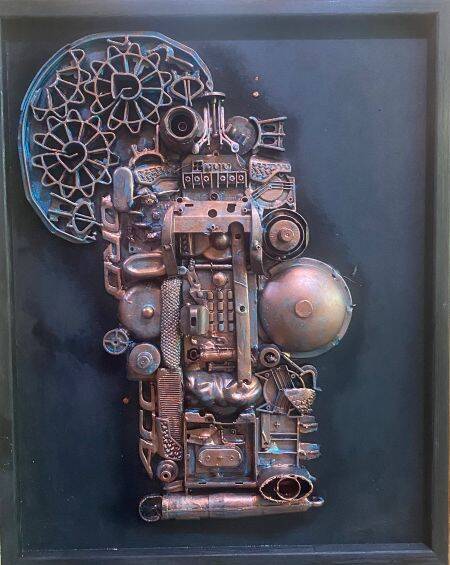
JEDDAH: Where others see scrap metal destined for the trash, Saudi artist Mishal Al-Amri sees opportunities to create artwork.
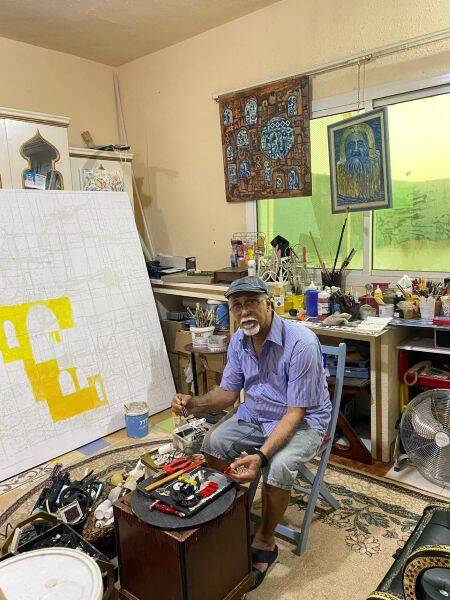
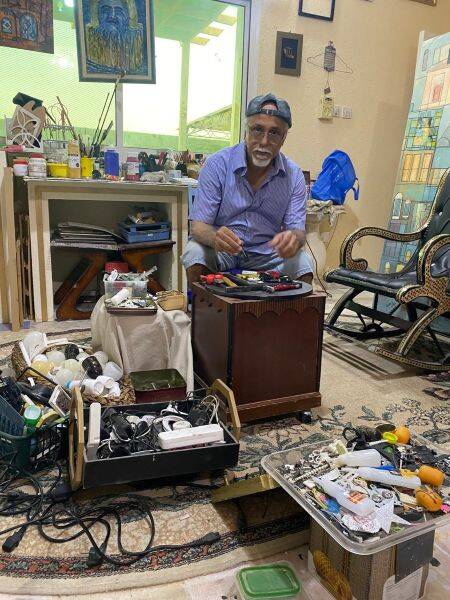
In his bustling studio in Jeddah, Al-Amri works to remove rust before cutting, rolling, shaping and joining thousands of pieces of shaped scrap metal by hand.
He has been upcycling unwanted bits of metal throughout his artistic career, which has spanned 20 years.
“The artist has an eye that sees what others cannot; an eye that captures the beauty in the heart of the damaged and neglected, and restores it to life and meaning. My ultimate hope and goal are to give scrap metal a new life,” Al-Amri told Arab News.
When growing up, Al-Amri loved to draw. As he got older, he started painting. It was not until he retired at the age of 59 that he discovered his true passion and began sculpting with recycled metal after teaching himself how to weld.
“As I said before, it was just a hobby and I stopped it for a long time after I joined the banking sector due to the difficulty of balancing the hobby, the job, and then the family later on.
“Anyhow, when I was approaching 40 years of age, and after having a family and professional job, I began to pursue my artistic journey once again. I worked on paintings during my free time and vacations, and I lived for nearly 26 years just painting, readings, attending art seminars, workshops, and holding exhibitions alongside other local artists.”
Speaking about how he started collecting scrap metal items from the street, the 65-year-old said: “The spark for this artistic journey was the first moments of an evening walk, when my eyes would trace the floor littered with scraps of plastic, scraps of iron and discarded remnants of lighting and plumbing, no longer fit for use or neglected.”
He added: “These pieces I picked up from the streets would become the core of my personal art collection — materials I plucked from the fate of neglect to submit to my ideas and participate in the creation of beauty.”
These materials can end up waiting for days and sometimes years in storage in his studio until an idea suddenly emerges.
