NEW YORK CITY: Even as the 78th session of the UN General Assembly came to an end on Tuesday, it was clear that the curtain was not about to come down on the conversations about the tensions between the Global North and the Global South, the UN’s role in an emerging multipolar world order, and the stubborn persistence of conflicts and inequalities worldwide.
In a candid interview on the sidelines of the event in New York, Sophia Tesfamariam, the permanent representative of Eritrea to the UN, shared with Arab News her insights on the current state of affairs in the world, with a particular emphasis on the situation in violence-torn Sudan and the dynamics of African diplomacy.
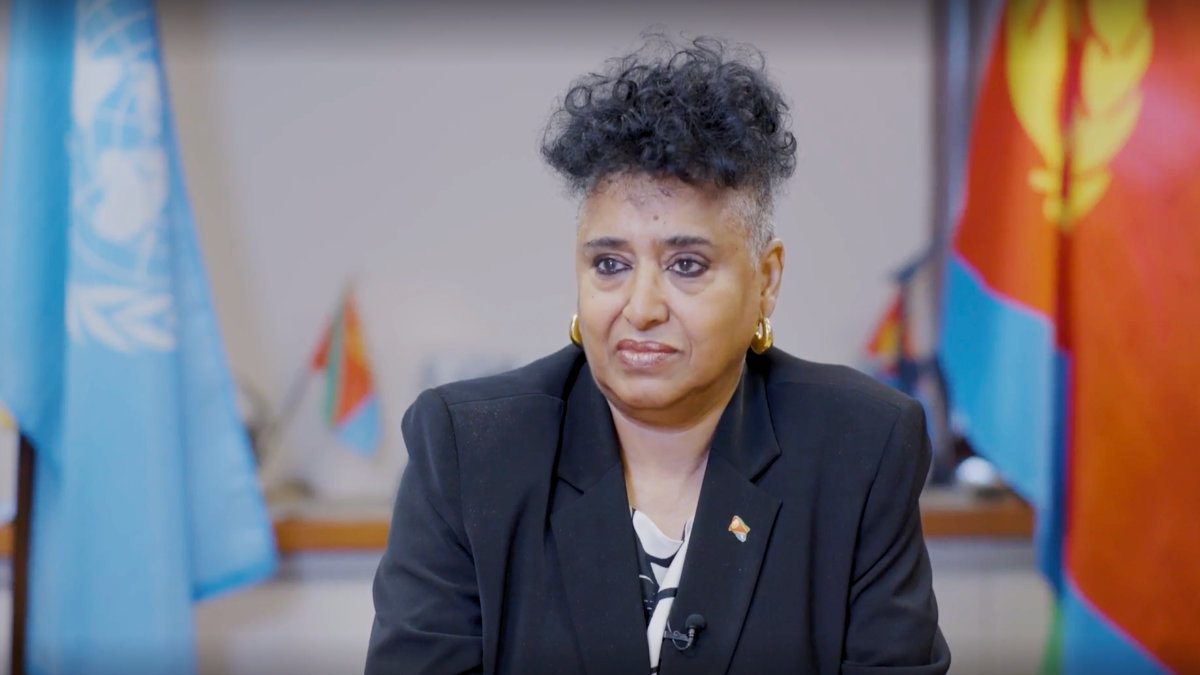

Sophia Tesfamariam, Eritrea's ambassador to the UN, believes the internecine conflict in Sudan is not just due to the big egos of rival warlords but also a result of "external interventions, historical and more recent, often driven by military and economic interests." (Arab News photo)
A seasoned diplomat, she pulled no punches in discussing the myriad challenges facing her region and the wider world, while underscoring the need for reforms to make the UN a more effectual institution, for the forging of true partnerships that respect African voices, and for African nations to take charge of their own destinies.
Tesfamariam also offered her perspective on the origins and consequences of the conflict in Sudan, Eritrea’s neighbor to the west, which continues to escalate and shows no sign of abating amid continual reports of atrocities and human rights violations, including sexual violence and the disposal of corpses in mass graves.
FASTFACTS
Eritrea, which gained independence from Ethiopia in 1993, occupies a strategically important area in the Horn of Africa.
The country’s representative to the UN, Sophia Tesfamariam, wants UN chief Antonio Guterres to be vocal about African issues.
