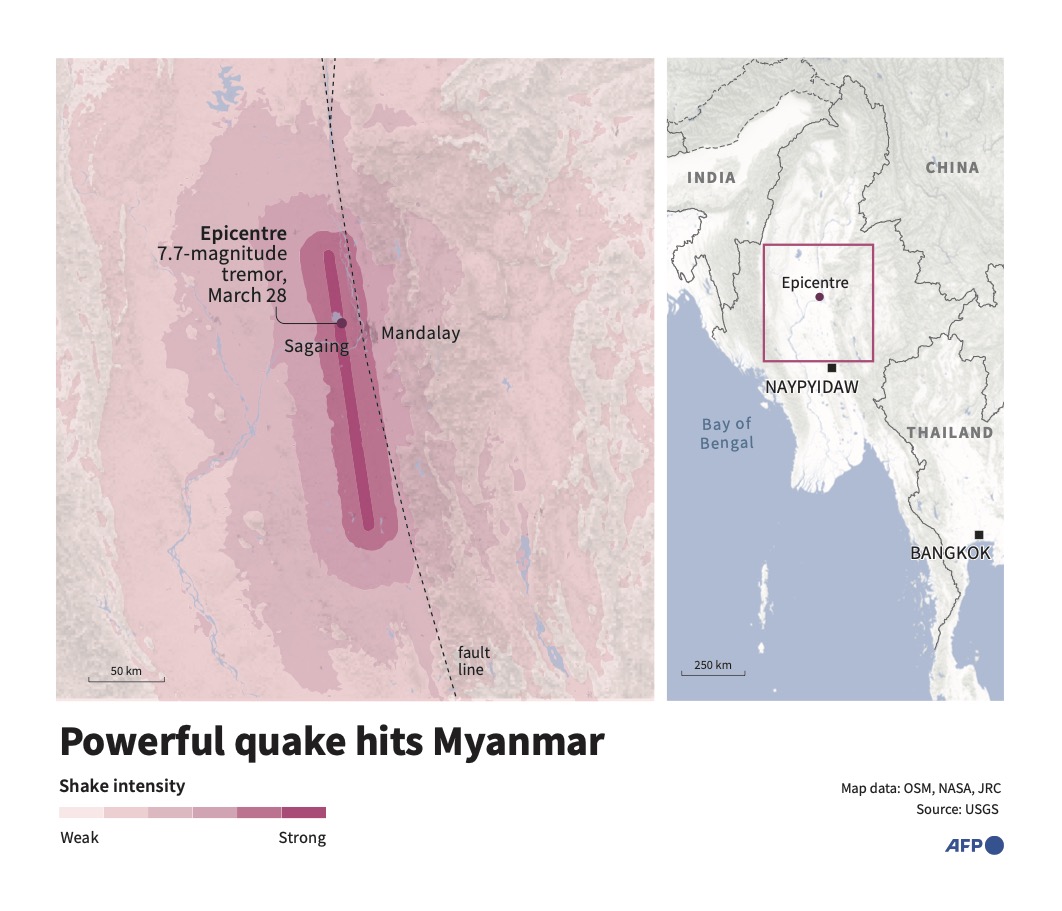
SINGAPORE: A powerful earthquake of magnitude 7.7 centered in the Sagaing region near the Myanmar city of Mandalay caused extensive damage in that country and also shook neighboring Thailand on Friday.
How vulnerable is Myanmar to earthquakes?
