FLORIDA: No mention of fire arms or gun control, President Donald Trump's statement on Twitter Thursday skirted the big issues and demanded to know how a “disturbed” former student with an obsession with firearms slipped through the net to sow carnage at a Florida high school, killing at least 17 people in the latest gun massacre to rock the nation.
The 19-year-old suspect Nikolas Cruz has been charged with 17 counts of premeditated murder over Wednesday’s deadly rampage at Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in Parkland, America’s worst school shooting since the Sandy Hook massacre left 20 children and six teachers dead in 2012.
After a night of questioning in police custody, the young man was reportedly transferred to a local Florida jail early yesterday.
Trump ordered flags to fly at half-staff and was to deliver a televised address later Thursday, to a nation stunned by the mounting toll of school shootings which US authorities have so far appeared powerless to stop.
Wednesday’s harrowing shooting spree saw terrified students hiding in closets and under desks as they texted for help, while the gunman stalked the school with a semi-automatic AR-15 rifle.
Fifteen people were killed at the school itself, and two later died in hospital. One of those killed was a football coach in Parkland, a city of about 30,000 people, located 50 miles north of Miami.
The president weighed in on the tragedy on Twitter by pointing to indications the shooter — who had been expelled for disciplinary reasons — was “mentally disturbed.”
“So many signs that the Florida shooter was mentally disturbed, even expelled from school for bad and erratic behavior,” Trump wrote.
“Neighbors and classmates knew he was a big problem. Must always report such instances to authorities, again and again!“
Cruz was reportedly known to have firearms at home and had talked about using them.
A teacher at the school said Cruz had been identified previously as a potential threat to his classmates.
“We were told last year that he wasn’t allowed on campus with a backpack on him,” math teacher Jim Gard said in a Miami Herald interview.
“There were problems with him last year threatening students, and I guess he was asked to leave campus.”
According to a BuzzFeed report, the FBI had been informed Cruz could carry out a school shooting last year, after the teen commented on a video: “I’m going to be a professional school shooter.”
The creator of the video tipped off both the FBI and YouTube, BuzzFeed said.
Florida Senator Marco Rubio on Thursday called Cruz a “deeply disturbed person,” and questioned how the teenager “escaped detection, was able to acquire this weapon, and then go on and kill 17 people and injure many more.”
“This was someone that people knew was a danger,” Rubio said.
The United States has been hit by almost 20 school shootings since the start of the year, a terrifying phenomenon that is part of a broader epidemic of gun violence in a country that loses 33,000 people to gun-related deaths each year.
While the latest mass shooting has inevitably reignited questions about America’s permissive gun laws, Trump — who is the first president to have addressed the NRA gun lobby — is staunchly opposed to any additional gun control.
Opponents of gun control have consistently sought to steer public debate away from the issue, and onto the behavior and motives of people using the weapons.
When questioned at a press conference late Wednesday, Florida Governor Rick Scott — who described the massacre as “just pure evil” — declined to make a statement on gun control.
“There’s a time to continue to have these conversations about how through law enforcement, how through mental illness funding that we make sure people are safe, and we’ll continue to do that,” said Scott, a Republican.
Cruz had mixed in with students fleeing the school before being caught, officials said.
“We have already begun to dissect his websites and things on social media that he was on and some of the things... are very, very disturbing,” Broward County Sheriff Scott Israel said.
“If a person is predisposed to commit such a horrific event by going to a school and shooting people ... there’s not anybody or not a lot law enforcement can do about it.”
“This is a terrible day for Parkland,” Israel said.
The FBI said it was assisting local law enforcement with the investigation.
Parkland Mayor Christine Hunschofsky said a police officer was always stationed at the school and there was a “single point of entry.”
Since January 2013, there have been at least 291 school shootings across the country — an average of about one a week, according to Everytown for Gun Safety, a non-profit group that advocates for gun control.
“It is pretty clear that we’re failing our kids here,” said Melissa Falkowski, a teacher who squeezed 19 students into a closet to shield them from harm.