The conflict in the country between the Sudanese Armed Forces and the Rapid Support Forces has so far killed more than 4,000 people and wounded at least 12,000. It has displaced 5.3 million within Sudan and sent a human tide of refugees into neighboring countries, including Eritrea. In the western Darfur region, the scene of a genocidal campaign in the early 2000s, the conflict has morphed into ethnic violence, with the UN and rights groups reporting that the RSF and allied Arab militias are attacking African tribes and clans.
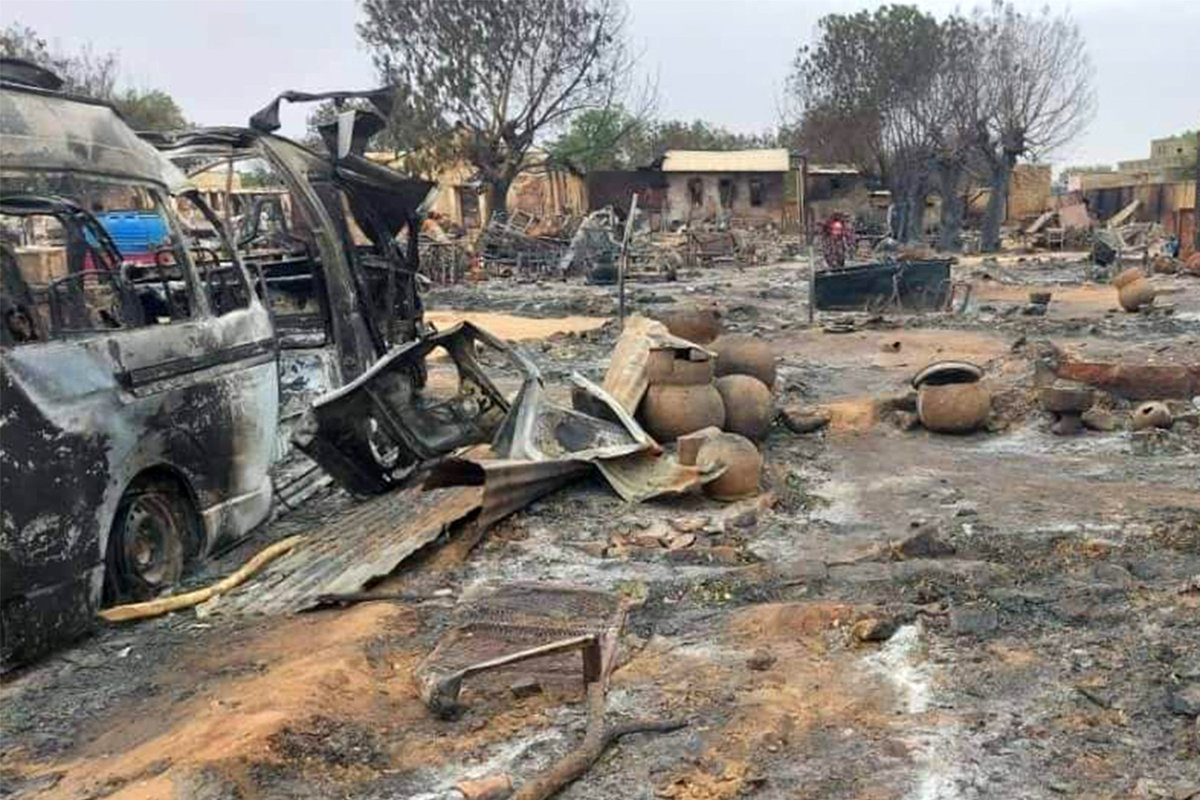

This picture taken on September 1, 2023 shows a view of destruction in a livestock market area in al-Fasher, the capital of Sudan's North Darfur state, amid the war between the Sudan Armed Forces and the paramilitary Rapid Security Forces. (AFP)
Tesfamariam described the shock that was felt in the region as Sudan descended into turmoil, saying it was something “that should have never happened” because it goes contrary to “the culture of the Sudanese people, their history, their background.”
She added: “For Sudanese people to have warring in the middle of their towns, the middle of the cities, this urban warfare is new. It’s not something that anybody can get used to.”

A handout picture taken on April 19, 2023 and obtained from Doctors Without Borders (MSF) on April 21 shows a crowded ward at a hospital in El Fasher in Sudan's North Darfur region, where multiple people have been wounded in ongoing battles there. (Photo by Ali Shukur/MSF/AFP)
The crisis cannot be attributed solely to a battle of egos between the leaders of the two military forces, Tesfamariam said. Rather, she believes “this final act” is the result of the external interventions, historical and more recent, often driven by military and economic interests, that have hindered the ability of the Sudanese people to take charge of their own destiny and development since gaining independence.
