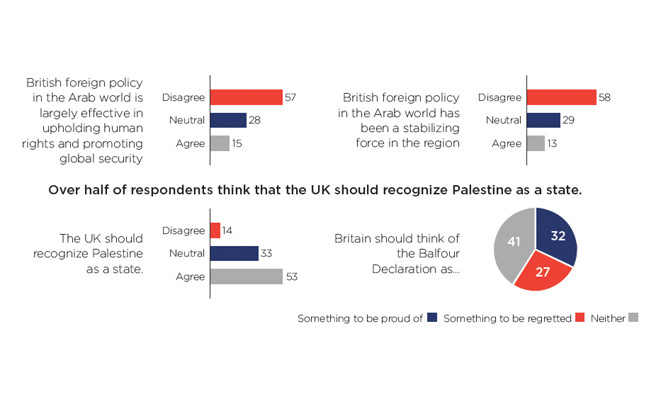
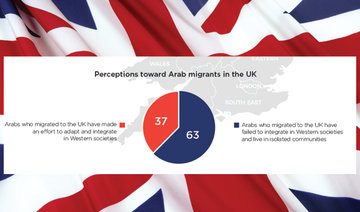
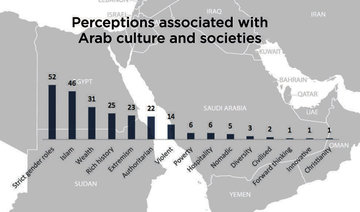
LONDON: The majority of Britons believe the UK’s foreign policy in the Arab world has been a failure, an exclusive poll by YouGov and this newspaper has revealed.
That has long been the view from the Arab street, influenced by events ranging from the Balfour Declaration of 1917 to the invasion of Iraq in 2003.
The “UK attitudes toward the Arab world” poll, conducted in August, indicates that at least some of those views are echoed in the streets of the UK, with 83 percent of those polled saying Britain was wrong to go to war in Iraq.
The consequences of the 2003 invasion by US and British forces can still be felt today, with some blaming the rise of Daesh on that fatal foreign foray.
Tellingly, the Arab News/YouGov poll found that 58 percent of Brits disagreed with the notion that the UK has been a stabilizing force in the Arab world.
Fawaz Gerges, professor of international relations at the London School of Economics, said this finding indicates a chasm between the government and public opinion.
“These results speak to the British public being ahead of the elite on these issues,” Gerges told Arab News.
“I think people in the Middle East would be surprised by these findings. There’s a kind of misunderstanding that there’s no distance between public opinion in the West and the views of governments and politicians. There is.”
Jane Kinninmont, deputy head of the Middle East and North Africa programme at Chatham House, said the invasion of Iraq under former Prime Minister Tony Blair still looms large in public perceptions of British foreign policy.
“There was a major breakdown of trust over Iraq. All the arguments used at the time to persuade the country to go to war have been debunked and Blair is now perceived as having lied, even though the inquests relating to the invasion haven’t said he lied,” Kinninmont said.
“Most of the British public would say Iraq is worse off now than before the invasion.”
Gerges said he was not surprised that most Brits believe the Iraq war was a mistake.
“Even at the time there was widespread opposition to the invasion, we saw that with the huge demonstrations and even then Tony Blair was in a minority position,” he said.
While the public is unequivocal about the issue of the Iraq invasion, 53 percent were found to support military action against Daesh, the poll found.
Gerges said he believes that is partly due to the level of media coverage about Daesh.
“They get too much coverage, which only serves to increase the spectacle of violence, brutality and savagery the group wants to display.
“The media has a key role to play. Ever since June 2014 the coverage of (Daesh) has influenced public opinion. Before then I am sure the idea of military intervention in the Middle East would not have been entertained, even in Washington DC.”
Kinninmont said there is a difference between the Iraq war and military strikes against Daesh, and that the British public recognizes this.
“There’s a sense (that Daesh) ‘started it’, that the terror attacks directed at the UK require some response,” she said.
“Iraq was about regime change, and the arguments and context (were) different to what we’re seeing today. People see that difference. There’s not complete opposition to military intervention, it’s just that people are more weary of grand political strategies, going to war to change regimes.”
While the Iraq invasion and its fallout is recent history, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a long-running sore which, many believe, is one of the main underlying causes of instability in the Middle East.
That seemingly has not gone unappreciated by the British public, with 53 percent wanting the UK government to recognize Palestine as a state, with only 14 percent against the idea, and 33 percent neutral on the issue.
Manuel Hassassian, the Palestinian ambassador to the UK, said that public opinion has been shifting over the last few years and support for a Palestinian state will continue growing.
“I have been here for 11 years and have noticed dramatic changes in the British public’s views on Palestine,” Hassassian said.
“That only 14 percent say they wouldn’t want the Palestinian state to receive recognition is an indication of the … Palestinian cause worldwide being accepted.”
According to Yossi Mekelberg, professor of international relations at Regent’s University London, such a finding will not go unnoticed in Israel. However, he claimed it will not make Benjamin Netanyahu’s government change course and actively seek a two-state settlement.
“There is a Palestinian president, a Palestinian delegation in London, so although there isn’t a state there is a lot of visibility,” Mekelberg said.
“Israel shouldn’t be surprised. It’s clear the majority of the international community would like to see a Palestinian state and a two-state solution.
“These figures won’t make Israel change its policies, but it does take notice of polls like these. It doesn’t want to lose the battle for public opinion.
“The figures will only go up and up, the more they build settlements the more the perception will be that Israel is blocking the peace process.”
One finding that perhaps contradicts the fact that the majority of Britons want the government to recognize the state of Palestine is that 32 percent think the Balfour Declaration — the first time the British announced support for the establishment of a “national home” for the Jewish people in Palestine — was something to be proud of.
“The Balfour Declaration is a badge of dishonour to the British colonial system and the government today shoulders a lot of the moral and historical responsibility,” Hassassian said.
“I have spoke to two government ministers who have told me that the Balfour Declaration won’t be complete until the UK recognizes the Palestinian state.
“So I think the figures show a lack of awareness among the British public about the Balfour Declaration. We are starting a campaign to raise awareness.”
Representatives of the UK government’s Foreign & Commonwealth Office did not respond to requests for comment when contacted by Arab News.
• For full report and related articles please visit: How Brits view Arab world