BEIRUT: After the French entered Lebanon in 1920 after the declaration of the State of Greater Lebanon, they reconfigured the capital Beirut to conform to the new political order.
Among the most visible transformations was the introduction of identity cards for residents, a move that sought to establish a Lebanese entity separated from other Arab states.
In 1921, the French mandate authorities conducted the first census of the Lebanese population, and on the basis of this the Lebanese were granted a new identity card in place of Ottoman tickets. The census was boycotted by those who refused to separate from Syria and recognize the new state.
The streets of Beirut, which were under Ottoman rule for more than four centuries, were referred to as haraat (alleyways).

The alleys were named after the families that inhabited them, leaders and princes, or even sects. The city’s markets were named after the professions found in them, according to the records of the Sharia court in Beirut.
The French mandate authorities, however, changed the names after modifying the city’s architecture. Twenty-meter streets were paved to connect the capital’s neighborhoods and make life easier. And while the neighborhoods preserved the names of the families that lived in them, such as Al-Barbir, Al-Bashoura, Karm Al-Zaitoun, Zaroub Saba and Zaroub Al-Arawi, the mandate left its mark on modern streets by naming them after French generals and high commissioners who ruled Lebanon after the fall of Ottoman rule.
Although Lebanon won its independence in 1943, some prominent streets in Beirut still have the names of French generals who became famous during the two world wars.
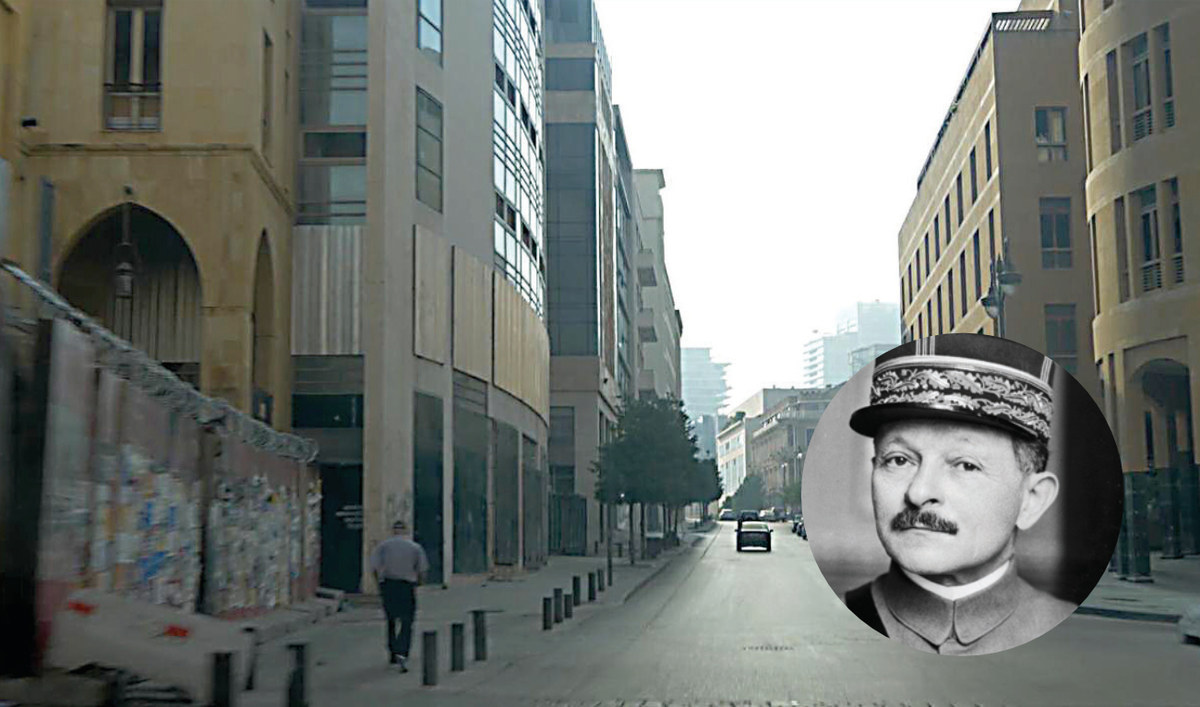
Rue Gouraud is a residential and commercial street in Gemmayzeh in the Achrafieh district of Beirut. It is one of the trendiest thoroughfares, full of fine restaurants, French cafes and jazz bars.
 General Henri Gouraud was the French high commissioner in Syria and Lebanon and army commander on the eastern side. Gouraud declared the State of Greater Lebanon from the porch of the Pine Residence in Beirut, and adopted the French military strategy known as “battle of annihilation.”