Although the Sudanese people initiated the revolution that led to the overthrow of President Omar Bashir in April 2019, their aspirations were seemingly hijacked by various external interests, regional and international, which contributed to the ongoing clashes between factions within the country, according to Tesfamariam.
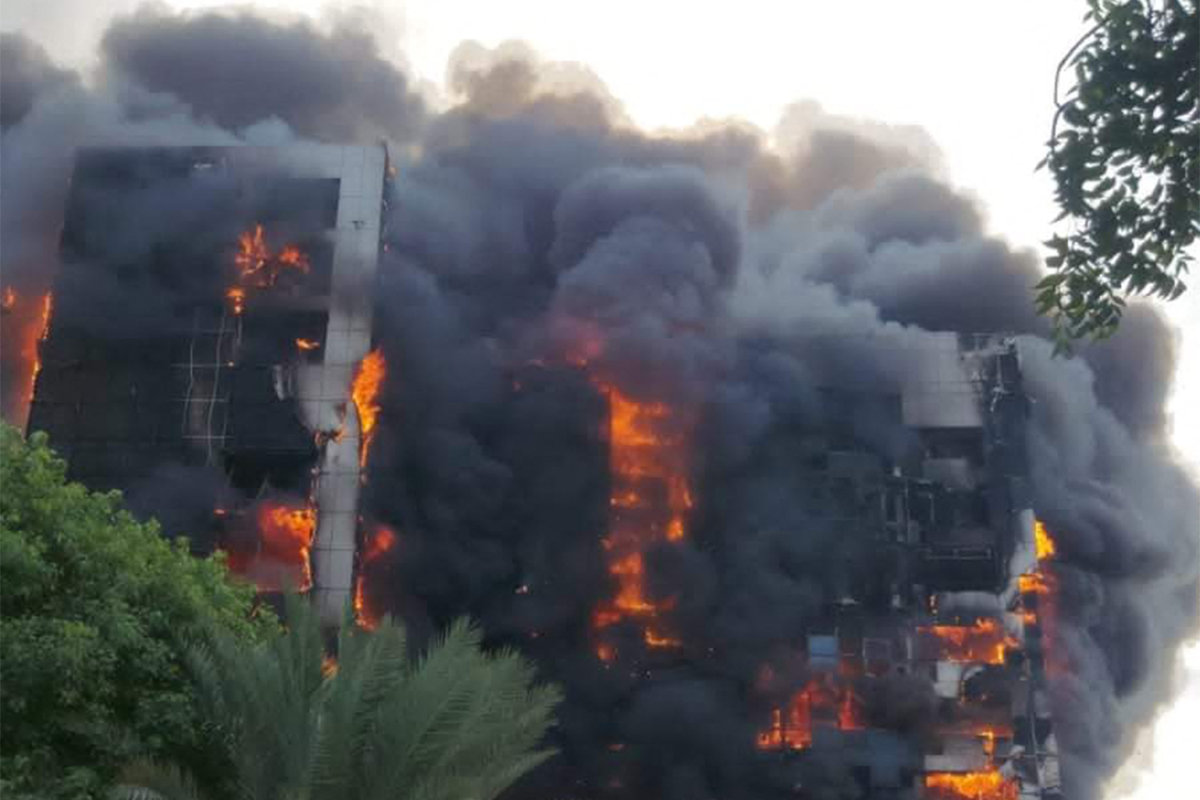

This picture taken on September 17, 2023 shows a raging fire at the Greater Nile Petroleum Oil Company Tower in Khartoum amid fighting between the regular army and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces. (AFP)
“And this, to me, looks like what triggered these two sides (the SAF and RSF) to finally see who gains an upper hand,” she said.
“If you’re going to peel back the pieces like an onion to see where the source of this conflict is, at the source of all this you will find intervention to be the culprit.”
The conflict, which began on April 15, came on top of an already dire humanitarian crisis that has been ravaging Sudan for decades. Things have become so desperate that about 25 million people need aid just to survive, but humanitarian agencies are hamstrung by lack of access, precarious conditions on the ground, and bureaucratic restrictions on their movement both into Sudan and then to the places where the needs are most acute.
Tesfamariam highlighted the historical relationship between her country and Sudan. There was a time, for example, when Sudan was a welcoming host of refugees from Eritrea, during the latter’s struggle for independence from Ethiopia, which lasted for decades and ended in 1991.
