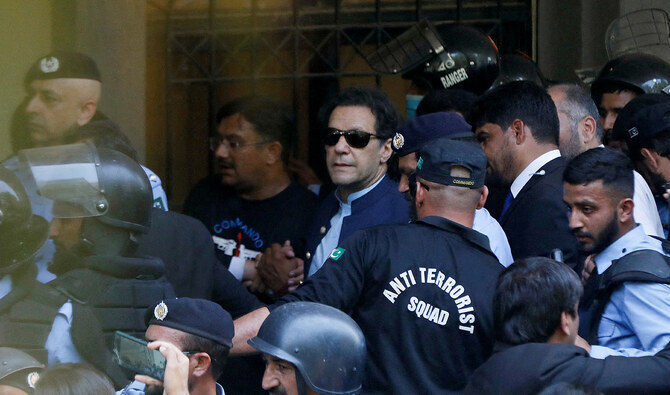ISLAMABAD: Pakistan’s capital Islamabad was gripped by violence on Tuesday as protesters demanding the release of former Prime Minister Imran Khan clashed with security forces near the parliament.
Here is a look at some of the allegations against the 72-year-old cricketer-turned-politician — named in dozens of cases since he left office in 2022 — that have kept him behind bars for more than a year.
GRAFT ALLEGATIONS
Khan was first arrested in May 2023 in relation to allegations that his wife, Bushra Bibi, and he received land worth up to 7 billion rupees ($25 million) as a bribe through a trust created in 2018, while he still held office.
His Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) party has maintained the land was donated for charitable purposes.
Khan was released on bail after three days in prison, during which his supporters attacked and set fire to military and other state installations, with eight people killed in the violence.
ABETTING VIOLENCE
Khan is facing anti-terrorism charges in connection with the violence that followed his arrest in May last year, and in relation to which several of his supporters have already been sentenced.
PTI said in July that authorities had issued fresh arrest warrants for him in three different cases related to the clashes.
STATE SECRETS
Khan was accused of making public a classified cable sent to Islamabad by Pakistan’s ambassador in Washington in 2022, while he still held office.
He was acquitted in the case in June.
UNLAWFUL MARRIAGE
Khan and his wife were accused of breaking Islamic law by failing to observe the mandated waiting period between Bibi’s divorce from her previous husband and their marriage in 2018 .