RIYADH: Somalia knows from bitter experience that a political end cannot be reached by means of violence, Hassan Sheikh Mohamud, the Somali president, has said, discussing the ongoing cycle of violence between Israel and the Palestinians.
After decades of political instability, terrorist violence, and foreign intervention, the war-scarred nation on the Horn of Africa has seen a gradual shift toward stabilization, reflected in its recent outreach to African neighbors and the Arab world.
Mohamud told Arab News that the violence between Israel and the Palestinian militant group Hamas would not address the root causes of the conflict — something that could only be achieved through a political agreement in the form of the two-state solution.
He said: “As Somalis, we have been in an environment of violence for a long time. We know where the violence ends up, and the consequences, and the result at the end of violence. No one can reach a political end by means of violence. It cannot happen.
“There is a worldwide accepted solution. Two states, Palestine and Israel, living together side by side, peacefully. And it can happen. It’s possible. Why don’t we go ahead with that?”
For more than a month, the Gaza Strip has been under intense Israeli bombardment in retaliation for the unprecedented Oct. 7 cross-border attack mounted by Hamas on southern Israel, in which 1,400 people were killed, most of them civilians, and 240 taken hostage.
Israel’s bombardment, and subsequent ground operation, has resulted in more than 11,000 deaths, according to the Hamas-run health ministry, and the displacement of more than half the population of Gaza.
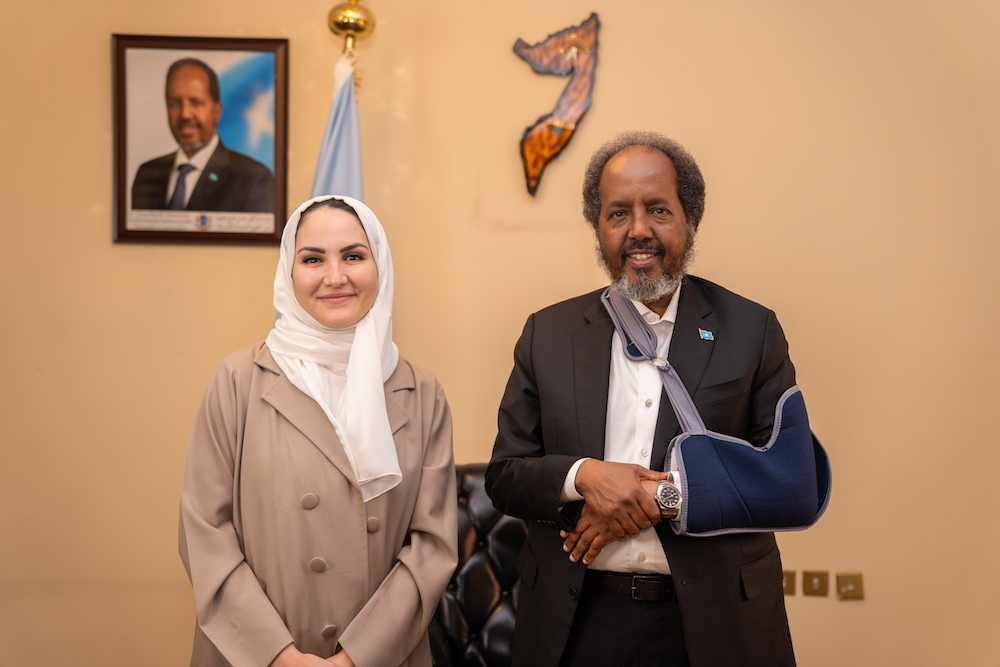

Somali President Hassan Sheikh Mohamud spoke to Arab News Assistant Editor-in-Chief Noor Nugali after the inaugural Saudi-African Summit and the fifth Arab-African Summit. (AN Photo/Abdulrhman Bin Shalhoub)
“What’s going on in Palestine, particularly today in Gaza, is a special case, something that is contrary to all human values in the moral sense.