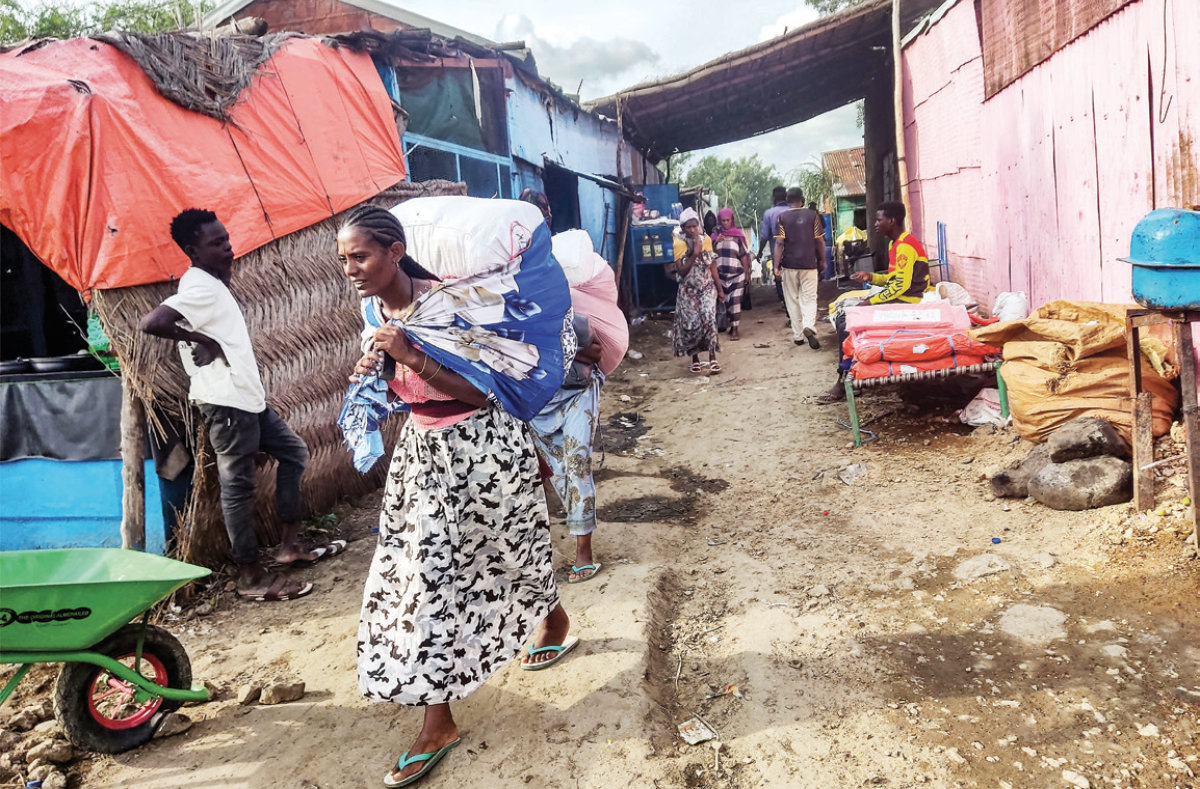

An Ethiopian woman walks carrying packages on her back in the border town of Metema in northwestern Ethiopia on August 1, 2023. (AFP/File Photo)
“We don’t do refugee camps,” she said. “These are Sudanese. This is their home. They can come any time. And if they need to take refuge in Eritrea today, the communities of Eritrea will welcome them as one of their own as they welcomed us when we were going to Sudan.
“So, the humanitarian situation for us is something of a historical necessity, almost, an opportunity to pay back the Sudanese people for what they did for us and are continuing to do for us all these years.”
As for the international community, Tesfamariam voiced disappointment about its failure to force the feuding factions to agree to a lasting truce, despite many attempts.
“24-hour ceasefire, 48-hour ceasefire — what do these mean?” she said. “How does it give you hope as a person living in a city to know that the guns are going to stop for 24 hours? And then what happens after 24 hours?
“So, these meaningless, endless ceasefire negotiations that go nowhere tell me the international community is not serious about bringing an end to the conflict in Sudan, and the warring parties are not serious in their commitments to their people.”
