BEIRUT: The conflict between Iran and the US that has created tensions throughout much of the Middle East is now also being felt in Lebanon, where Washington has slapped sanctions on the Iran-backed Hezbollah and warned they could soon expand to its allies, further deepening the tiny Arab country’s economic crisis.
The Trump administration has intensified sanctions on the Lebanese militant group and institutions linked to it to unprecedented levels, targeting lawmakers for the first time as well as a local bank that Washington claims has ties to the group.
Two US officials visited Beirut in September and warned the sanctions will increase to deprive Hezbollah of its sources of income. The push is further adding to Lebanon’s severe financial and economic crisis, with Lebanese officials warning the country’s economy and banking sector can’t take the pressure.
“We have taken more actions recently against Hezbollah than in the history of our counterterrorism program,” Sigal P. Mandelker, undersecretary for terrorism and financial intelligence at the US Treasury, said in the United Arab Emirates last month.
Mandelker said Washington is confident the Lebanese government and the central bank will “do the right thing here in making sure that Hezbollah can no longer have access to funds at the bank.”
Hezbollah, whose Arabic name translates into “Party of God,” was established by Iran’s Revolutionary Guard after Israel’s invasion of Lebanon in 1982. The group, which enjoys wide support among Lebanon’s Shiite community, runs institutions such as hospitals, clinics and schools — but it also has tens of thousands of missiles that Hezbollah’s leadership boasts can hit anywhere in Israel.
The group is designated as a terrorist organization by the United States, some Gulf Arab countries and few Latin American nations, while the European Union considers only Hezbollah’s military wing of the group to be a terrorist group.
Today, it is among the most effective armed groups in the Middle East with an arsenal more powerful than that of the Lebanese army, and has sent thousands of its fighters to Syria to back President Bashar Assad’s forces in that country’s civil war. Hezbollah and its allies have more power than ever in parliament and government and President Michel Aoun is a strong ally of the group.
Hezbollah has acknowledged the sanctions are affecting them, but it says it has been able to cope with sanctions imposed by the US for years. The group, however, warned that it is the job of the Lebanese state to defend its citizens when they come under sanctions simply because they belong to the group, are Shiite Muslims, or are Hezbollah sympathizers.
In July, the Treasury Department targeted two Hezbollah legislators, Amin Sherri and Mohammad Raad, in the first such move against lawmakers currently seated in Lebanon’s parliament. A month later, the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control sanctioned Jammal Trust Bank for what it called “knowingly facilitating banking activities.” The bank, which denied the charges, was forced to close afterward.
Neither Sherri nor Raad responded to requests for comment from The Associated Press.
So far, all the figures who have come under sanctions have been either Hezbollah officials or Shiite Muslim individuals who Washington says are aiding the group.
Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah said the group will “study well our alternatives” now that the US is targeting banks that Hezbollah does not own or deal with, as well as rich individuals and merchants simply because of their religious affiliation.
“We said it in the past that when we are subjected to injustice we can be patient, but when our people are subjected to injustice we should behave in a different way,” he said.
Nasrallah said the state and the government should defend Lebanese citizens. In an apparent reference to the Lebanese central bank that implements US sanctions, Nasrallah said: “Some state institutions should not rush to implement the American desires and orders this way.”
Walid Marrouch, an associate professor of economics at the Lebanese American University, says Lebanon’s economy is 70% dollarized and since Lebanon is using this currency, Beirut has to abide by (US) laws.
“We’re already living in a crisis and it will only make it worse,” he said of sanctions and if Lebanon decides to stop abiding by US Treasury Department orders.
Antoine Farah, who heads the business section of the daily Al-Joumhouria newspaper, wrote that if Hezbollah’s desires turn out to be orders, “we will be facing a confrontation such that no one would want to be in our shoes.”
“If Hezbollah decides to fight America with the money of the Lebanese we guarantee a quick collapse and staying at the bottom for a long time, like Venezuela,” he wrote.
During a visit to Beirut, David Schenker, the US’s assistant secretary of state for near eastern affairs, said Washington will designate in the future “individuals in Lebanon who are aiding and assisting Hezbollah, regardless of their sect or religion.”
Schenker did not elaborate in his interview with local LBC TV but local TV stations said Washington could start targeting Christian allies of the militant group, which has 14 members in parliament and three Cabinet ministers, including the Health Ministry.