General Henri Gouraud was the French high commissioner in Syria and Lebanon and army commander on the eastern side. Gouraud declared the State of Greater Lebanon from the porch of the Pine Residence in Beirut, and adopted the French military strategy known as “battle of annihilation.”
General Gouraud, who led the French forces in the famous Battle of Maysalun, lived on this street in Beirut.
A parallel street, Rue Pasteur, was named after the famous French scientist Louis Pasteur. It is also a commercial street and features shops of Lebanese innovators. Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) was a French chemist and one of the most important founders of medical microbiology. His medical discoveries contributed to reducing the fatality rate of puerperal fever, and he prepared vaccines against rabies and anthrax. He was known to the general public for inventing a method for pasteurizing milk.
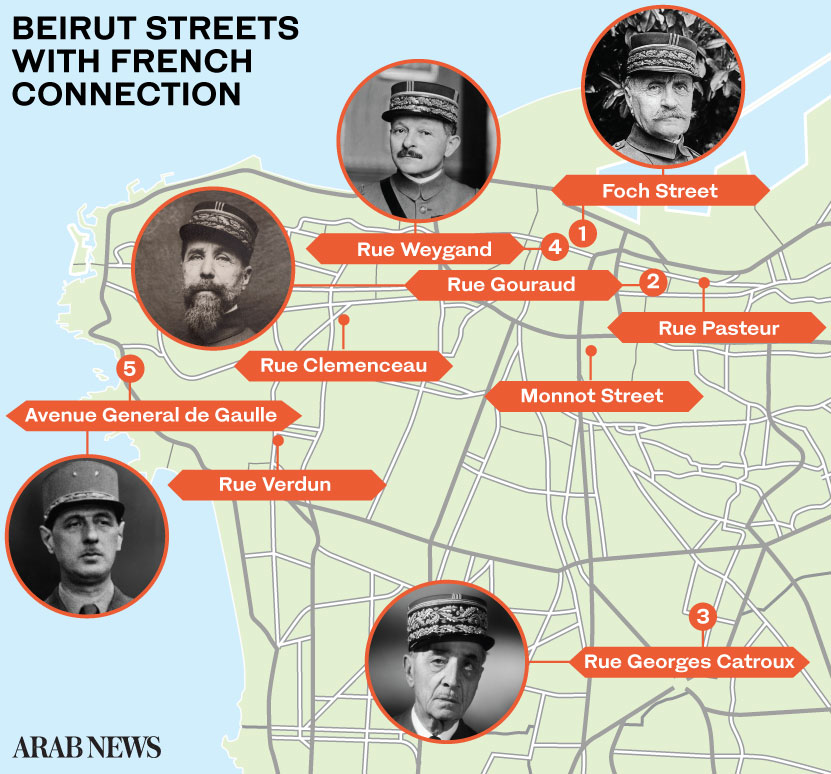
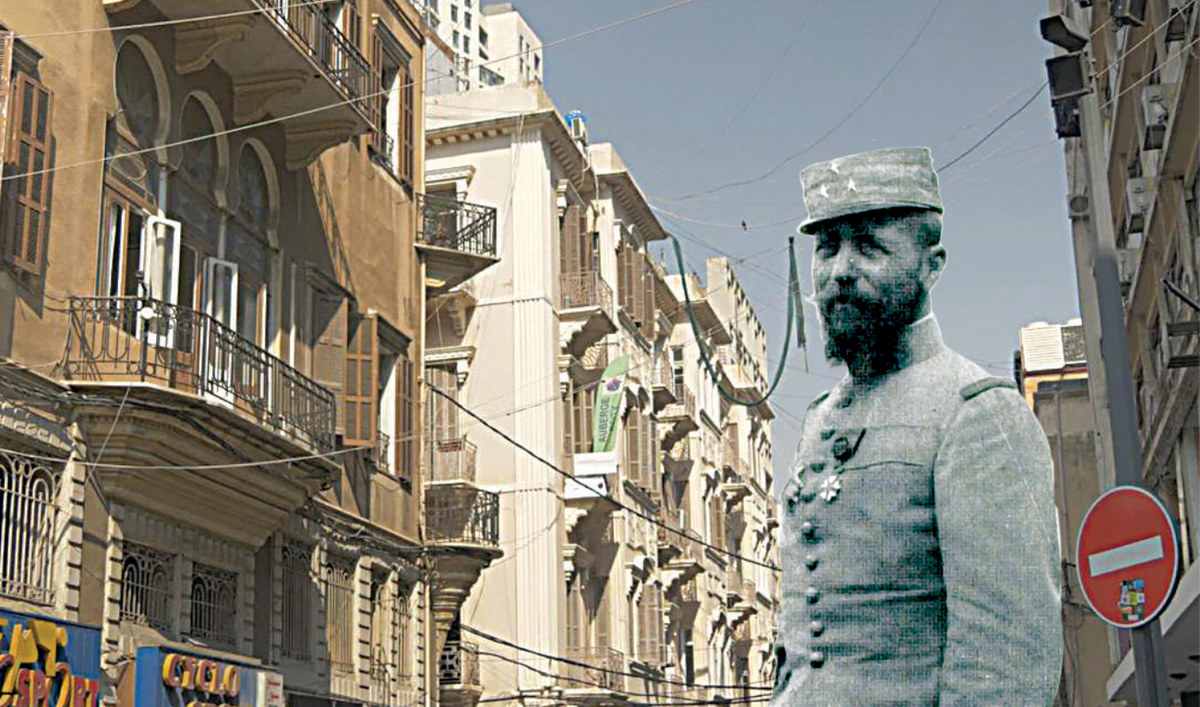
