IRBIL, IRAQI KURDISTAN: With the evidence available, independent analysts are hesitant to pin the blame on any specific group for Monday’s rocket strike on Irbil in Iraqi Kurdistan. But what they all agree on is that both the timing and nature of the attack, which principally targeted a base in the city’s airport hosting US military personnel, strongly suggest that it was the handiwork of one or more Iran-backed militias.
According to reports, a volley of approximately 14 rockets hit Irbil international airport and nearby residential areas, killing a civilian contractor and injuring up to nine people. Clips of the incident quickly flooded social media and prompted an extended debate on Twitter among defense analysts over the correct course of US action in the situation.
David Pollock, Bernstein Fellow at the Washington Institute, pointed out that the Saraya Awliya Al-Dam, the self-proclaimed Shiite militia that has claimed responsibility for the attack, has threatened via the Telegram messaging app more operations targeting what it calls the “American occupation” of Iraq.
“Iran has officially denounced the attack, but that’s just the usual propaganda,” Pollock told Arab News while emphasizing the fact that the culprits have yet to be identified. He added: “The Iranians may actually support (the attack) to pressure the US to leave Iraq, in line with all their other threats.”
The autonomous Kurdistan Region has long been viewed as a distinctly stable and secure area compared with other parts of Iraq. However, incidents such as the Feb. 15 attack could change international perception of the region.
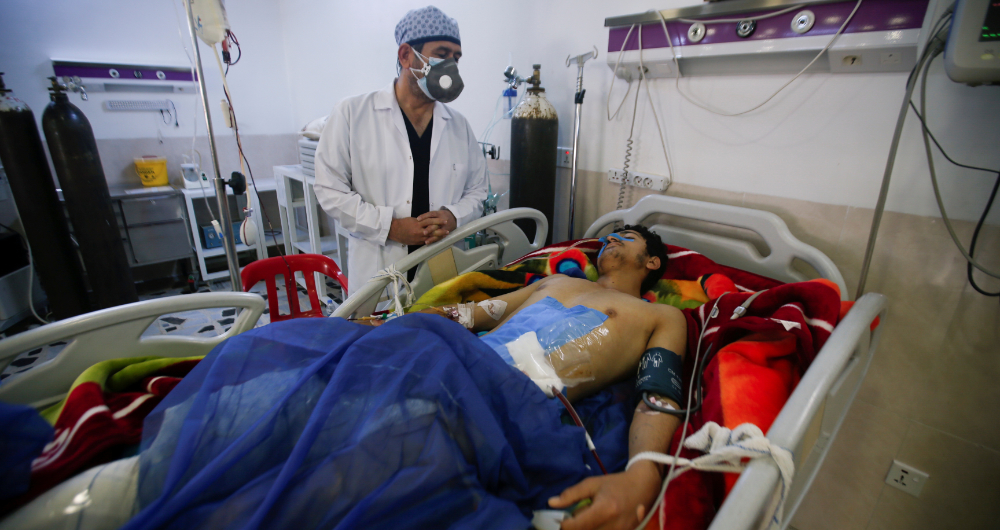
A volley of approximately 14 rockets hit Irbil international airport and nearby residential areas, killing a civilian contractor and injuring up to nine people. (Reuters)
The Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) is all too aware of this possibility. “Our concern is primarily due to the fact that Kurdistan is not used to this kind of attacks and instability,” Safeen Dizayee, head of the Foreign Relations Department of the KRG, told Arab News.
“Kurdistan has been renowned for its stability; coexistence; economic and political development; and prosperity. Therefore, when such incidents occur, it is of concern to the community, to the government, and to all those who live here, and also to our friends elsewhere.”
Dizayee asserted that the relevant department of the KRG will “continue to provide utmost security and will work hard to find the culprits and perpetrators of this attack, as well as those who we believe are responsible for the last couple of attacks.”
At the same time, he stressed the importance of stronger cooperation between KRG and federal security forces for the prevention of such incidents in the future.
Significant security gaps between the federal forces’ positions and the Kurdish Peshmerga in disputed territories, such as Kirkuk and Sinjar, have been known to exist since late 2017. Daesh and other actors, whom Dizayee described as “loose guns who behave outside the control of the state,” have exploited these gaps.
Among the actors in question are militias that operate under the broad umbrella of the Iraqi state-sanctioned and predominantly Shiite Hashd Al-Shaabi (PMF), but whose loyalty primarily is to Iran and its interests in Iraq. These groups have used attacks against American troops repeatedly in recent years ostensibly as a pressure tactic to force a US military pullout from Iraq.
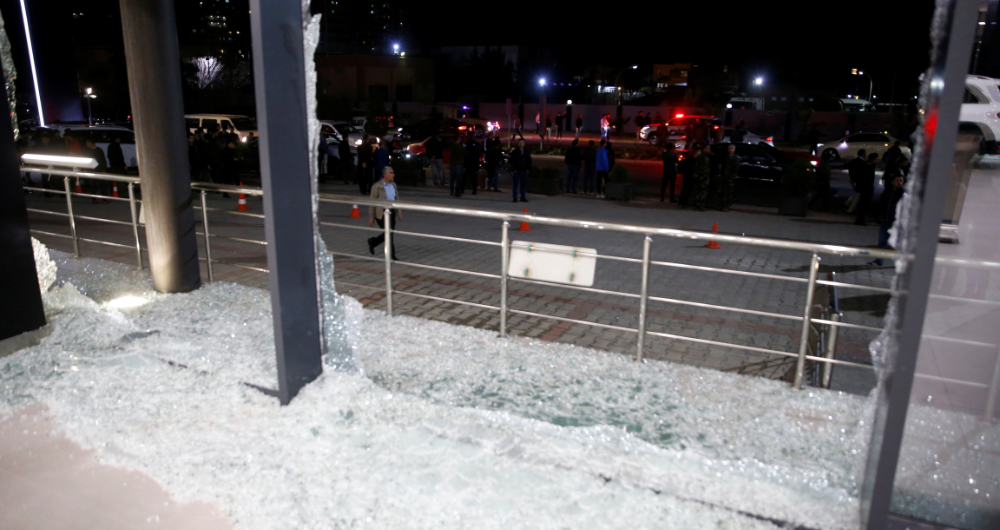

Some security analysts have questioned why the US has reacted angrily to the targeting of its forces, yet has neither announced nor taken any retaliatory action. (Reuters)
Pollock believes that tensions in the security gaps between the Kurdish Peshmerga and the PMF in “seam” areas around Kirkuk and Sinjar are “probably part of the story.”