Health Minister Jamil Jabbak, who is not a member of Hezbollah but is believed to be close to the group’s leader, was not granted a US visa to attend the UN General Assembly in late September.
Treasury Assistant Secretary for Terrorist Financing Marshall Billingslea visited Lebanon last week and a US Embassy statement said he would “encourage Lebanon to take the necessary steps to maintain distance from Hezbollah and other malign actors attempting to destabilize Lebanon and its institutions.”
At the end of his visit, Billingslea met a group of journalists representing local media and told them that the US Treasury was posting a $10 million reward for anyone who provides “valuable information on Hezbollah’s finances,” according to the Daily Star.
He said the main goal of the US Treasury “was to deprive Hezbollah of all financial support, whether from Iran or through any other means.” Billingslea said Iran used to send the group $700 million a year, adding that US sanctions on Iran have “diminished considerably” the cash inflow.
Imad Marmal, a journalist close to Hezbollah who has a talk show on the group’s Al-Manar TV, wrote that the group wants the Lebanese state to put forward a national plan to face the “American siege” that will end up affecting not only Shiites but the country’s economy generally. He added that those who are being targeted by the sanctions are Lebanese citizens, whom the state should protect.
Hezbollah “is not going to scream in pain as the United States is betting, neither today nor tomorrow and not even in a hundred years.”
US sanctions squeezing Iran-backed Hezbollah in Lebanon
US sanctions squeezing Iran-backed Hezbollah in Lebanon

- The group is designated as a terrorist organization by the United States, some Gulf Arab countries and few Latin American nations, while the European Union considers only Hezbollah’s military wing of the group to be a terrorist group
- The Trump administration has intensified sanctions on the Lebanese militant group and institutions linked to it to unprecedented levels
US starts building Gaza aid pier

- It is expected to be operational in early May
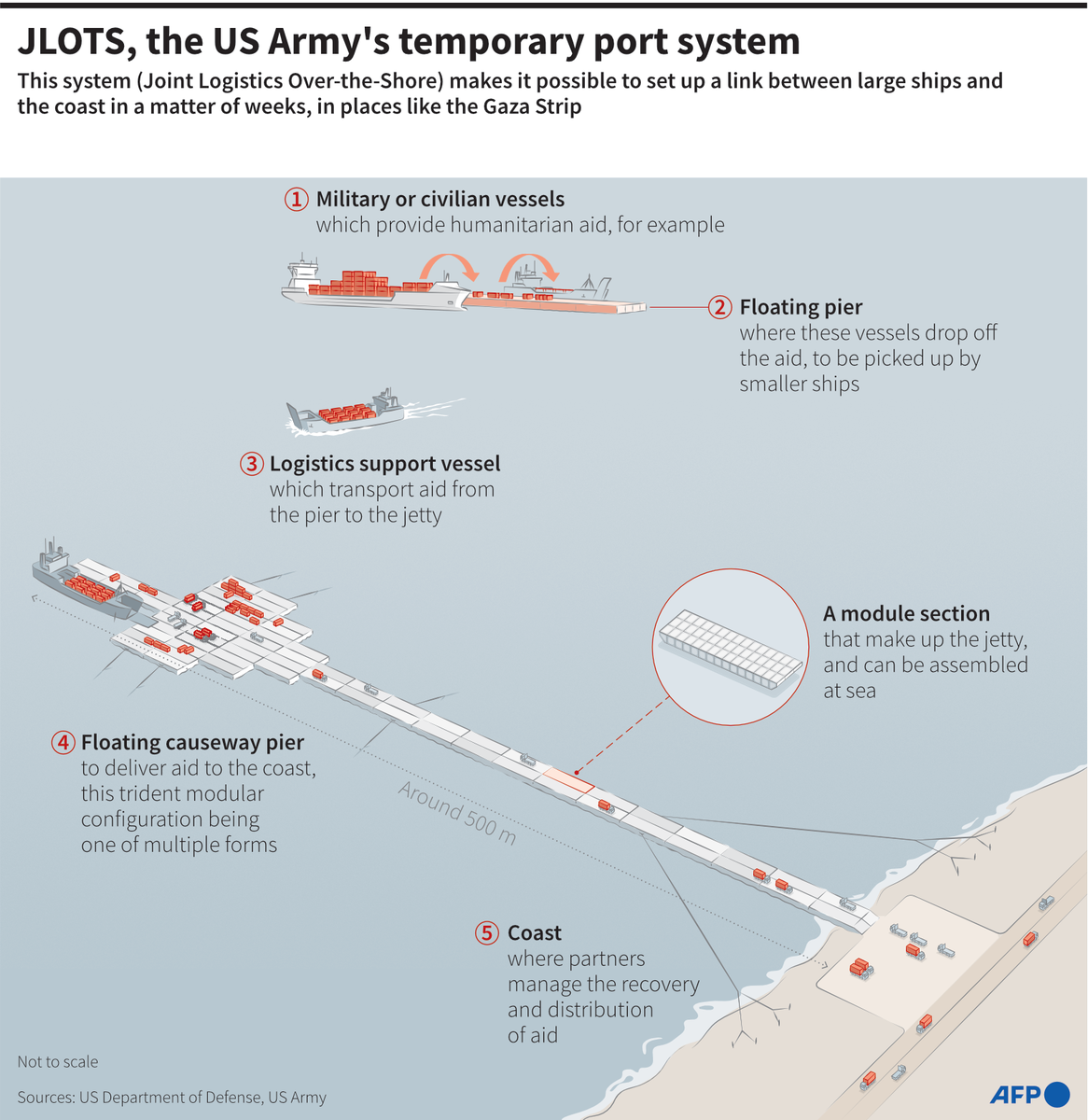
WASHINGTON: The US military has begun construction on a pier meant to boost deliveries of desperately needed aid to Gaza, the Pentagon said on Thursday.
The small coastal territory has been devastated by more than six months of Israeli bombardment and ground operations against Hamas militants, leaving the civilian population in need of humanitarian assistance to survive.
“I can confirm that US military vessels... have begun to construct the initial stages of the temporary pier and causeway at sea,” Pentagon spokesman Major General Pat Ryder told journalists.
Indications are that the pier will be operational in early May, and “everything is on course at this point,” he said.
