RIYADH: In a groundbreaking scientific effort, researchers have leveraged artificial intelligence to unlock a powerful new tool in the fight against microplastic pollution — microscopic protein fragments known as peptides.
These AI-engineered peptides can bind to plastic particles, making it possible to remove microplastics from water more efficiently.

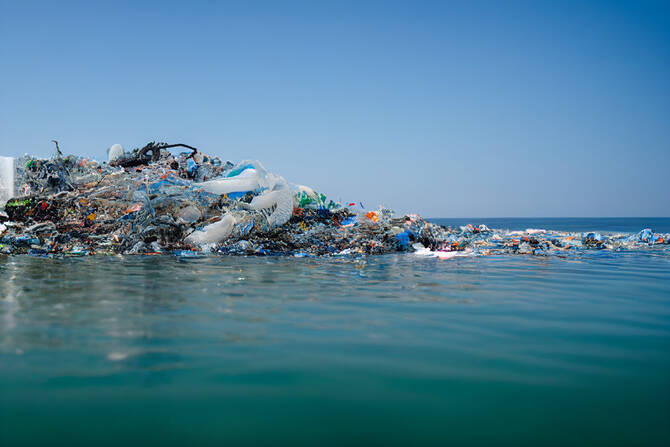
A large accumulation of plastic waste floating in the ocean. Researchers are now turning to AI-designed biodegradable peptides to tackle microplastic buildup in marine environments. (Getty Images)
Microplastics — tiny plastic fragments smaller than five millimeters — are now alarmingly widespread in oceans, rivers, soil, and even human bodies. These particles persist in the environment for centuries, threatening ecosystems and public health.
Traditional cleanup methods have struggled to address this growing crisis. Now, a team of scientists from Saudi Arabia, the US and beyond has unveiled a revolutionary solution: biodegradable peptides that latch onto microplastic particles with impressive precision.
Discovered using advanced deep learning models, these peptides could mark a turning point in the global fight against plastic pollution.

“We combined advanced biophysical simulations, which show how short proteins behave on plastic surfaces, with deep learning or AI to spot hidden patterns in those simulations,” Abdulelah Al-Shehri, assistant professor of chemical engineering at King Saud University and the study’s co-author, told Arab News.
“This allowed us to pinpoint specific peptides that latch onto microplastics up to 34 percent more effectively than older methods.”
Unlike conventional filtration methods, these AI-guided peptides offer a scalable, biodegradable alternative that could transform microplastic remediation.
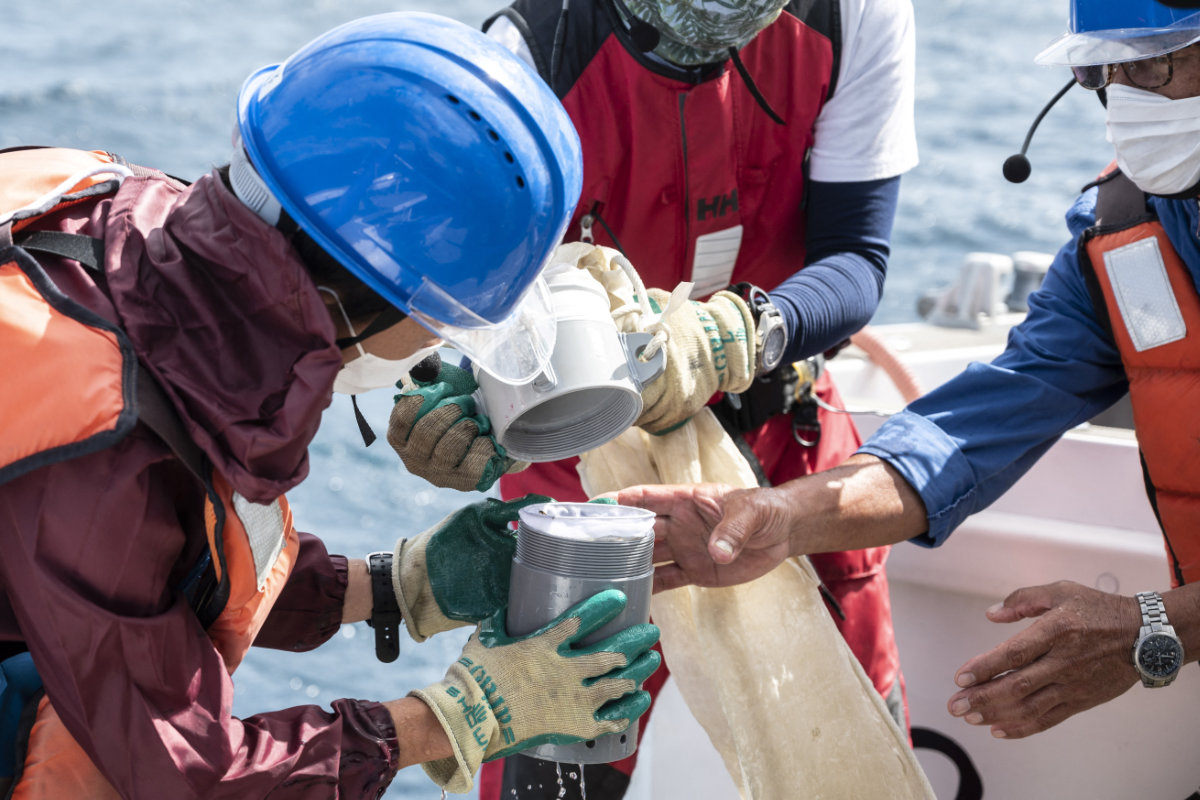

