AMSTERDAM: Global chemical weapons investigators have gone to Turkey to collect samples as part of an inquiry into an alleged chemical weapons attack in neighboring Syria last week that killed 87 people.
The fact-finding mission was sent by the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) in The Hague to gather bio-metric samples and interview survivors, sources told Reuters on Thursday.
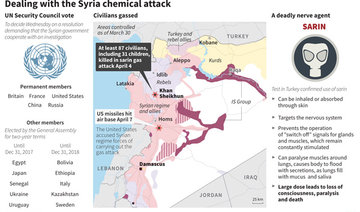
The toxic gas attack on April 4, which killed scores of people including children, prompted a US cruise missile strike on a Syrian air base and widened a rift between the United States and Russia, a close ally of Syrian President Bashar Assad in his conflict with rebels and militants fighting to oust him.
Syrian authorities have repeatedly denied using any chemical weapons. Russian officials said the gas had been released by an air strike on a poison gas storage depot controlled by rebels. Washington said that account was not credible, and rebels have denied it.
Samples taken from the poison gas site in Syria’s Idlib governorate tested positive for the nerve agent sarin, the British delegation at the OPCW said on Thursday.
“UK scientists have analyzed samples taken from Khan Sheikhoun. These have tested positive for the nerve agent sarin, or a sarin-like substance,” the delegation said during a special session on Syria at the OPCW in The Hague.
The UK result confirmed earlier testing by Turkish authorities that concluded that sarin had been used for the first time on a large scale in Syria’s civil war since 2013.
The OPCW mission will determine whether chemical weapons were used, but is not mandated to assign blame. Its findings, expected in 3-4 weeks, will be passed to a joint United Nations-OPCW investigation tasked with identifying individuals or institutions responsible for using chemical weapons.
International investigators have concluded that sarin, chlorine and sulfur mustard gas have been used in Syria’s six-year-old conflict, with government forces using chlorine and Daesh militants using sulfur mustard.
Last week’s poison gas attack in the town of Khan Sheikhoun in the rebel-held province of Idlib near the Turkish border was the most lethal since a sarin attack on Aug. 21, 2013 killed hundreds in a rebel-controlled suburb of the capital Damascus.
Chemical weapons experts in Turkey to investigate; UK confirms sarin use
Chemical weapons experts in Turkey to investigate; UK confirms sarin use

International law at ‘breaking point’ amid ‘epidemic’ of conflicts: Survey

- Gaza war highlighted as one of the most concerning areas; atrocities in Sudan also noted
- ‘Well over’ 100,000 civilians have been killed in past 18 months amid ‘rampant impunity’
LONDON: A new survey of 23 conflicts worldwide has said more than 100,000 civilians have been killed in the past 18 months, with adherence to international humanitarian law reaching “a critical breaking point.”
The “War Watch” survey highlighted the war in Gaza as one of the most concerning areas in an “epidemic” of violence, while also noting concerning levels of atrocities in Sudan.
Taken under the auspices of the Geneva Academy of International Humanitarian Law and Human Rights, the survey covers July 2024 to the end of 2025.
Lead author Stuart Casey-Maslen said: “Atrocity crimes are being repeated because past ones were tolerated. Our actions — or inaction — will determine whether international humanitarian law vanishes altogether.”
In Gaza, local authorities say 18,592 children and 12,400 women have been killed since Israel invaded the Palestinian enclave in October 2023.
The report said Gaza’s overall population had declined by “about 254,000 people, a 10.6 percent decline compared with pre-conflict estimates,” making it one of the most deadly conflicts in the world. It noted that despite a ceasefire being agreed late last year, civilian casualties have continued.
In Sudan, after the fall of the city of El-Fasher to the Rapid Support Forces last October, widespread reports of survivors “being gang-raped by RSF fighters” — including in the presence of relatives — were recorded in numerous instances.
The survey said: “We do not know how many civilians have been killed in the conduct of hostilities during armed conflicts in 2024 and 2025, but we do know that the number is well over 100,000 in each of the two years.”
It added that “serious violations of international humanitarian law (IHL) were wrought … on a huge scale and with rampant impunity.”
The report said IHL and the laws of armed conflict, established after the Second World War to protect civilians, must be upheld by every state under the Geneva Conventions “in all circumstances.”
It added: “Addressing widespread impunity for serious violations of international law should be treated as a policy priority.”
The report suggested several policy ideas to reduce the number of people suffering, including arms export bans for countries “where there is a clear risk that the arms or ammunition to be delivered will be used to commit or facilitate serious violations” of IHL.
It also proposed limiting the use of drones and artificial intelligence targeting in civilian areas, as well as unguided gravity bombs or inaccurate long-range artillery.
In addition, it called for “systematic prosecution of war crimes,” saying more political and financial support need to be given to the International Criminal Court by members of the international community.