Highlighting the dangers in Gaza, Ryder said that “some type of mortar attack” caused minimal damage near an onshore area that will eventually be a delivery site for aid.
The Israeli defense ministry body responsible for Palestinian civil affairs said militants fired mortars Wednesday at a humanitarian work site in northern Gaza during a visit by UN personnel, with no casualties reported.
A senior US military official told journalists that “we don’t assess that the attack had anything to do with the (aid pier) mission or delivery of humanitarian assistance from the sea.”
The military official also outlined how the maritime aid delivery process will work, saying assistance will first come into Cyprus, where it will be screened and prepared for delivery.
Aid will then be loaded onto commercial vessels for transportation to a floating platform miles off the coast of Gaza. There, it will be transferred to smaller vessels that will take the assistance to a pier that is anchored to the shore.
Trucks will then drive the aid down the platform, where a distribution partner will take it into Gaza, the official said, noting that initial operating capacity will be 90 trucks of assistance per day, later rising to 150 trucks a day.
The senior military official reiterated that there will be no US “boots on the ground,” saying an Israeli military unit will be responsible for anchoring the pier to the shore.
A senior US administration official said that the US Agency for International Development “will partner with UN organizations to deliver the life-saving aid once it gets to Gaza through the maritime corridor.”
The official painted a dire picture of the situation in Gaza and the urgent need for aid, saying “the entire population of Gaza — 2.2 million people — is facing acute food insecurity.”
“More than half of the population in northern Gaza is facing catastrophic levels of food insecurity,” while “in southern Gaza, nearly a quarter of the population is facing this kind of catastrophic food insecurity,” the official said.
Hamas official says Israel ‘will not achieve’ goals in Rafah

- “Even if (Israel) enters and invades Rafah, it will not achieve what it wants,” Ghazi Hamad said
- “This will undoubtedly threaten the negotiations because it is clear from this declared position that Israel is interested in continuing the war“
GAZA STRIP, Palestinian Territories: A senior Hamas official told AFP on Thursday that Israel would fail to meet its stated goals of defeating the Palestinian militant group and freeing hostages by invading the southern Gaza city Rafah.
“Even if (Israel) enters and invades Rafah, it will not achieve what it wants,” Ghazi Hamad said in an interview over the phone from Qatar, where a number of senior figures from Hamas’s political bureau are based.