This photo taken on October 14, 2021 shows researchers taking samples collected by a funnel-shaped net nicknamed "the sock" during a joint project of the French Tara Ocean Japan. (AFP)
“Essentially, AI guided us to protein sequences that traditional approaches might miss, leading to stronger and more efficient cleanup capabilities,” Al-Shehri added.
While this discovery was initially made in a computational setting, laboratory tests have confirmed the peptides’ real-world potential.
“We recently ran experiments to evaluate how strongly the AI-designed peptides bind to plastic,” Michael Bergman, a PhD candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at North Carolina State University, told Arab News
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
“No one has designed plastic-binding peptides before, and we relied solely on computational predictions for peptide design, so we were curious to see how our computational predictions bear out in experiment.
“Excitingly, the AI-designed peptides did very well. The peptides had much higher affinity for plastic compared to random sequences of amino acids and performed as well as our best biophysical designs.
“This work will hopefully be published in the coming months. Having checked this box, the next step is to apply the peptides to remediate microplastic pollution.”
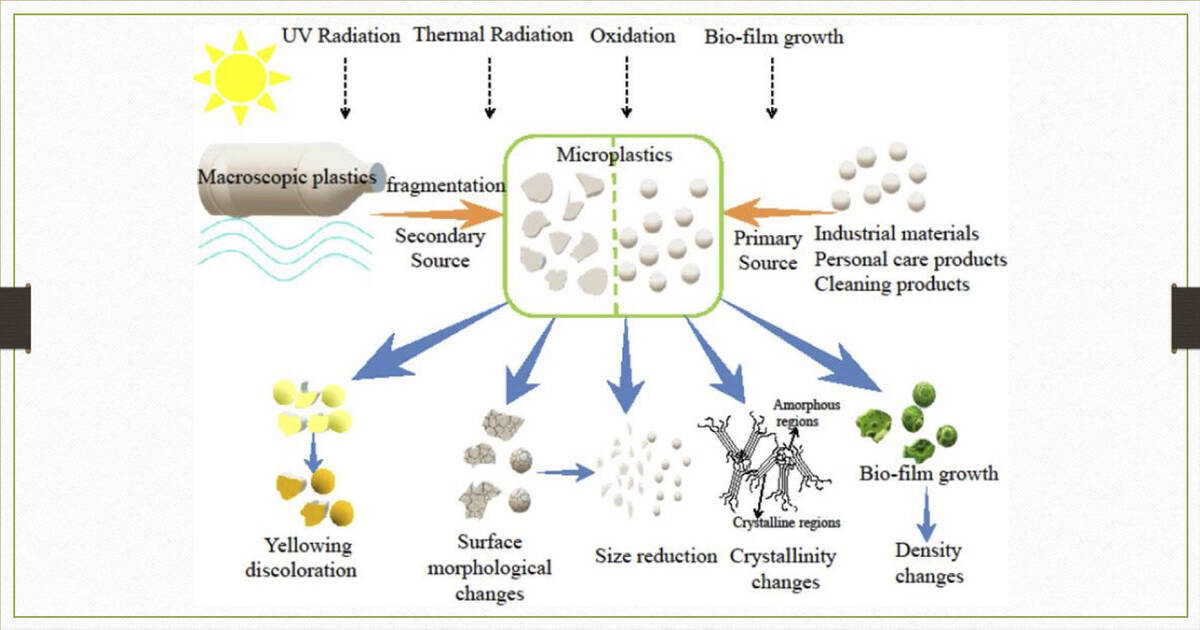
Infographic courtesy of King Saud University website
Bringing these peptides from the lab to real-world applications presents a major challenge: scalability.
“A major obstacle is producing these specialized peptides on a large scale while ensuring they remain stable and effective in different aquatic environments, whether in fresh, salt or even grey water,” Al-Shehri said.
“Beyond manufacturing, there needs to be close collaboration among researchers, policymakers and industry to streamline regulations, secure funding and ensure safe, cost-effective deployment where pollution is most critical.”

