USA: Earth sizzled in July and became the hottest month in 142 years of recordkeeping, US weather officials announced.
As extreme heat waves struck parts of the United States and Europe, the globe averaged 62.07 degrees (16.73 degrees Celsius) last month, beating out the previous record set in July 2016 and tied again in 2019 and 2020. the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said Friday. The margin was just .02 degrees (.01 Celsius),
The last seven Julys, from 2015 to 2021, have been the hottest seven Julys on record, said NOAA climatologist Ahira Sanchez-Lugo. Last month was 1.67 degrees (0.93 degrees Celsius) warmer than the 20th century average for the month.
“In this case first place is the worst place to be,” NOAA Administrator Rick Spinrad said in a press release. “This new record adds to the disturbing and disruptive path that climate change has set for the globe.”
“This is climate change,” said Pennsylvania State University climate scientist Michael Mann. “It is an exclamation mark on a summer of unprecedented heat, drought, wildfires and flooding.”
Earlier this week, a prestigious United Nations science panel warned of worsening climate change caused by the burning of coal, oil and natural gas and other human activity.
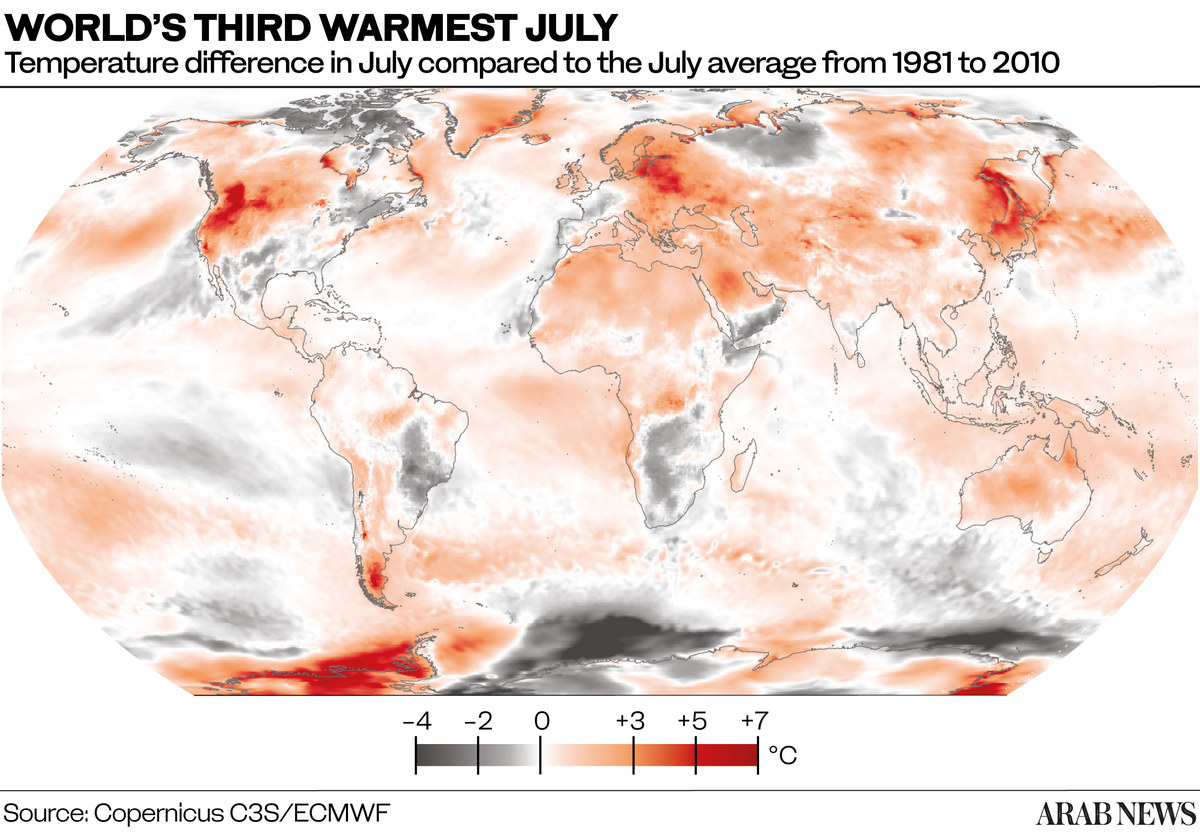
Warming on land in western North America and in parts of Europe and Asia really drove the record-setting heat, Sanchez-Lugo said. While the worldwide temperature was barely higher than the record, what shattered it was land temperature over the Northern Hemisphere, she said.
Northern Hemisphere temperatures were a third of a degree (.19 degrees Celsius) higher than the previous record set in July 2012, which for temperature records is “a wide margin,” Sanchez-Lugo said.
July is the hottest month of the year for the globe, so this is also the hottest month on record.

One factor helping the world bake this summer is a natural weather cycle called the Arctic Oscillation, sort of a cousin to El Nino, which in its positive phase is associated with more warming, the NOAA climatologist said.
Even with a scorching July and a nasty June, this year so far is only the sixth warmest on record. That’s mostly because 2021 started cooler than recent years due to a La Nina cooling of the central Pacific that often reduces the global temperature average, Sanchez-Lugo said.
“One month by itself does not say much, but that this was a La Nina year and we still had the warmest temperatures on record ... fits with the pattern of what we have been seeing for most of the last decade now,” said University of Illinois meteorology professor Donald Wuebbles.
While the world set a record in July, the United States only tied for its 13th hottest July on record. Even though California, Nevada, Oregon and Washington had their hottest Julys, slightly cooler than normal months in Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, Arkansas, Missouri, Alabama, Maine, Vermont and New Hampshire kept the nation from approaching record heat levels.
The last time the globe had a July cooler than the 20th century average was in 1976, which was also the last year the globe was cooler than that normal.
“So if you’re younger than 45 you haven’t seen a year (or July) where the mean temperature of the planet was cooler than the 20th century average,” said Princeton University climate scientist Gabriel Vecchi.
















