BERN, Switzerland: America is back. That was the message Joe Biden wanted to drive home during his first foreign foray as US president — an eight-day Europe tour in June.
The soft-power offensive has been welcomed by America’s European allies after four years of turbulence in transatlantic ties. But it has also brought the West’s long-simmering rivalries with Russia and China to the surface — including the possibility of a nasty confrontation over the Arctic region.
The Arctic is a physical space where geopolitics meets climate change, and where competition over access to natural resources collides with contested commercial and military shipping routes. These are matters that will have serious ramifications well beyond the handful of nations that border the North Pole.
The poles are often described as the Earth’s thermostat, reacting to even the slightest changes in sea temperature. The Arctic has warmed at twice the pace of the rest of the globe and, according to NASA, its sea ice has declined by 13.1 percent during the past decade.
Melting sea ice is contributing to rising sea levels, causing Arctic coastlines to gradually vanish. The process is being accelerated by the thawing of permafrost, which releases long-trapped pockets of carbon dioxide and methane gas into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change.
The rapid retreat of Arctic ice is opening up long-frozen sea lanes for the first time in millennia, exposing the region’s natural resources and shipping lanes to commercial and military exploitation.
According to Bloomberg, about 30 percent of undiscovered gas reserves and 13 percent of oil reserves are estimated to lie beneath the Arctic region. However, the race to claim these vast riches collides with the emerging global consensus of achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
The Arctic Council deliberated over these issues in late May when its members met in the Icelandic capital, Reykjavik. The multilateral body of eight member states bordering the Arctic region and 13 observer nations was founded 25 years ago to address such issues as the rights of indigenous groups, climate change, oil and gas development, and shipping. Its mandate does not, however, extend to the realm of defense.
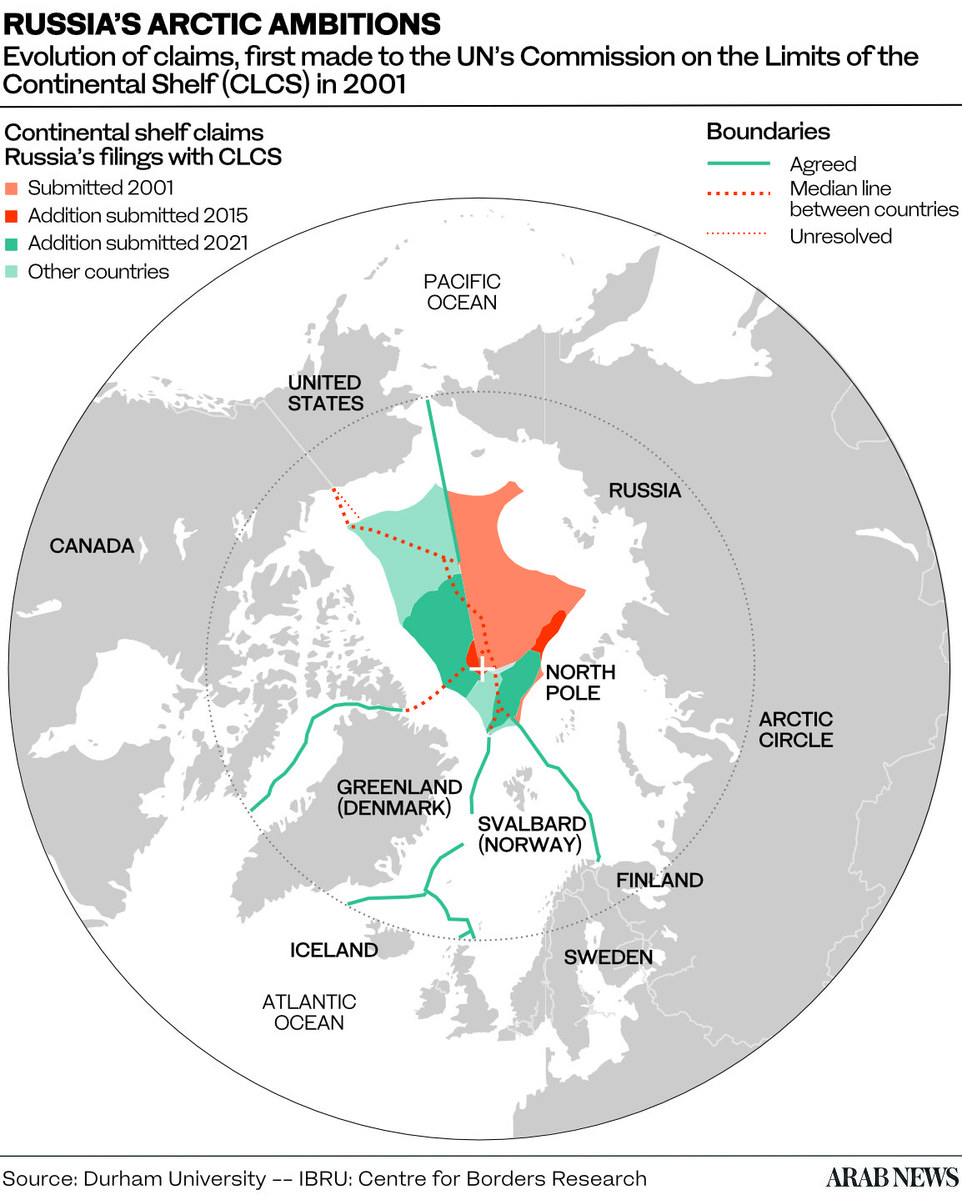
When Iceland passed the two-year rotating presidency of the organization to Russia last month, divergent views and geopolitical tensions came to the fore. The summit coincided with US Secretary of State Antony Blinken’s first meeting with his Russian counterpart, Sergei Lavrov. The latter had stirred the pot by declaring “the Arctic is our land and our waters.
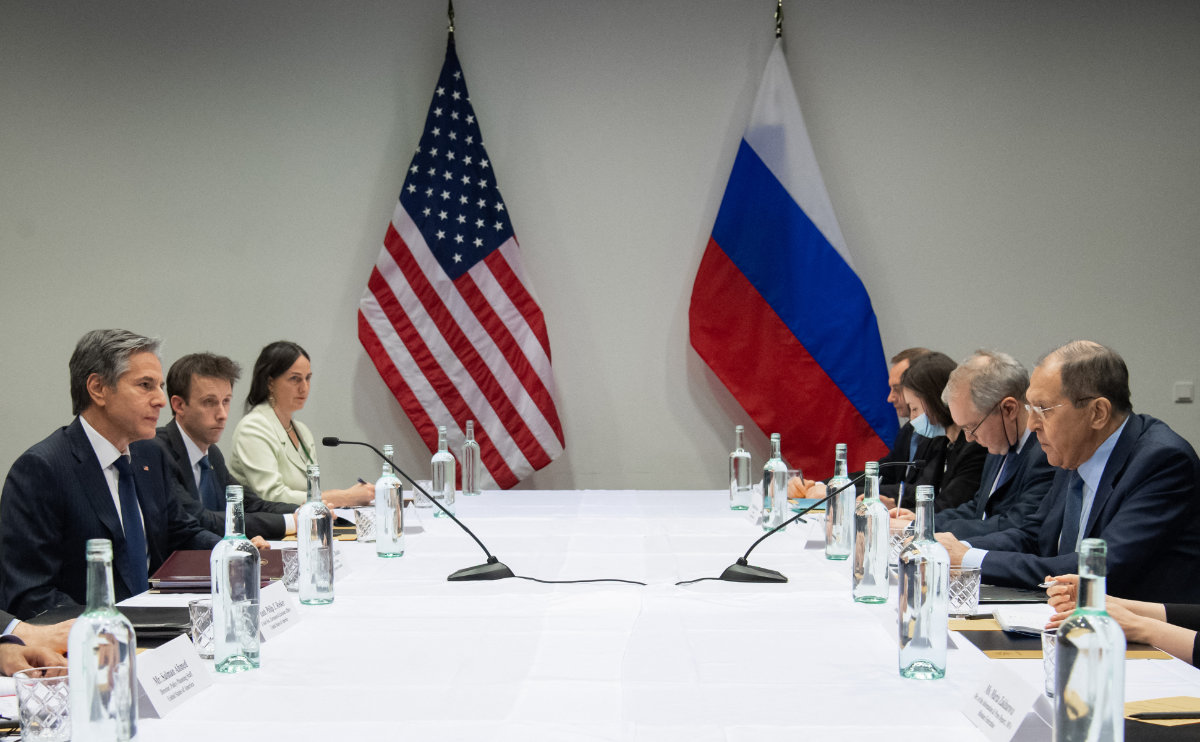

US Secretary of State Antony Blinken (L) meets with Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov (R) at the Harpa Concert Hall in Reykjavik, Iceland, on May 19, 2021. (Saul Loeb / Pool / AFP)
The sentiment is understandable from Lavrov’s perspective, given that Russia extracts about 90 percent of its natural gas, 17 percent of its oil, and 90 percent of its nickel from the Arctic, which also contains the majority of its platinum and palladium reserves.