Abdulelah Al-Shehri, assistant professor of chemical engineering at KSU. (Supplied)
Bergman agrees, highlighting the vast potential applications of these peptides.
“We see many possible applications, such as detecting (and perhaps quantifying) microplastic pollution in water using a biosensor, removing microplastics either through filtration or by inducing aggregation, and aiding the adhesion of plastic-degrading organisms to microplastics,” he said.
This breakthrough is particularly relevant for Saudi Arabia, which is balancing its ambitious sustainability goals with its role as a global petrochemical leader.
Key milestones in AI-driven environmental cleanup
2022 Initial AI experiments in peptide-based plastic binding begin.
2023 AI-enhanced biophysical modeling predicts plastic-binding peptides with greater precision.
2024 AI-designed peptides successfully tested using extensive molecular dynamics simulations, outperforming previous solutions.
2025 Researchers at King Saud University, North Carolina State, and Cornell publish findings on biodegradable peptides with record-breaking plastic adhesion.
FUTURE AI-driven peptide research expands to augment capture and detection technologies and broader environmental remediation efforts.
Maher Al-Rashed, associate professor in plastics science at King Saud University, sees this dual role as an opportunity rather than a conflict.
“Saudi Arabia’s ongoing transition toward sustainability, particularly through Vision 2030, offers a fertile ground for the integration of AI-driven biodegradable peptides as part of a multifaceted strategy to combat plastic pollution,” he told Arab News.
“A practical application could involve incorporating these peptides into wastewater treatment plants in cities like Riyadh and Jeddah, where microplastic contamination in water sources has been documented.”
He also referenced international benchmarks such as France’s Carbios and Japan’s Ideonella sakaiensis as models for Saudi Arabia to adapt and lead in this space.
“Saudi Arabia could adopt similar AI-engineered enzymatic solutions, particularly in industrial zones like Jubail and Yanbu, where high plastic waste output necessitates sustainable disposal methods,” he said.
While peptides offer a powerful new tool for microplastic cleanup, experts stress that they are not a replacement for reducing plastic waste at its source. “Reducing plastic use is crucial to stem the flow of new pollutants,” said Al-Shehri.