“It’s not about religion only, it’s not about Arab only, it’s not about regionalism. This is humanity. Children are dying. Mothers are suffering. Innocent civilians are suffering,” Mohamud added.
The president spoke to Arab News following the inaugural Saudi-African Summit and the fifth Arab-African Summit, which took place in Riyadh on Nov. 11 and 12, bringing together representatives from both regions to discuss trade and cooperation.
He welcomed closer ties between Somalia and Saudi Arabia, highlighting their shared history, religious bonds, and common security interests.
Mohamud said: “Somalia and Saudi Arabia have a very, very long and historical relationship because of the proximity of our geographic locations and because of the common values that we have — the Islamic religion, the way of life, the Arab values and culture, of course. So, there’s a lot of issues that link us with Saudi Arabia.
“The 21st century and globalism is another challenge that makes us get together. We have a common enemy like the extremists, like the terrorists, like the fundamentalism in the wrong direction.
“Since we all have the common place of Islam, our heritage has always been linked together. So, that is the background that we are coming from,” he added.
Mohamud pointed out that he was especially grateful for the Kingdom’s humanitarian assistance, counterterrorism expertise, and diplomatic support, at a time when Somalia has suffered insurgency, instability, and economic crisis.
“Somalia has been in a difficult situation for the last three decades. And Saudi Arabia has always been with Somalia for all these three decades in terms of humanitarian, in terms of security, in terms of global politics and diplomatic support provided to Somalia. That is the level of our relationship.
“And today, under the leadership of King Salman and Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, we are improving. Every day there is a new progress in our relationship, new confidence, new relations, new areas on that,” he said.
Mohamud noted that security and counterterrorism were a particularly strong area of cooperation.
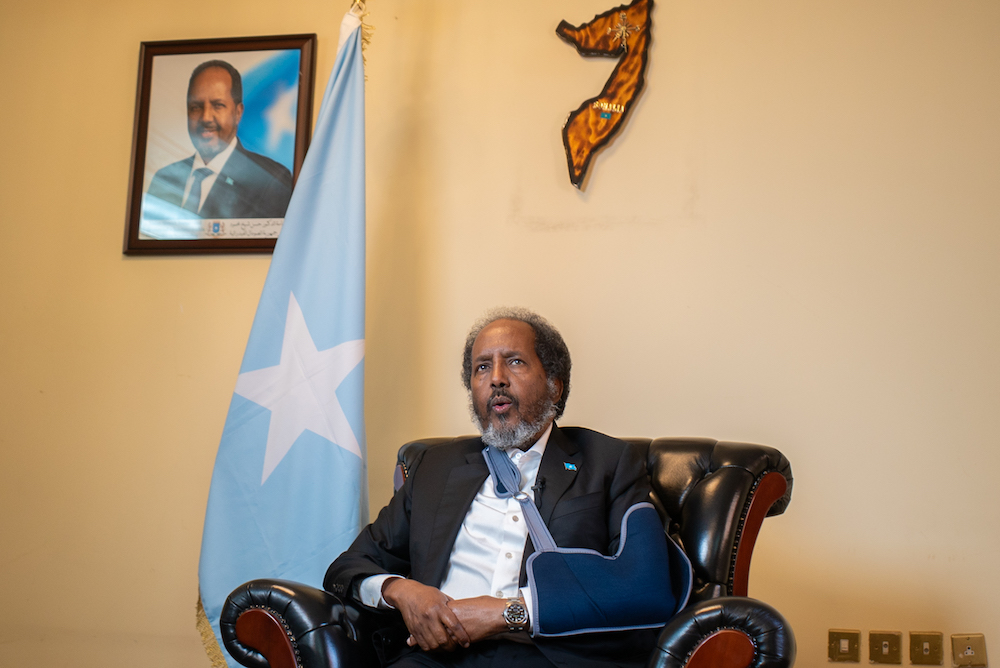

Mohamud has been Somalia’s president since May 2022, having served in the same post from 2012 to 2017. (AN Photo/Abdulrhman Bin Shalhoub)
“Somalia is a country that’s coming out of a long, long-term conflict. We went into a war with the terrorists, as did Saudi Arabia sometime in the past and succeeded. There is no better place than Saudi Arabia to seek advice and experience in the war against terrorism,” he added.