“It’s noteworthy that many high-level statements from various KRG, UN and Iraq government officials now repeat calls for better security coordination in those places,” he said.
Some security analysts have questioned why the US has reacted angrily to the targeting of its forces, yet has neither announced nor taken any retaliatory action. But Pollock says that in any event, the Irbil attack will serve “to strengthen US resolve to stay in Iraq, including Kurdistan.”
His views are echoed in part by Nicholas Heras, director of government relations at the Institute for the Study of War in Washington D.C., who believes it is “within character” for Iran-backed groups to want to test US resolve through attacks.
In addition, Heras suspects that the latest attack could be a warning from the powerful Iraqi Kata’ib Hezbollah militia, which has targeted American troops in Iraq in the past, to the KRG against cooperating with Turkey.
“How much Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) controls these shadowy militias, or even a group like Kata’ib Hezbollah, is a point of strong disagreement among analysts,” he told Arab News.
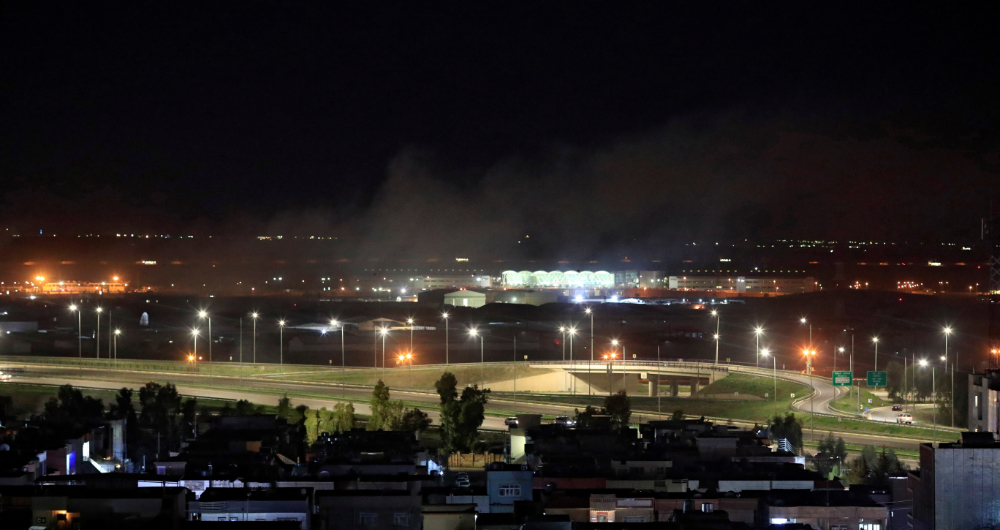

Osamah Golpy thinks the fact that the rockets were launched from a location close to Irbil and struck residential areas for the first time suggests that Iran-backed militias believe that US military personnel in Iraq are increasingly relocating to the Kurdistan region. (Reuters)
He said some analysts believe that following the US elimination of the Quds Force commander Qassem Soleimani in January 2020, the IRGC has had trouble keeping the shadowy armed groups under its control.
But others think that these groups are merely a front for Kata’ib Hezbollah and Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, providing them the “plausible deniability” they need to harm US interests in Iraq with impunity.
Still other analysts believe that “the ecosystem of Kata’ib Hezbollah groups in Iraq is all just different heads of the hydra, with the body being the IRGC,” Heras told Arab News.
Osamah Golpy, a senior editor at the Rudaw Media Network in Irbil, says that while Iran may not have directly orchestrated the attack on Irbil, this is something it wanted to happen. He cites a Kurdish proverb that he says sums up Tehran’s position: “I wish it happens (I wholeheartedly want it to happen), but not at my hands.”
He pointed out that a media network close to the IRGC recently released a video clip with an actor depicting Kurdish leader Masoud Barzani as helplessly weak in the face of Daesh’s threat to Irbil in 2014, only to be saved by a heroic Soleimani. The KRG has denounced the video.
Tehran claimed that that the video did not necessarily represent its view, even though Iran’s media is strictly censored and heavily controlled by the regime.
“I believe we should look at the attacks within the same framework,” Golpy told Arab News. The scenario he describes is one in which Iran’s authorities officially deny having any links to the groups launching the rockets even though they are aware of who they are and their intentions.
Golpy also does not rule out the possibility that Iran is directing some of these groups’ actions through the Quds Force, which is one of five IRGC branches specializing in unconventional warfare and military intelligence operations.
In his opinion, the fact that the rockets were launched from a location close to Irbil and struck residential areas for the first time suggests that Iran-backed militias believe that US military personnel in Iraq are increasingly relocating to the Kurdistan region.
Put simply, Golpy says, the militias are seeking to “create an atmosphere here in Irbil similar to the one they created in Baghdad.”
Twitter: @pauliddon
