Hamad said Israel had “spent nearly seven months in Gaza and invaded all areas and destroyed a lot, but so far has not been able to achieve anything of its main goals, whether eliminating Hamas or returning the captives.”
Israel has vowed to move on with the planned military operation in Rafah, despite international outcry and concern for about 1.5 million Palestinians sheltering in the city.
There are fears of huge civilian casualties and countries including Israel’s top ally and weapons supplier the United States have warned Israel against sending troops into Rafah.
“We have spoken with all parties involved in the conflict... about the seriousness of invading Rafah and that Israel is heading toward committing additional massacres and additional genocide,” Hamad said.
“This will undoubtedly threaten the negotiations because it is clear from this declared position that Israel is interested in continuing the war and aggression and has no intention of continuing negotiations and reaching an agreement,” he said.
Qatar, the United States and Egypt, have been mediating talks to secure a truce and the release of hostages, but those have stalled for days.
An Egyptian delegation is however set to travel to Israel on Friday to kickstart a new round of talks, Israeli media reported citing unnamed officials.
Israeli government spokesman David Mencer said Israel’s war cabinet was meeting Thursday “to discuss how to destroy the last battalions of Hamas.”
On Wednesday, Mencer said that since Israel began its ground invasion of Gaza on October 27, the army has destroyed “at least 18 or 19 of Hamas’s 24 battalions.”
Officials say the remaining battalions are in Rafah — the main target of the impending assault.
Most Gazans taking refuge in Rafah are sheltering in makeshift camps, and even before the start of the expected ground invasion, the city near the Egyptian border has been suffering regular Israeli bombings.
Hamad argued the planned invasion was exposing contradictions in Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s stance on Gaza.
“Netanyahu is stumbling because, on the one hand, he wants to return the captives to their families, as he says, but at the same time, he puts them in great danger, as his army deliberately killed many hostages.”
Israel’s army has admitted to mistakenly killing some hostages in Gaza.
Hamad accused Netanyahu of “manipulating and procrastinating” in a bid to “deceive the Israeli public that there are negotiations and deceive the international community as well that there are negotiations.”
He said the Israeli prime minister was “trying to twist the truth” and claim that “Hamas is the obstacle in these negotiations.”
Hamad said Qatar and Egypt were “making great efforts to reach an agreement,” but argued “the Israeli side unfortunately deals with the matter foolishly and is very confused.”
Hamad also told AFP that Hamas, which took power in Gaza in 2007, was already working on plans for the territory after the war.
He said the group was “working on the post-war phase to ensure that there is a great effort to rebuild the Gaza Strip and provide the necessities for a decent life.”
Palestinian militants took around 250 hostages to Gaza during Hamas’s October 7 attack that triggered the war.
Israeli officials say 129 hostages are still held in Gaza, including 34 the military says are dead.
The attack on southern Israel resulted in the deaths of 1,170 people, Israelis and foreigners, according to an AFP tally based on official Israeli figures.
Israel’s retaliatory offensive against Hamas in Gaza has killed 34,305 people, most of them women and children, according to the territory’s health ministry.
Shawarma restaurant in Cairo brings taste of home for displaced Palestinians

CAIRO: A Palestinian businessman displaced by the war in Gaza is bringing a taste of home for fellow refugees with a shawarma restaurant he has opened in Cairo.
“The Restaurant of Rimal Neighborhood” offers shawarma, a Middle Eastern dish of thinly sliced meat, and other Palestinian and Arab dishes.
“The name comes to eternalize Rimal, my neighborhood, and my homeland too,” said Basem Abu Al-Awn.
“It is also to replace the restaurant I once had in Gaza. Two restaurants of mine, in addition to my house and the houses of my relatives, were destroyed,” he said.
Abu Al-Awn hopes his time outside Gaza will be temporary, and he is determined to return to the enclave once the war between Israel and Hamas is over.
“I will return, even if I have to set up a tent near the rubble of my house. We are going back to Gaza, and we will rebuild it,” he said.
Rimal was Gaza City’s busiest shopping center, with large malls and main bank offices before Israeli forces reduced most of it to rubble.
It was also home to Gaza’s most famous shawarma places.
“The taste is the same. People tell us it tastes as if they are eating it in Gaza,” said Ahmed Awad, the new restaurant’s manager.