The Saudi-African Summit was organized in recognition of Africa’s growing importance as an emerging player in world trade and diplomacy.
Mohamud said: “In the 21st century, Africa is the destination. Destination in terms of economic development. Destination in terms of human capital. Destination in terms of resources. Destination in terms of strategy, you name it. So, the whole world is looking.
“If yesterday it was colonialism, if it was exploitation, in the 21st century (new change) is possible. It is a partnership, shared interests.”
He noted that Somalia, with the longest coastline on the African continent, a dynamic youth population, ample untapped natural resources, and the potential to become a major regional logistics hub, was ready for investment.
“For a long time, we have been struggling to stabilize Somalia. Make a safe and secure place. Only then we can hope investment will come. We are succeeding in this now. We are in the final stages of the stabilization and safety, and security of Somalia.
“We are defeating the terrorist groups that denied this right to the Somali people. Once we do that, that’s the right time — a conducive environment is created, enabling an environment that is created for investment.
“Somalia is a white paper. Every place is an opportunity. The blue economy is an opportunity. Food security is an opportunity. Minerals, rich in minerals: gold, uranium, copper, cobalt. All types of natural rare elements are available in Somalia.
“Somalia has close to 9 million hectares of arable land, with two permanent rivers throughout the year and a good number of rainy seasons. Somalia has one of the largest livestock (numbers) in the world.
“So, in Somalia, areas to invest, the sky’s the limit and it’s untapped and it’s unoccupied,” Mohamud added.
Somalia’s poor development is owed in large part to its decades of civil war, which have been prolonged by the involvement of international terrorist networks, including Al-Shabaab.
The terrorist group, which is based in Somalia but active elsewhere in East Africa, has been affiliated with Al-Qaeda since 2012, with suspected ties with Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb and Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula.
With international support, Somalia has been fighting back against Al-Shabaab with conventional military means and counter-radicalization campaigns, and by cutting off the group’s means of financing its activities.
Mohamud said: “The Somali government and the world supporting Somalia, international partners, international community, international organizations, all of them that have been supporting Somalia, for which we are very much grateful, in the fight against terrorism.