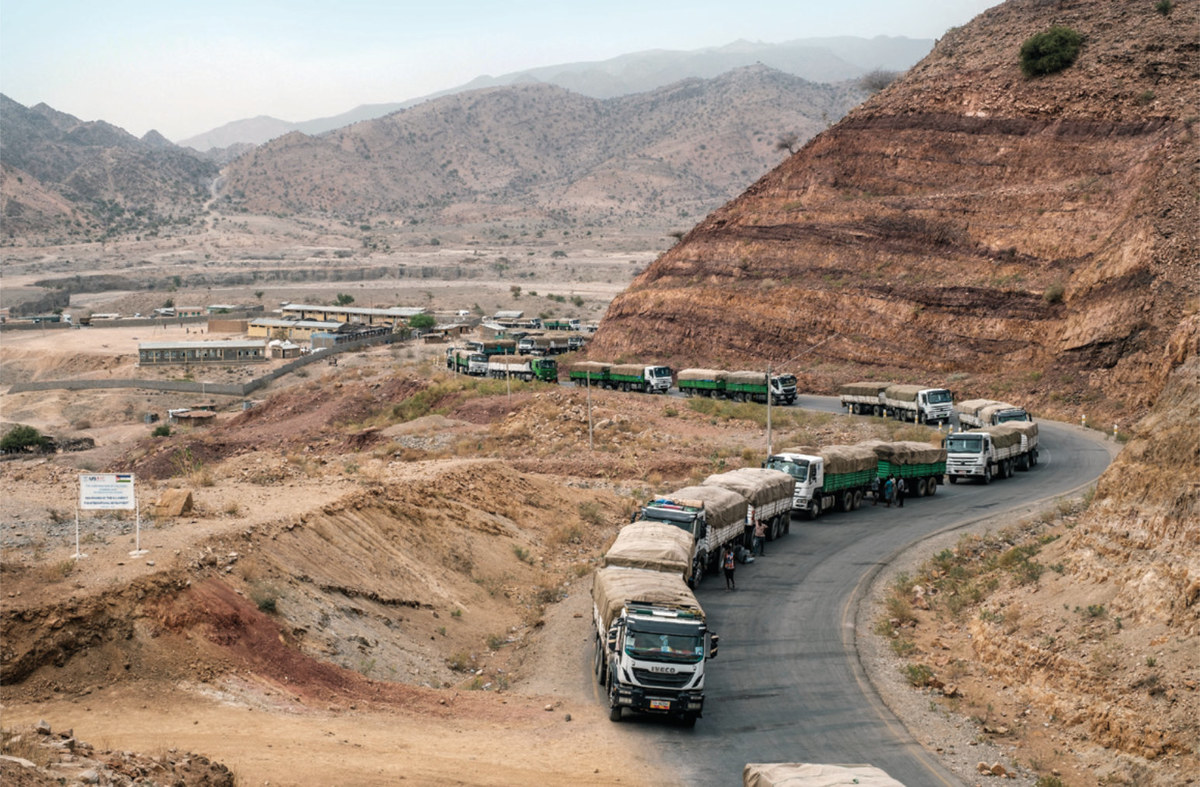

A convoy of the World Food Programme (WFP) are seen in the village of Erebti, Ethiopia, on June 9, 2022, on their way to Tigray, where hundreds of thousands of people were displaced from their homes by war. (AFP/File Photo)
Tesfamariam reflected on what she described as “the total ineptitude and total failure” of the UN system, including the Security Council, where, in her view, double standards are now the order of the day.
“Where is the interest?” she asked. “There are people dying on the streets of Sudan. But you have spent many, many meetings, and even many General Assembly meetings, on Ukraine. Why is Sudan not an important issue for you?
“I think this total lack of interest says a lot about the UN and its structures, and the way it works and its failures and its inadequacies to resolve issues for which it has been created.
“(The total lack) of any credible action by the (Security) Council tells me that it may not be what we think it is — this governing body that can bring peace and security to all of us — and maybe they’re leaving us to our own devices. And that’s a dangerous way to go.
“What exactly is the UN here for? It makes me wonder. So this continuous call for reform of the Security Council, reform of the General Assembly and what it can do and what is viable to do, I think, will continue. And these will be the examples that we will raise in the future to say, ‘Where was the UN?’ And I am sure future generations will also be inquiring about that.”

Eritrea's UN envoy Sophia Tesfamariam laments “the total ineptitude and total failure” of the UN system in seeking a solution to the Sudan crisis. (AFP/File photo)
Tesfamariam called on Antonio Guterres, the UN’s secretary-general, to “pay attention” and be vocal about African issues.
“Right now, there is no voice for Africa,” she said. “Yes, it is good they tell you ‘African solutions for African problems.’ But when you come right down to it, if there’s no third party involved, nothing happens. Nothing moves.”