“The Egyptians who get to try our place keep coming back. They tell us the taste is nice and is different from the shawarma they usually get,” Awad said.
Gaza shawarma spices are unique and scarce in Cairo, so credit goes to Awad’s father, who mixes those available to give the dish a special Palestinian taste.
Many thousands of Palestinians have arrived in Gaza since the war began last October.
Awad, his wife, and four children arrived in Cairo three months ago.
In Gaza, he used to work in restaurants specializing in oriental and Western dishes.
With an end to the war looking like a distant prospect, Awad urged Palestinians not to give up.
“I advise them to work and take care of their lives. Their houses and everything may have gone, but no problem; it will come back again,” he said.
“Once things are resolved, we will return home, work there, and rebuild our country.”
Palestinians now stranded in Cairo include businessmen, students, and ordinary families who say they seek temporary legal residency to pursue investment and study plans until a ceasefire is in place.
Om Moaz, from Rafah in the southern Gaza Strip, had been struggling to pay for a rented house and treatment for her husband and daughter in Cairo. She began working from home, offering Palestinian food through social media.
She found there was a strong demand from both Egyptians and Palestinians.
“Some were in the war and came to Egypt. So they started ordering my food. And thank God, it’s a successful business, and hopefully, it continues,” she said.
‘Let’s help Yemen regain ability to chart its own future,’ US envoy Tim Lenderking tells Arab News

- Lenderking says it would be a ‘terrible tragedy’ to squander progress in Yemen peace process amid ‘competing crises’
- US envoy calls on Iran to stop fueling the conflict in Yemen and halt smuggling weapons to the Houthi militia
NEW YORK CITY: Houthi attacks on international shipping in the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden in response to Israel’s military offensive against Hamas in Gaza must not derail the peace process in Yemen, Tim Lenderking, the US special envoy for Yemen, has said.
Since the war in Gaza began in October last year, attacks by the Houthis on commercial and military vessels in the strategic waterways have caused significant disruption to global trade.
The Iran-backed armed political and religious group, formally known as Ansar Allah, views itself as a part of the Iranian-led “Axis of Resistance” against Israel, the US and the wider West.
It has threatened to continue its attacks on vessels until Israel ends its assault on Gaza. Since January, the UK and the US, in coalition with five other countries, have responded with retaliatory strikes against Houthi targets in Yemen.
The US will halt these retaliatory strikes when the Houthi militia stops its attacks on shipping, Lenderking told Arab News in an interview, placing responsibility for de-escalating the situation in the militia’s hands.

“The onus (is) on the Houthis to stop the Red Sea attacks,” he said. “That can prompt us all to begin to dial back, to de-escalate, to return the situation in Yemen to where it was on Oct. 6, which had considerably more promise and possibility than what exists now, and that’s where we want to return the focus.”
Lenderking called on Iran to “stop fueling the conflict (and) stop smuggling weapons and lethal material to Yemen, against UN Security Council resolutions.”
Yemen had never been so close to peace before the process was derailed by the latest regional turmoil, said Lenderking. The Yemeni civil war has gone on too long, he said: “It must stop.”
“The Yemeni people (have) suffered from this war for eight years now. They want their country back. They want their country (to be) peaceful. They don’t want foreign fighters in Yemen. They don’t want the Iranians in Sanaa. They don’t want the IRGC, the (Islamic) Revolutionary Guard (Corps) wandering around in Sanaa.
“Let’s help Yemen regain its country and its ability to chart its own future. That’s what the US so, so dearly wants.”
He added: “We’re trying very hard to marshal and maintain an international effort to keep the focus on Yemen’s peace process, on the very critical humanitarian situation.
“But look at what’s crowding us out: Terrible tragedy unfolding in Gaza. Russia’s war in Ukraine. Afghanistan. Sudan. There are many competing crises that are dominating the attention of the US and the international community.”

While the war in Yemen is linked to other conflicts raging in the region, the UN has recently said the world owes it to the Yemenis to ensure that resolving the war in Yemen is not made contingent upon the resolution of other issues, and that Yemen’s chance for peace does not become “collateral damage.”
“We cannot escape what’s happening in Gaza,” said Lenderking. “Not one single day goes by when the people I talk to about Yemen don’t also talk about Gaza. So we know this is a searing and very, very important situation that must be dealt with.