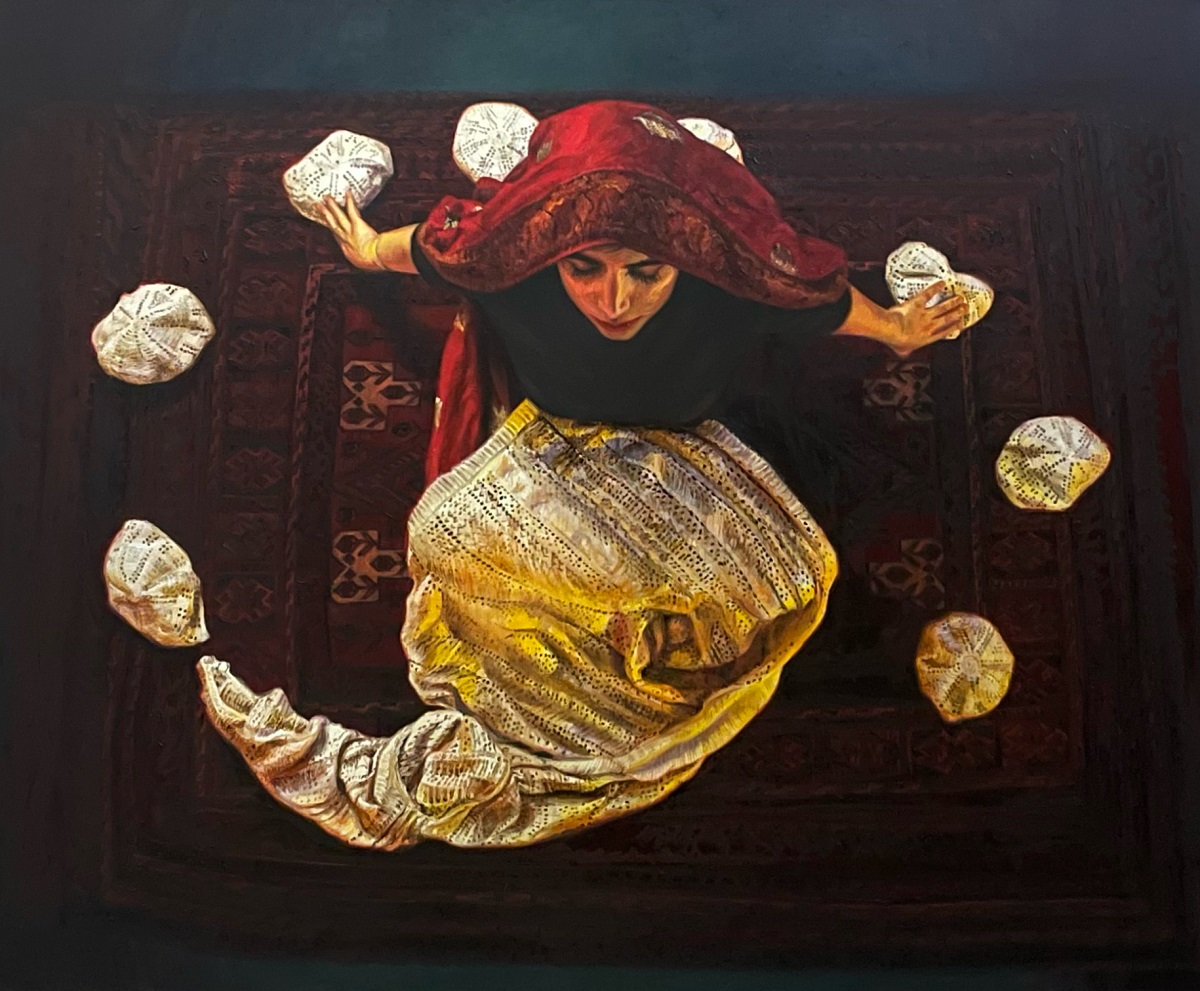
“The journey of constructing the painting or sculpture begins; from choosing the colors and sizes of the pieces, to weaving the relationships between them into an artistic composition that gives it a new spirit.”
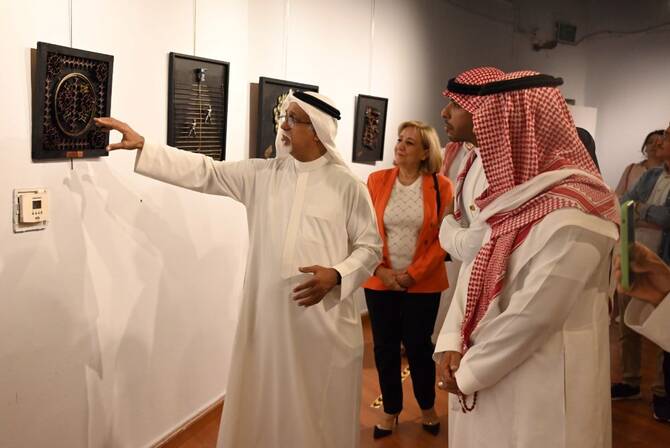
The Saudi Arabian Society for Culture and Arts recently hosted his first solo exhibition showcasing under the theme “The Neglected.”
“This exhibition is the fruit of those moments; an invitation to see the beauty in the unusual, and to contemplate art’s ability to redefine what is damaged and neglected to ultimately become more precious and valuable,” he said.
“My artistic experience in this exhibition is based on two complementary principles: First, protecting the environment from the effects of pollution and human-caused damage, by collecting remnants of harmful materials in the soil and saving them from becoming a burden on the earth.
“Second, sustaining the usefulness of objects, by recycling them and using them in the field of art after their original function has ended, reborn as works of art that convey an aesthetic, humanitarian and environmental message.
Al-Amri says that he plans to continue creating scrap metal sculptures and paintings.
“On a personal level, I want to reopen the Cezanne Fine Arts Center, which I founded years ago and continue to cultivate art until its very end.
“On a more general level, I strive to raise environmental awareness, enabling people to respect and preserve the environment.”