Trump demands answers after 17 gunned down at Florida school
Trump demands answers after 17 gunned down at Florida school
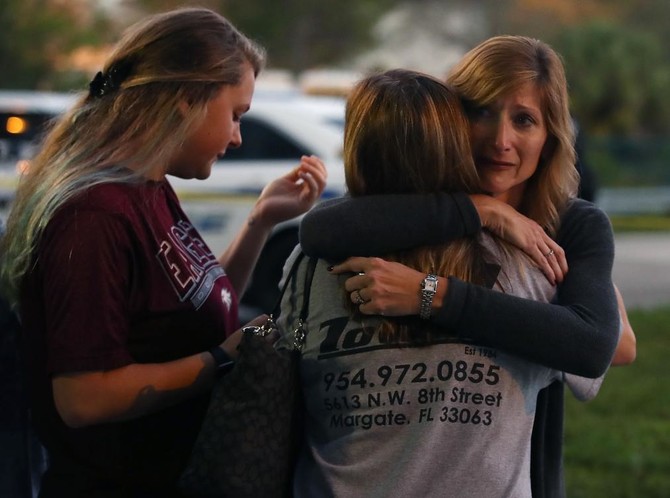
World not ready for rise in extreme heat, scientists say

- In a new study, they looked at different global warming scenarios to project how often people in the future might experience temperatures considered uncomfortably hot or cold
PARIS: Nearly 3.8 billion people could face extreme heat by 2050, and while tropical countries will bear the brunt, cooler regions will also need to adapt, scientists said Monday.
Demand for cooling will “drastically” increase in large countries like Brazil, Indonesia, and Nigeria, where hundreds of millions of people lack air conditioning or other means to beat the heat.
But even a moderate increase in hotter days could have a “severe impact” in nations not accustomed to such conditions, such as Canada, Russia, and Finland, said scientists from the University of Oxford.
In a new study, they looked at different global warming scenarios to project how often people in the future might experience temperatures considered uncomfortably hot or cold.
They found “that the population experiencing extreme heat conditions is projected to nearly double” by 2050 if global average temperatures rise 2°C above preindustrial times.
But most of the impact would be felt this decade as the world fast approaches the 1.5°C mark, said the study’s lead author Jesus Lizana.
“The key takeaway from this is that the need for adaptation to extreme heat is more urgent than previously known,” said Lizana, an environmental scientist.
“New infrastructure, such as sustainable air conditioning or passive cooling, needs to be built out within the next few years to ensure people can cope with dangerous heat.”
Prolonged exposure to extreme heat can overwhelm the body’s natural cooling systems, causing symptoms ranging from dizziness and headaches to organ failure and death.
It is often called a silent killer because most heat deaths occur gradually as high temperatures and other environmental factors work together to undermine the body’s internal thermostat.
Climate change is making heatwaves longer and stronger, and access to cooling — especially air conditioning — will be vital in the future.
The study, published in the journal Nature Sustainability, projected that 3.79 billion people worldwide could be exposed to extreme heat by mid century.
This would “drastically” increase energy demand for cooling in developing nations where the gravest health consequences would be felt. India, the Philippines, and Bangladesh would be among the countries with the largest populations affected.
The most significant change in “cooling degree days” — temperatures hot enough to require cooling, such as air conditioning or fans — was projected in tropical or equatorial countries, particularly in Africa.
Central African Republic, Nigeria, South Sudan, Laos, and Brazil saw the biggest rise in dangerously hot temperatures.
“Put simply, the most disadvantaged people are the ones who will bear the brunt of this trend, our study shows for ever hotter days,” said urban climate scientist and research co-author Radhika Khosla.
But wealthier countries in traditionally cooler climates also “face a major problem — even if many do not realize it yet,” she added.
Countries like Canada, Russia, and Finland may experience steep drops in “heating degree days” — temperatures low enough to require indoor heating — under a 2°C scenario.
But even a moderate rise in hotter temperatures would be felt more acutely in countries not designed to withstand heat, the authors said.
In these countries, homes and buildings are usually built to maximize sunlight and minimize ventilation, and public transport runs without air conditioning.
Some cold-climate nations may see a drop in heating bills, Lizana said, but over time these savings would likely be replaced by cooling costs, including in Europe, where air conditioning is still rare.
“Wealthier countries cannot sit back and assume they will be OK — in many cases, they are dangerously underprepared for the heat that is coming over the next few years,” he said.