The Russian economy is highly dependent on mineral extraction. In 2019 the Ministry of Natural Resources and the Environment estimated that oil, gas, mining and raw materials amount to about 60 percent to Russia’s gross domestic product.
Moscow and Washington have differing visions on matters concerning the Arctic, among them the fine balance between energy production, natural-resource extraction and the quest to halt climate change.
At the start of his term, Biden suspended the oil-drilling rights north of the Arctic circle that his predecessor, Donald Trump, had granted. The Kremlin, however, intends to expand its drilling operations.
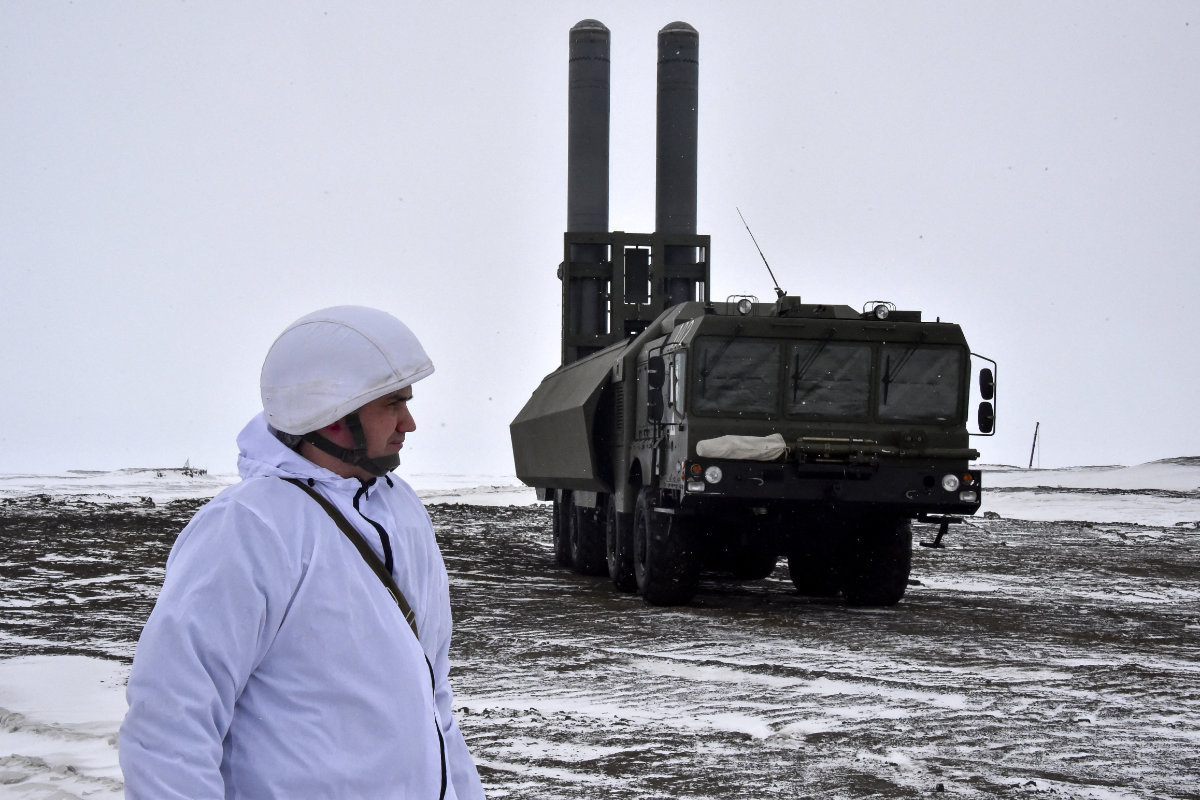

A soldier stands near a Russia's Bastion mobile coastal defense missile system on the island of Alexandra Land, part of the Franz Josef Land archipelago, on May 17, 2021. (Maxime Popov / AFP)
Novatek’s LNG (liquefied natural gas) project on the Arctic Yamal peninsula is producing at 114 percent of capacity on its four trains. In March the company approved external financing for the $11 billion Arctic LNG 2 project, which will start production in 2023. The project is expected to reach a production level of 20 million tons by 2026. Fundraising efforts will take place in Russia, China, Japan and Europe.