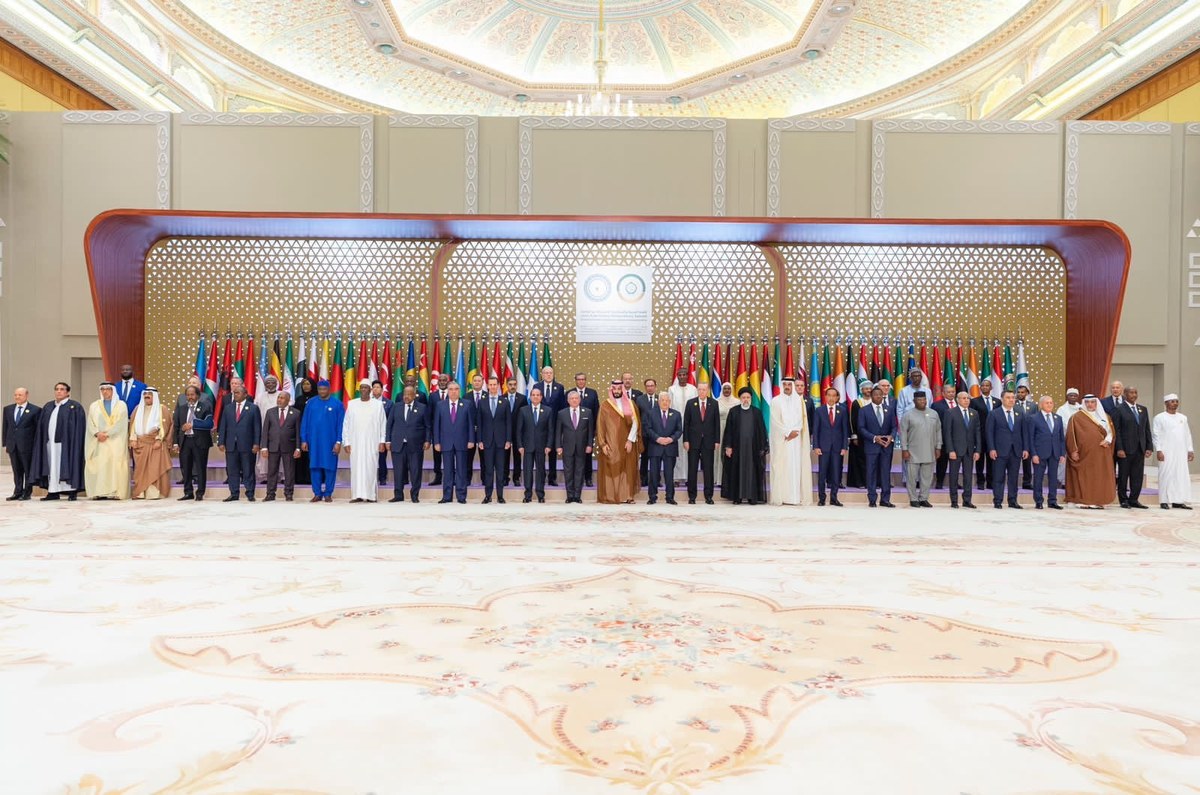

The president spoke to Arab News following the inaugural Saudi-African Summit and the fifth Arab-African Summit, which took place in Riyadh on Nov. 11 and 12. (SPA)
“Al-Shabaab is not a local organization. It’s a global, regional (organization). It just happened to be in Somalia, because in Somalia there was a great space that was ungoverned for a long time. That is what makes them stay there.
“Secondly, we have been fighting with Al-Shabaab, the terrorists, with one method, which is the military. All the time we have been fighting with them in terms of military. We strengthened and increased the military front, but we’re at another front. We are at ideological war since Al-Shabaab is an ideology-based organization — we fight with them over ideology.
“The ideology they use is Islam. And they are not using it in the right way. So, no one is much better than us to express and explain to our people the right path of Islam. And that’s what we are doing.
“The third is the issue of the economy. Al-Shabaab is collecting a huge amount of money from our people. They call it zakat (tax), or they call it tabaro’at (charity). They give it so many names. But at the end of the day, it is our local resources.
“We have restricted those resources, closing the taps flowing to them. So, that is what makes the success that we are seeking, and we are achieving right now,” he added.
Despite the demands of his role, Mohamud was determined to continue serving the interests of the Somali people as the nation moved toward a more stable and prosperous future.
He said: “Of course, I’m not a young man, but Alhamdulillah, I’m healthy. I don’t smoke, I don’t drink. I don’t stay up late. I do enough work, not just mentally, but exercise as well. So, Alhamdulillah, I’m healthy. I’m the father of a good family and I have been serving Somalia all my life.”
Mohamud has been president since May 2022, having previously served in the same position from 2012 to 2017. Before entering politics, he was a civil rights activist and a professor and dean at SIMAD University in Mogadishu.
In 2013, he was named in the Time 100, Time magazine’s annual list of the 100 most influential people in the world, for his efforts at advancing national reconciliation, anti-corruption measures, and socio-economic and security sector reforms in Somalia.
“I’m someone whose background comes from education and humanity and serving the lives and the interests of the people. And I believe, still, I’m serving the people. What makes me happy, what gives me self-satisfaction, is how much I help a human being,” Mohamud added.