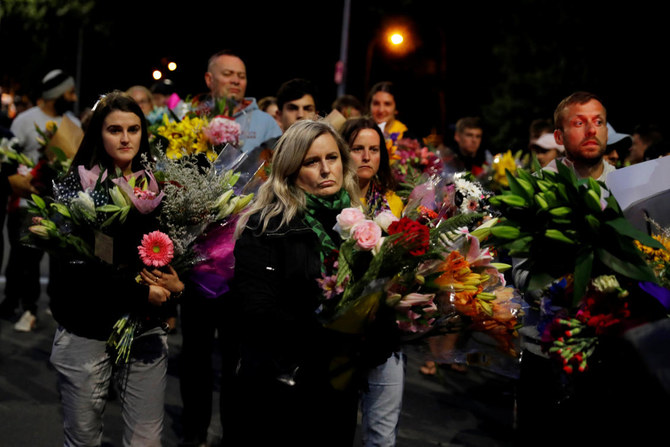CHRISTCHURCH: New Zealand’s stricken residents reached out to Muslims in their neighborhoods and around the country on Saturday, with a fierce determination to show kindness to a community in pain as a 28-year-old white supremacist stood silently before a judge, accused in mass shootings at two mosques that left 49 people dead.
Brenton Harrison Tarrant appeared in court amid strict security, shackled and wearing all-white prison garb, and showed no emotion when the judge read him one murder charge. The judge said “it was reasonable to assume” more such charges would follow. Tarrant, who posted an anti-immigrant manifesto online and apparently used a helmet-mounted camera to broadcast live video of the slaughter in the city of Christchurch, appeared to make a hand sign, similar to an OK sign, that is sometimes associated with white nationalists.
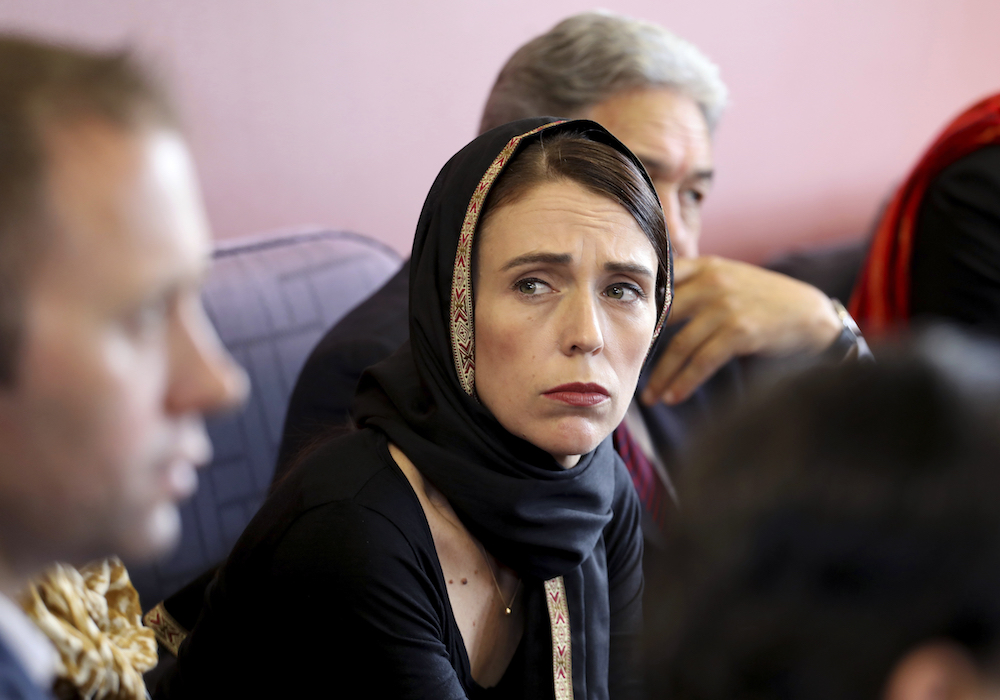

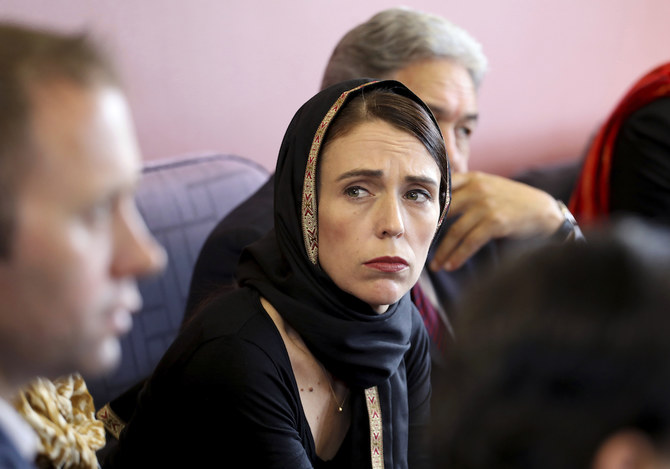
Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern meets representatives of the Muslim community in Christchurch. (AP)
The massacre during Friday prayers prompted a heartfelt response from Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern, who pronounced it “one of New Zealand’s darkest days” and said the shooter, an Australian native, had chosen to strike in New Zealand “because we represent diversity, kindness, compassion.”