Small fragments of plastic and debris floating in contaminated seawater. Experts warn that microplastics can persist in ecosystems for centuries and pose risks to human health. (Getty Images)
“However, we already have a staggering amount of microplastics in circulation, some of which may persist for centuries. AI-powered strategies like our peptide designs serve as a necessary complement to source reduction, actively targeting and removing existing contaminants while broader efforts to improve recycling continue.”
Al-Rashed agrees but adds that for these peptides to be effective long term, they must be optimized for various types of plastics and environmental conditions.
“One fundamental challenge is ensuring that these peptides exhibit substrate specificity… meaning they must effectively degrade a variety of plastic polymers such as polyethylene, polypropylene and PET without harming natural organic matter,” he said.
He also emphasized the importance of ensuring environmental safety.
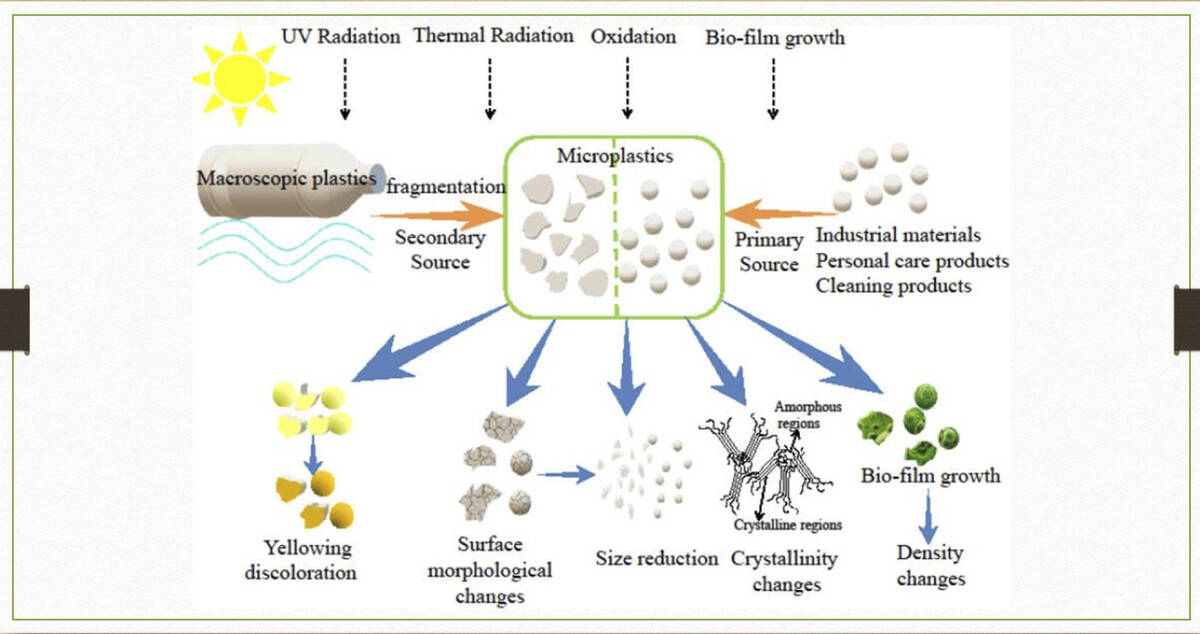
Infographic courtesy of King Saud University website
“AI-driven peptides must degrade into environmentally safe byproducts. Research conducted by Saudi Arabia’s King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology is exploring how peptide-mediated polymer degradation can be designed for maximum ecological safety.”
Bringing these peptides from theory to widespread use requires clear regulatory frameworks. Al-Rashed stressed the need for biosafety and industrial scalability.
“From a regulatory perspective, Saudi Arabia would need to establish stringent biosafety and environmental risk assessment protocols before approving the environmental release of AI-engineered peptides,” he said, referencing the role of the Saudi National Center for Environmental Compliance.
On an industrial level, he pointed out that cost efficiency and integration with existing waste management systems would be key factors in success.
“Saudi Arabia’s municipal waste collection and processing facilities are currently optimized for mechanical and chemical recycling, meaning that transitioning to bioenzymatic plastic degradation would require significant infrastructure modifications,” he said.

A photo taken on December 8, 2022, in Vaasa, Finland, shows plastic pieces in frozen water. (AFP)
As Saudi Arabia explores this innovation, researchers like Al-Shehri emphasize the importance of framing the message carefully — especially in a country where the plastics industry is economically significant.
“In essence, microplastic research is as critical as the plastics industry itself,” Al-Shehri said. “We must balance the lifesaving benefits of plastic with urgent research to eliminate and remove these tiny particles from our environment.
“Propelled by innovative academic efforts, short peptides now shine as a new technology in the global effort to combat microplastic pollution. Yet forging true progress — and preserving the plastics industry’s long-term viability — demands concerted efforts and research among governments, industries, academic institutions, and communities alike.”

South Korean environmental activists hold placards reading "I will protect the sea from microplastics" during a campaign to mark World Water Day at a park along the Han River in Seoul on March 22, 2022. (AFP)
As researchers worldwide explore how AI can revolutionize science and sustainability, the development of microplastic-binding peptides stands out as a clear example of how data, biology, and innovation intersect.
“There are almost endless possibilities in combining AI with biophysics,” said Bergman. “Of particular relevance to plastic and microplastic pollution is the development of enzymes that break down plastics.
“In recent years, biophysics-guided AI helped optimize an enzyme that rapidly breaks down the plastic PET. Other researchers are looking to optimize similar enzymes for other common plastics like polystyrene and polyethylene.”
From the lab benches of Riyadh to simulation labs in North Carolina, one message rings clear: AI has the potential to reshape how we approach one of the planet’s most pressing environmental challenges — and Saudi Arabia is ready to lead the charge.


