The street adjacent to Beirut Municipality, Rue Weygand, bears the name of Maxime Weygand, a high-ranking officer in the Mandate-era French Army. He was the second high military commissioner appointed by France to rule Syria and Lebanon, from April 1923 to Nov. 29, 1924. Weygand, who saw action in both the world wars, died in 1965.
Rue Georges Catroux is located in Beirut’s Badaro residential area. Catroux was a general in the French Army (1877-1969), a diplomat who served in World War I and II, and an adviser in the Legion of Honor.
Rue Clemenceau, located in Ras Beirut, is named after the French prime minister Georges Benjamin Clemenceau (1841-1929). He was a statesman, doctor and journalist who was elected twice to head the French government.
His first term was between 1906 and 1909, while his second was during the critical period 1917-1920 during World War I. One of the leading architects of the Treaty of Versailles, he was nicknamed Father of Victory and the Tiger.
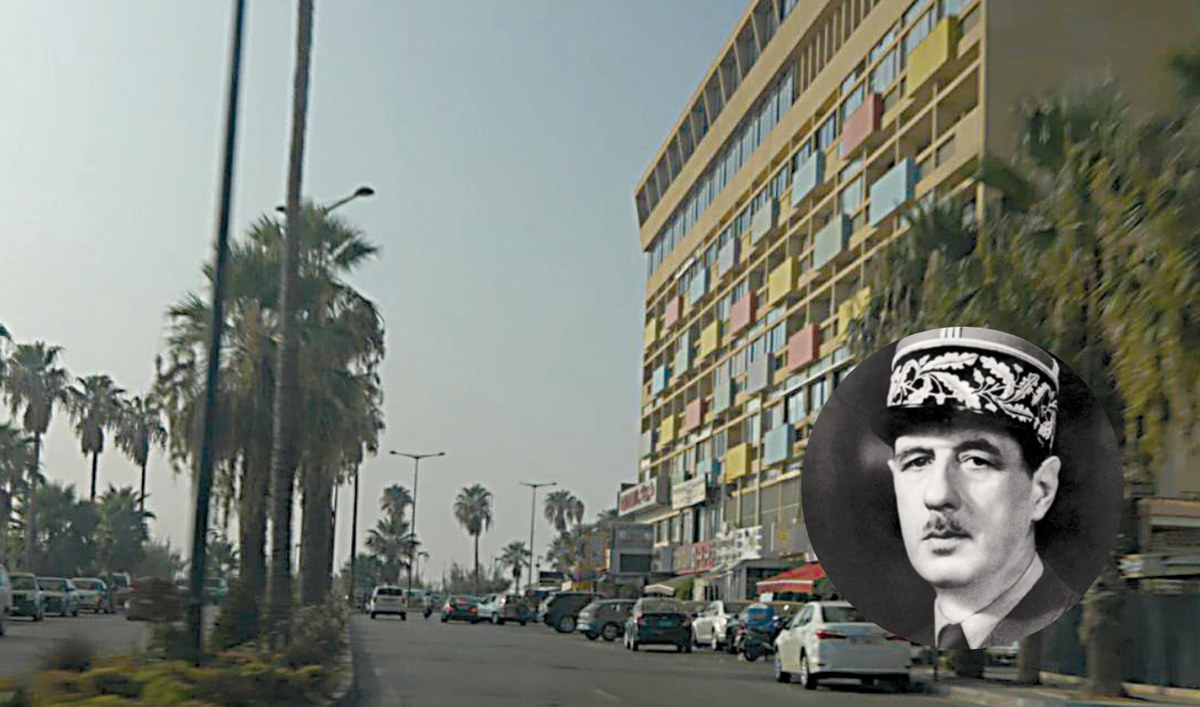

Avenue General de Gaulle (1890-1970) is the waterfront road of Beirut and named after the most prominent French figure during the Second World War. Charles de Gaulle lived in Lebanon for two years (1929-1931) when he was a major in the French army. He went on to serve as president of France.