Energy is where China enters the fray. Saudi Arabia and Russia alternate as Beijing’s largest oil supplier. In 2020, China received 16.8 percent of its crude oil from the Kingdom and 15.3 percent from Russia.
CLIMATEFACTS
Sea ice keeps polar regions cool, helps moderate global climate.
Ice surface reflects back into space 80% of the sunlight that hits it.
As sea ice melts in the summer, it exposes the dark ocean surface.
Temperatures rise as the ocean absorbs 90% of sunlight and heats up.
The poles are the regions of the Earth most sensitive to climate change.
Owing to an especially cold winter, China’s pipeline imports of natural gas via Russia’s eastern (Siberian) route reached 28.8 million cubic meters a day in early 2021 — double the 2020 contract, according to S&P Global Platts. In 2020, Russia was the sixth-largest LNG supplier to China after Australia, Qatar, the US, Malaysia and Indonesia, according to Argus.
China has become an important financier of major energy-infrastructure projects in Russia’s Arctic region and Siberia. One reason for this is that US sanctions imposed on Russia in 2014 coincided with China’s growing thirst for energy and rising affluence.
However, some Russian experts are concerned about the growing dependence on Chinese money to fund the Arctic expansion, an undertaking of vital national importance to Moscow. Arctic Council members and observers are therefore watching the Sino-Russian relationship very closely.
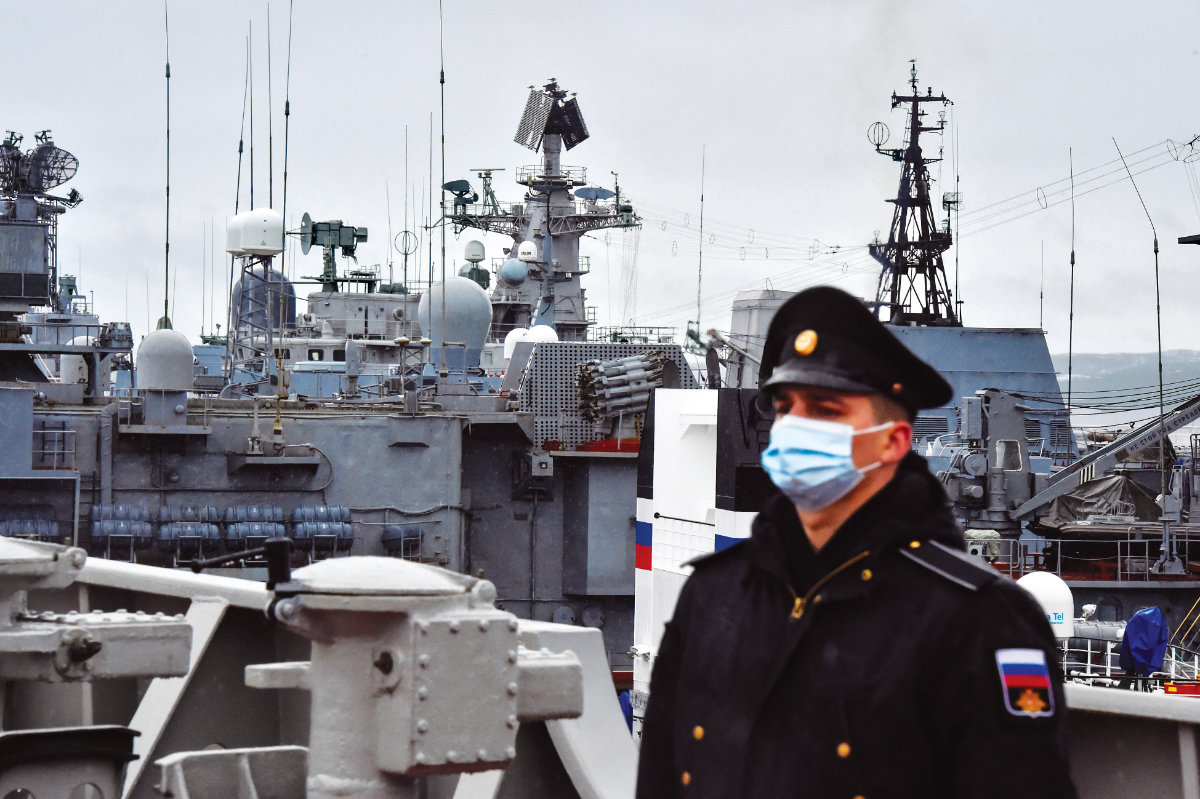

Russian warships at the Arctic base of Severomorsk. The changing geography of the Arctic increases the risk of confrontation between the major powers. (AFP)
The valuable resources beneath the seafloor are not the only prize at stake in this polar scramble. The Arctic shipping route, from the Bering Strait to the Barents Sea, stretches for 5,550 kilometers and constitutes the shortest possible route between Asia and Europe.
The Northern Sea Route used to be open to ships for only 80 days of the year, frozen over for the remaining 285. Now it allows passage for 120 to 150 days, courtesy of the melting ice caps. Researchers at Kyoto University expect this time window will widen to 225 days.