Her fellow countrymen seemed to want to prove her right by volunteering acts of kindness. Some offered rides to the grocery store or volunteered to walk with their Muslim neighbors if they felt unsafe.
In online forums, people discussed Muslim food restrictions as they prepared to drop off meals for those affected.
*********
READ MORE:
Christchurch massacre proves terror has no color, faith or gender
The day peaceful, welcoming New Zealand lost its soul
Saudi man killed in New Zealand mosque attack
World reacts to New Zealand terrorist attacks on mosque
New Zealand mosque shooter a white nationalist seeking revenge
*********
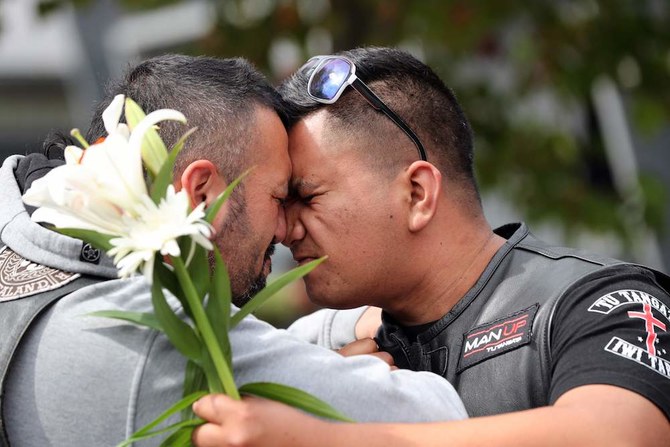
“Love always wins over hate. Lots of love for our Muslim brothers,” read a handwritten card on a wall of flowers in a historic part of the city that stretched a full block.
Still, Muslims were advised to stay away from mosques while the nation’s security alert remained at the second-highest level a day after the deadliest shooting in modern New Zealand history.
Ardern said 39 survivors remained hospitalized Saturday, with 11 critically wounded. But updates were slow to come, and many families were still waiting to hear whether their loved ones were among the victims.
Outside one of the two mosques, 32-year-old Ash Mohammed pushed through police barricades in hopes of finding out what happened to his father and two brothers, whose cellphones rang unanswered. An officer stopped him.
“We just want to know if they are dead or alive,” Mohammed told the officer.
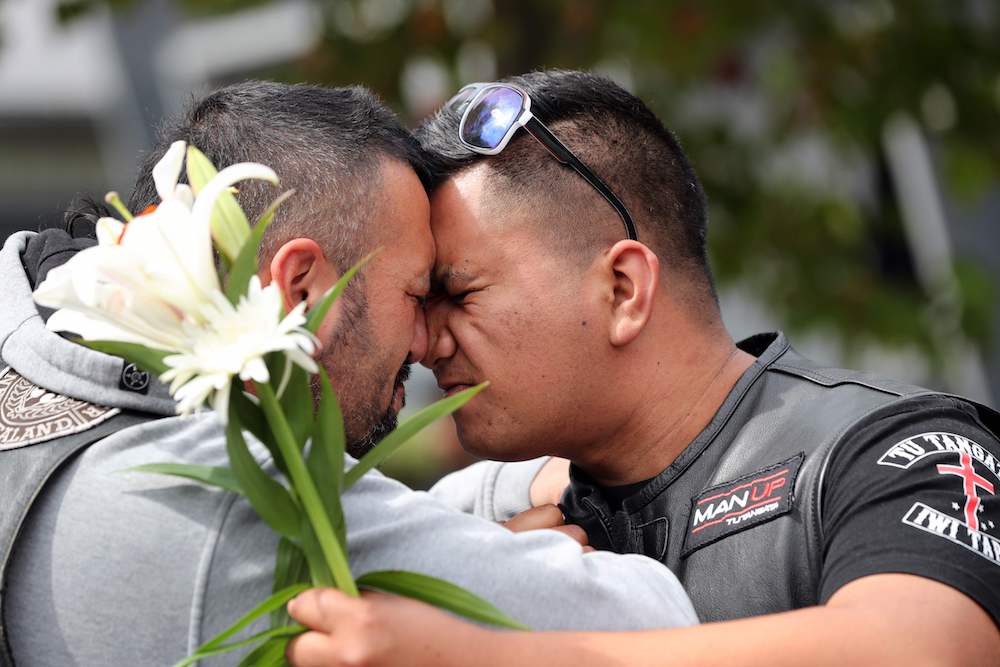

Residents pay their respect at Hagley College for the victims of the mosques attacks in Christchurch. (AFP)
Hungry for any news, families and friends of the victims gathered at the city’s Hagley College, near the hospital.