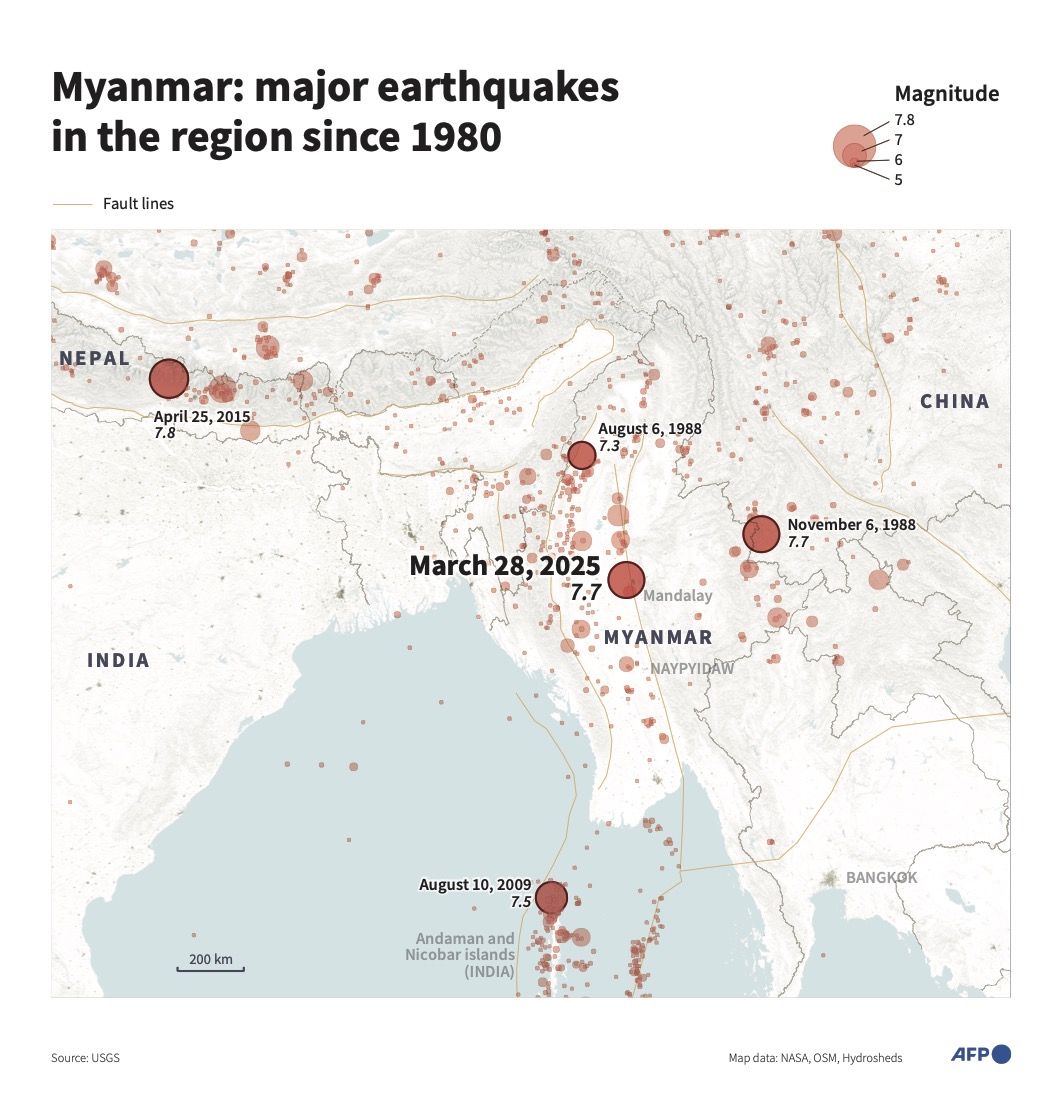
Myanmar lies on the boundary between two tectonic plates and is one of the world’s most seismically active countries, although large and destructive earthquakes have been relatively rare in the Sagaing region.
“The plate boundary between the India Plate and Eurasia Plate runs approximately north-south, cutting through the middle of the country,” said Joanna Faure Walker, a professor and earthquake expert at University College London.
She said the plates move past each other horizontally at different speeds. While this causes “strike slip” quakes that are normally less powerful than those seen in “subduction zones” like Sumatra, where one plate slides under another, they can still reach magnitudes of 7 to 8.
Why was Friday’s quake so damaging?
Sagaing has been hit by several quakes in recent years, with a 6.8 magnitude event causing at least 26 deaths and dozens of injuries in late 2012.
But Friday’s event was “probably the biggest” to hit Myanmar’s mainland in three quarters of a century, said Bill McGuire, another earthquake expert at UCL.
Roger Musson, honorary research fellow at the British Geological Survey, told Reuters that the shallow depth of the quake meant the damage would be more severe. The quake’s epicenter was at a depth of just 10 km (6.2 miles), according to the United States Geological Survey.
“This is very damaging because it has occurred at a shallow depth, so the shockwaves are not dissipated as they go from the focus of the earthquake up to the surface. The buildings received the full force of the shaking.”
“It’s important not to be focused on epicenters because the seismic waves don’t radiate out from the epicenter — they radiate out from the whole line of the fault,” he added.
How prepared was Myanmar?
The USGS Earthquake Hazards Program said on Friday that fatalities could be between 10,000 and 100,000 people, and the economic impact could be as high as 70 percent of Myanmar’s GDP.
Musson said such forecasts are based on data from past earthquakes and on Myanmar’s size, location and overall quake readiness.
The relative rarity of large seismic events in the Sagaing region — which is close to heavily populated Mandalay — means that infrastructure had not been built to withstand them. That means the damage could end up being far worse.
Musson said that the last major quake to hit the region was in 1956, and homes are unlikely to have been built to withstand seismic forces as powerful as those that hit on Friday.
“Most of the seismicity in Myanmar is further to the west whereas this is running down the center of the country,” he said.
