“This situation is holding up our ability to return the focus to the peace process in Yemen, to take advantage of a road map that was agreed to by the Yemeni government and by the Houthis in December, and get the Houthis to refocus their priorities not on Red Sea attacks — which are hurting Yemenis by the way, hurting Yemen — but to the peace effort in Yemen itself.”
Speaking during a UN Security Council briefing last week, Hans Grundberg, the UN envoy for Yemen, said the threat of further Houthi attacks on shipping persists in the absence of a ceasefire in Gaza — the urgent need for which was underscored by the recent escalation in hostilities between Israel and Iran.
Lenderking said: “We continue to hear from the Houthis that these (two) issues are linked and that (the Houthis) will not stop the attacks on Red Sea shipping until there’s a ceasefire in Gaza.

“We believe there’s essential progress that could be done now. There are 25 members of the Galaxy Leader crew, the ship that was taken by the Houthis on Nov. 19 last year, still being held.
“They’re from five different countries. There is no reason why these individuals, who are innocent seafarers, are being detained in Hodeidah by the Houthis. Let them go. Release the ship. There are steps that could be taken. We could continue working on prisoner releases.
“These kinds of things will demonstrate to the Yemeni people that there’s still hope and that the international community is still focused on their situation.”
Lenderking said it would be a “terrible tragedy” to squander the progress toward peace that had been made in the previous two years.
A truce negotiated in April 2022 between the parties in Yemen had initially led to a reduction in violence and a slight easing in the dire humanitarian situation in the country. Two years on, the UN has lamented there is now little to celebrate.
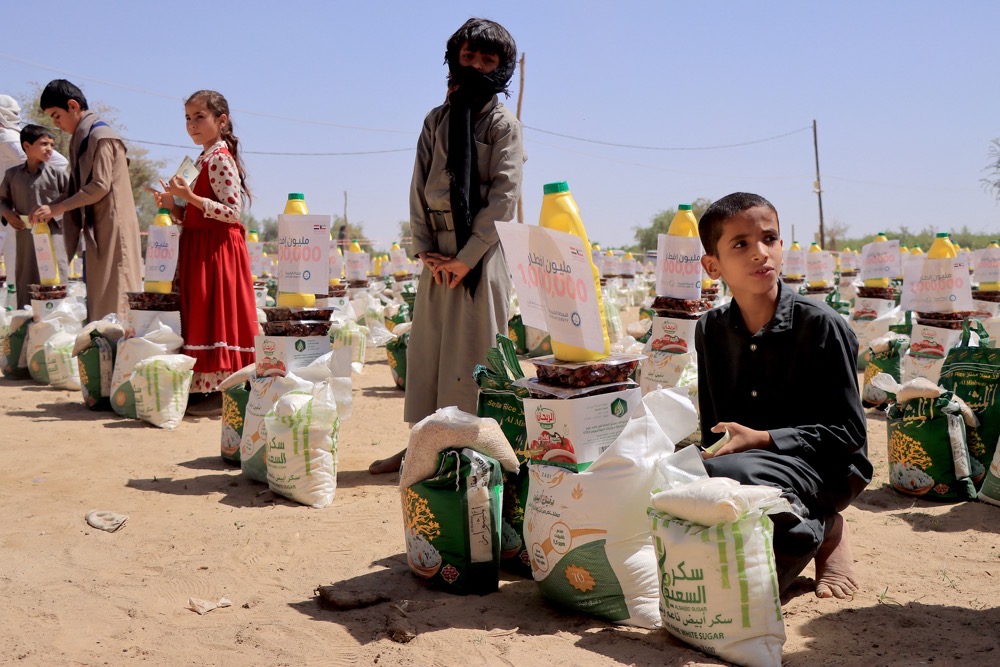

“Detainees we had hoped would be released in time to spend Eid with their loved ones remain in detention,” said UN envoy Grundberg. “Roads we had hoped to see open remain closed.
“We also witnessed the tragic killing and injury of 16 civilians, including women and children, when a residence was demolished by Ansar Allah (Houthi) individuals in Al-Bayda governorate.”
The humanitarian situation in Yemen has also become markedly worse in recent months amid rising food insecurity and the spread of cholera.
Edem Wosornu, director of operations and advocacy at the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, told the Security Council in the same briefing that the situation had deteriorated further after the World Food Programme suspended the distribution of food aid in areas controlled by the Houthis in December 2023.