They included Asif Shaikh, 44, who said he was among more than 100 people at the Al Noor mosque when the attacker came in. He said he survived by playing dead, but was desperate to know what happened to his friends who were there with him.
“It’s been 36 hours, I haven’t heard anything about them,” he said.
Nearby, Akhtar Khokhur leaned on the shoulders of her friend and cried as she held up her cellphone with an image of her husband.
“I still don’t know where he is,” she said.
Khokhur, 58, and husband Mehaboobbhai Khokhur, 65, had traveled from India to spend time with their son Imran, their first visit in the eight years since he moved to New Zealand. The couple was due to fly out Sunday.
Imran had dropped off his father, an electrical engineer, at the Al Noor mosque on Friday and was looking for a parking space when the shooting began. They have not heard from him since.
The gunman had posted a jumbled, 74-page manifesto on social media in which he identified himself as an Australian and white supremacist who was out to avenge attacks in Europe perpetrated by Muslims.
He livestreamed 17 minutes of the rampage at the Al Noor mosque, where, armed with at least two assault rifles and a shotgun, he sprayed worshippers with bullets, killing at least 41 people. More people were killed in an attack on a second mosque a short time later.
Facebook, Twitter and Google scrambled to take down the gunman’s video, which was widely available on social media for hours after the bloodbath.
The second attack took place at the Linwood mosque about 5 kilometers (3 miles) away.
The video showed the killer was carrying a shotgun and two fully automatic military assault rifles, with an extra magazine taped to one of the weapons so that he could reload quickly. He also had more assault weapons in the trunk of his car, along with what appeared to be explosives.
Two other armed suspects were taken into custody Friday while police tried to determine what role, if any, they played in the cold-blooded attack that stunned New Zealand, a country so peaceful that police officers rarely carry guns.
Tarrant’s relatives in the Australian town of Grafton, in New South Wales, contacted police after learning of the shooting and were helping with the investigation, local authorities said. Tarrant has spent little time in Australia in the past four years and only had minor traffic infractions on his record.
New Zealand Police Commissioner Mike Bush confirmed Tarrant was involved in both shootings but stopped short of saying he was the sole gunman.
During the Saturday morning hearing, a man who was not in court was charged with using writings to incite hatred against a race or ethnicity, but it was not clear if his case was related to the mosque attacks.
“We appear to primarily be dealing with one primary perpetrator, but we want to make sure that we don’t take anything for granted in ensuring New Zealanders’ safety,” Prime Minister Ardern said.
New Zealand, with a population of 5 million, has relatively loose gun laws and an estimated 1.5 million firearms, or roughly one for every three people. But it has one of the lowest gun homicide rates in the world. In 2015, it had just eight.
Ardern said Tarrant was a licensed gun owner who bought the five guns used in the crimes legally.
“I can tell you one thing right now, our gun laws will change,” Ardern said.
She did not offer too much detail, but said a ban on semi-automatic weapons would be looked at. Neighboring Australia has virtually banned semi-automatic rifles from private ownership since a lone gunman killed 35 people with assault rifles in 1996.
Before Friday’s attack, New Zealand’s deadliest shooting in modern history took place in 1990 in the small town of Aramoana, where a gunman killed 13 people following a dispute with a neighbor.