogue, a large crowd jeered the country’s ultranationalist national security minister, Itamar Ben-Gvir, chanting “shame” as he exited the building following a Passover gathering. One protester banged on Ben-Gvir’s car and was pushed away by police as it drove off.
Hamas and other militants abducted around 250 people in the Oct. 7 attack and killed around 1,200, mostly civilians. They are still believed to be holding around 100 hostages and the remains of some 30 others. Most of the rest were freed in November in exchange for the release of 240 Palestinians imprisoned by Israel.
Khalil Al-Hayya, a senior Hamas official, said Goldberg-Polin’s family had asked mediators to inquire about his fate for humanitarian reasons.
His family was “searching the world for any sign of him,” Al-Hayya said in an interview with Hamas-run Al-Aqsa TV broadcast on Wednesday. Hamas’ armed wing ”sent a strong message by publishing this young man’s message directed at Netanyahu,” Al-Hayya said.
The US, Qatar and Egypt have spent months trying to broker another ceasefire and hostage release, but the talks appear to have stalled. Hamas has said it will not release the remaining hostages unless Israel ends the war, which has killed over 34,000 Palestinians, according to local officials.
Netanyahu has rejected those demands, and says Israel remains committed to destroying Hamas and bringing all the hostages home. He has come under mounting criticism in Israel, where some say it will be impossible to do both.
Wars in Gaza and Sudan ‘drive hunger crisis affecting 280 million worldwide’

- New report on global food insecurity says outlook for 2024 is ‘bleak’
JEDDAH: More than 280 million people worldwide suffered from acute hunger last year in a food security crisis driven by conflicts in Gaza and Sudan, UN agencies and development groups said on Wednesday.
Economic shocks also added to the number of victims, which grew by 24 million compared with 2022, according to a report by the Food Security Information Network.
The report, which called the global outlook for this year “bleak,” is produced for an international alliance of UN agencies, the EU and governmental and non-governmental bodies.
Food insecurity is defined as when populations face food deprivation that threatens lives or livelihoods, regardless of the causes or length of time. More geographical areas experienced “new or intensified shocks” and there was a “marked deterioration in key food crisis contexts such as Sudan and the Gaza Strip,” said Fleur Wouterse, a senior official at the UN’s Food and Agricultue Organization.
Since the first report by the Global Food Crisis Network covering 2016, the number of food-insecure people has risen from 108 million to 282 million, Wouterse said. The share of the population affected within the areas concerned had doubled from 11 percent to 22 percent, she said.
Protracted major food crises are ongoing in Afghanistan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Syria and Yemen. “In a world of plenty, children are starving to death,” UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said.
“War, climate chaos and a cost-of-living crisis, combined with inadequate action, mean that almost 300 million people faced acute food crisis in 2023. Funding is not keeping pace with need.”
According to the report, situations of conflict or insecurity have become the main cause of acute hunger. For 2024, progress would depend on the end of hostilities, said Wouterse, who said aid could rapidly alleviate the crisis in Gaza or Sudan, for example, once humanitarian access to the areas was possible.
Yemen’s Houthis say they targeted American and Israeli ships
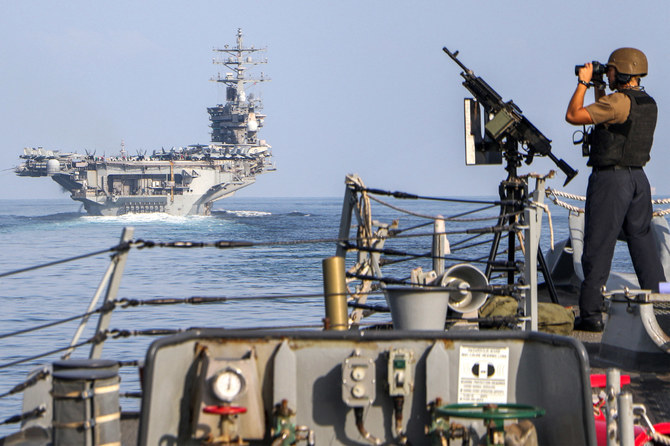

- The Iran-aligned group said it targeted the US ship Maersk Yorktown, an American destroyer in the Gulf of Aden and Israeli ship MSC Veracruz in the Indian Ocean
- US military confirms attack and said it downed one anti-ship missile and four drones on Wednesday
CAIRO/DUBAI: Houthi militants in Yemen have attacked what they said were two American ships and an Israeli vessel, the group’s military spokesman said on Wednesday, the first such attack in more than two weeks.
The Iran-aligned group said it targeted the US ship Maersk Yorktown, an American destroyer in the Gulf of Aden and Israeli ship MSC Veracruz in the Indian Ocean, the spokesman, Yahya Sarea, said in a televised speech.
American authorities confirmed the attack and said US-led coalition forces off the coast of Yemen shot down four drones and an anti-ship missile launched by the Houthis.
In a statement on X, formerly Twitter, the US Central Command (CENTCOM) said that just before noon Sanaa time (0900 GMT) a coalition vessel "successfully engaged one anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM)" launched from Houthi controlled areas of Yemen.
It was determined that the ASBM and UAVs (drones) presented an imminent threat to US, coalition, and merchant vessels in the region," CENTCOM said.
Yemen’s Houthis have been attacking ships in the Red Sea region since November in what they say is a campaign of solidarity with Palestinians fighting Israel in Gaza.
“The Yemeni armed forces confirm they will continue to prevent Israeli navigation or any navigation heading to the ports of occupied Palestine in the Red and Arabian Seas, as well as in the Indian Ocean,” Sarea said on Wednesday.
Separately, British maritime security firm Ambrey said earlier on Wednesday that it was aware of an incident southwest of the port city of Aden, an area where the Houthis often target ships they say are linked to Israel or the United States.
The vessel reported an “explosion in the water” approximately 72 nautical miles east-southeast of Djibouti, an updated advisory from Ambrey said.
Houthi attacks have disrupted global shipping through the Suez Canal, forcing firms to re-route to longer and more expensive journeys around southern Africa. The United States and Britain have launched strikes on Houthi targets in Yemen.





