The Northern Sea Route shortens the passage from China to Europe by 10 to 12 days, compared with the sea journey via the Strait of Malacca and the Suez Canal. Although the route is relatively shallow, limiting the size of vessels able to traverse it, control of it has obvious strategic and commercial benefits.
During his European tour, among engagements designed to shore up Western solidarity, Biden attended the UK-hosted G7 summit in Cornwall, met with NATO chiefs in Brussels and held his first tete-a-tete with his Russian counterpart in Geneva. Relations between Vladimir Putin-led Russia and the West are currently too frosty to patch up without addressing the many underlying differences.
Take Arctic freight traffic. Putin wants to expand its volume by 2.5 times to 80 million tons by 2024. This “Polar Silk Road” would have serious ramifications far beyond the Arctic circle, placing it in direct competition with the Suez Canal and major ports from the Mediterranean and the Middle East to Southeast Asia.
There is also a defense dimension to the changing geography of the Arctic. Mikhail Gorbachev, the former president of the Soviet Union, famously called the Arctic a peaceful place. The great powers and their armed forces had little choice but to avoid creating conflict there, given the inhospitable climate and impassable sheets of ice

Russian icebreaker ships and LNG transport vessels cruise in the Arctic. (REUTERS/Olesya Astakhova)
Not so now. With sea lanes open much longer than ever before and competition over natural resources in full swing, the potential for a confrontation between the big powers, and their air and naval forces, is growing ever more likely.
Jens Stoltenberg, the secretary general of NATO, recently voiced such concerns over the mounting Russian and Chinese military presence in the region at the same time as US forces are shifting strategic emphasis toward the Arctic.
To sum up, climate change is upsetting both the environmental and strategic balance of the Arctic, with far-reaching ramifications for the hydrocarbon economy, maritime trade — and perhaps even peaceful coexistence.
_________
• Cornelia Meyer is a Ph.D.-level economist with 30 years of experience in investment banking and industry. She is chairperson and CEO of business consultancy Meyer Resources. Twitter: @MeyerResources





