Rue Verdun is one of the most high-end lively residential streets in Beirut. It has luxury retail stores, beauty and hair salons, and several cafes. In the center of the street is the Lycée Franco-Libanais school. The French St. Joseph School was situated on this street before it moved to a new location outside the capital. Although this street has been renamed after former Prime Minister Rashid Karami following his assassination in 1987, the name Verdun has remained popular.
Rue Verdun was so named in honor of the victims of the Battle of Verdun, which took place during World War I.
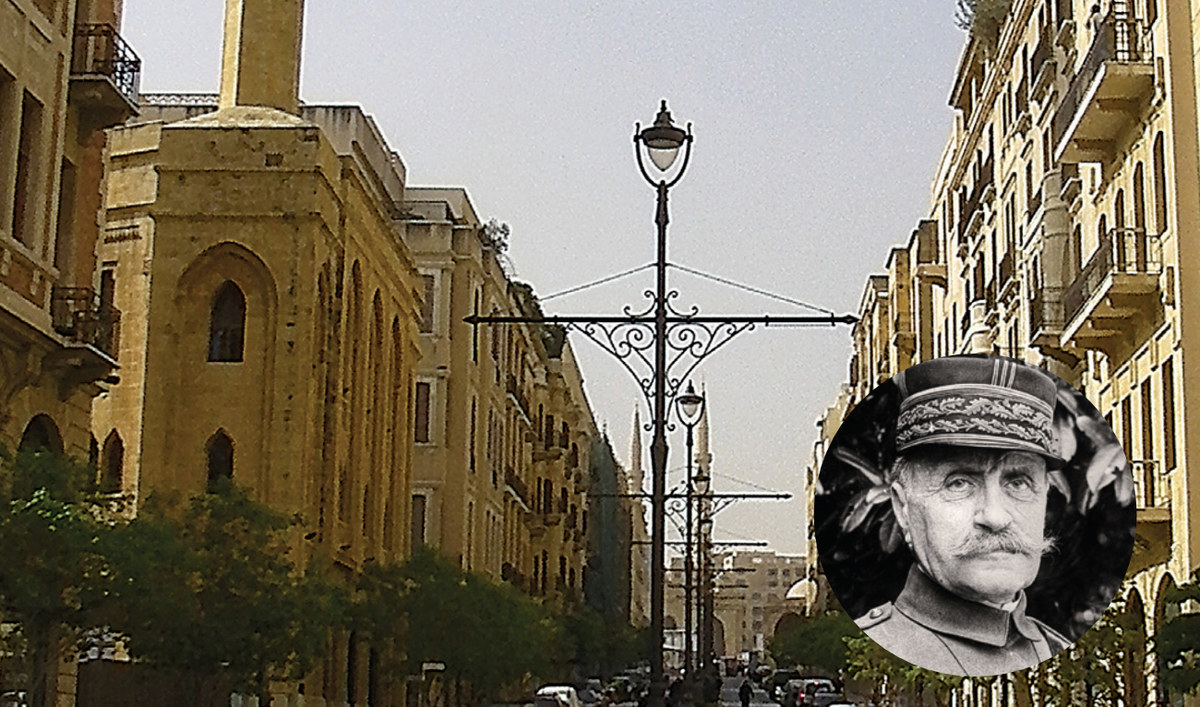

Foch Street, or Marshal Ferdinand Foch Street, is in the commercial heart of Beirut. Foch was a supreme Allied general in the World War I. One of Beirut’s streets was named after him following the Allies’ victory over the Germans.
Monnot Street, located on the eastern side of Beirut’s central district, is full of restaurants, bars and libraries. It hosts painters and creative events and holds concerts and plays in its famous theater, which is named after Father Ambroise Monnot, the head of the Jesuit mission to Lebanon in the late 19th century.
Father Monnot contributed to the establishment of schools and printing presses so that Lebanon could become a cultural and intellectual center in the Near East.
Twitter: @najiahoussari




