This pause followed disagreements with local authorities over who should receive priority assistance and was compounded by the effects of a severe funding crisis on WFP humanitarian efforts in Yemen.
“The most vulnerable people — including women and girls, marginalized groups such as the Muhamasheen, internally displaced people, migrants, asylum seekers and refugees, and persons with disabilities — still depend on humanitarian assistance to survive,” said Wosornu.
Wosornu also voiced concern about an increase in cases of cholera in Yemen amid the deterioration of public services and institutions.
“The re-emergence of cholera, and growing levels of severe malnutrition, are telling indicators of the weakened capacity of social services,” she said.
“Almost one in every two children under five are stunted, more than double the global average: 49 percent compared to 21.3 percent.
“Emergency stocks of essential supplies are almost depleted. And water, sanitation and hygiene support systems need urgent strengthening.”
The humanitarian response plan for Yemen is only 10 percent funded, with funding for its food security and nutrition programs standing at just 5 percent and 3 percent respectively, according to an informal update presented to the Security Council by the OCHA this week.

Wosornu appealed to the international community to take urgent action to help fill the funding gaps.
Commenting on the funding shortage, Lenderking said: “When there’s a genuine possibility of a Yemen peace process, donors will take note of that and respond. But the fact that we’re in this limbo, where the peace process is on hold while the Houthi is continuing these attacks (in the Red Sea), that I think is to be blamed on the Houthis because they’re derailing what was a legitimate peace process.
“But once we can get back to that, I think we could call on the international community to say, look, there is a ray of hope. There is a process. There is a commitment. The US is supporting an international effort. We can get the donors to come back to Yemen, despite all of the competition for these very scarce resources.”

British Royal Navy shoots down missile for first time since Gulf War in 1991 amid Houthi attacks on shipping
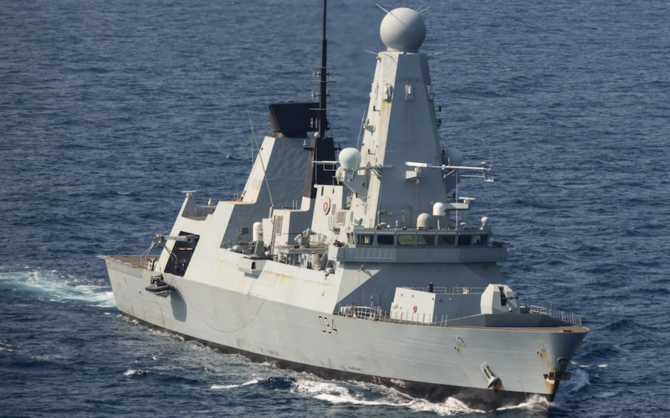

- Iran-backed group said its missiles targeted US ship Maersk Yorktown, an American destroyer in the Gulf of Aden and Israeli ship MSC Veracruz
LONDON: A British Royal Navy destroyer shot down a ballistic missile on Wednesday for the first time since the first Gulf War in 1991, the UK’s defense secretary told The Times newspaper.
In a report published Thursday, Grant Shapps told the newspaper that HMS Diamond used its “Sea Viper” missile system to target the weapon, which Yemen’s Houthi militia said they used to target two American ships in the Gulf of Aden and an Israeli vessel in the Indian Ocean.
The Iran-backed group said its missiles targeted US ship Maersk Yorktown, an American destroyer in the Gulf of Aden and Israeli ship MSC Veracruz in the Indian Ocean, its military spokesman Yahya Sarea confirmed.
It is the first such attack from the Yemeni militia in two weeks in the region, where Royal Navy Type 45 destroyers have been deployed to protect commercial ships since the Houthis initiated strikes on global shipping in November last year in solidarity with Palestinians in Gaza.
“The Yemeni armed forces confirm they will continue to prevent Israeli navigation or any navigation heading to the ports of occupied Palestine in the Red and Arabian Seas, as well as in the Indian Ocean,” Sarea said on Wednesday.
Shapps said the latest Houthi attack was an example of how dangerous the world was becoming and how “non-state actors were now being supplied with very sophisticated weapons” from states such as Iran.
His comments came after UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak this week pledged to increase spending on British defense to 2.5 percent of national income, something Shapps said was “so vital” given continued tensions in the Middle East.