While there is indeed a growing sense that African issues should primarily be addressed by the African Union and sub-regional organizations, Tesfamariam said she has noticed a big discrepancy between theory and reality.
Despite the rhetoric of “African solutions for African problems,” she contended, the AU does not seem to be afforded the same weight or resources as its European counterparts, including the EU.
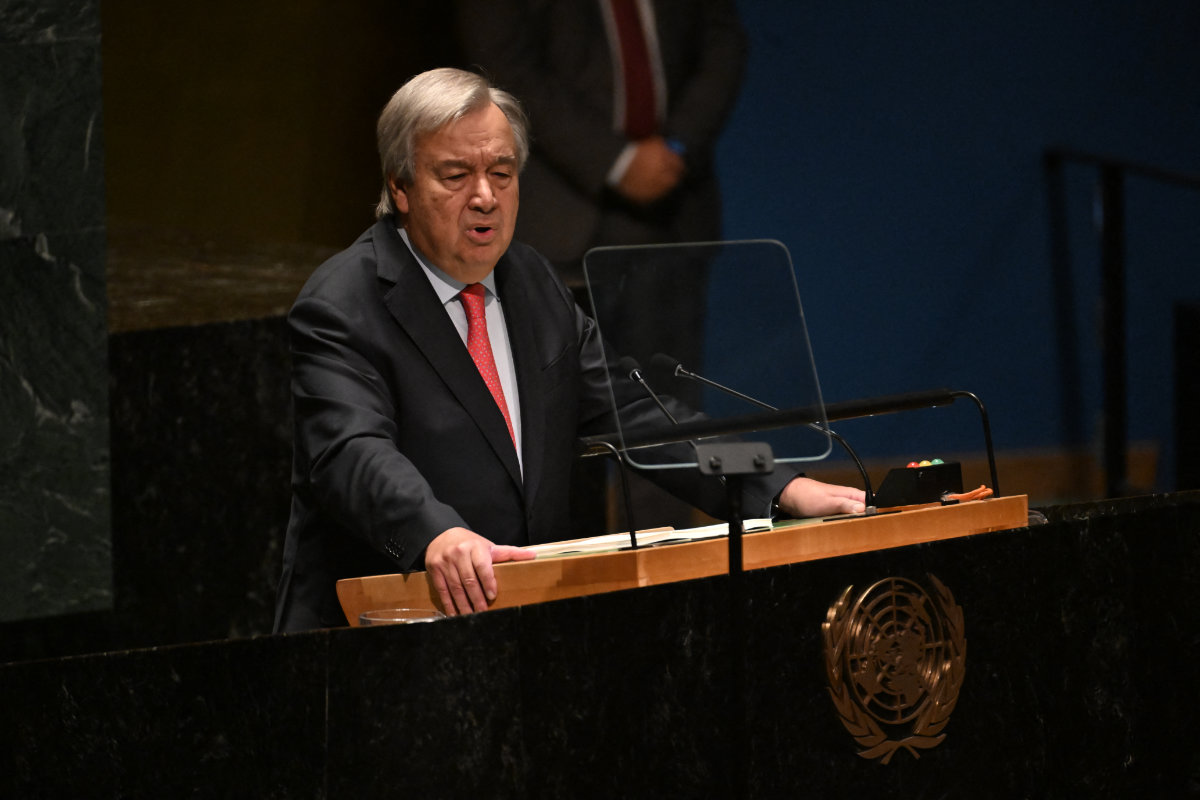

US Secretary-General Antonio Guterres should “pay attention” and be vocal about African issues, according to Eritrean Ambassador Tesfamariam. (AFP)
“Is the AU office here (at the UN) as fortified and given all the resources and attention and ability, and even the mandate, to interact with the UN the same way as the EU is?” she asked.
“I don’t think so. I don’t think it’s there. But can we just blame it on the EU or the UN and others for not taking an interest? What are Africans doing, also?”
She continued: “Why is it that when the AU meets every year, the first wave of people who come in, sit down to listen to your discussions are the Europeans and the Americans? Do you get the same respect and luxury to go and sit in the EU meetings in Europe to find out what they are discussing? No.
“So why do you continuously relegate yourself to these kind of positions for Africans? But when you cannot pay your own bills, when everybody else is funding every single project that you have all over the place, he who pays the piper picks the tune.
“How do you say no to the largesse that’s coming from EU, from the UN and other agencies that will dictate what should be done with your agency? Why does finance have to be the center of it all? I think if Africans come up with the solution, they will also find ways to finance the projects and initiatives they are trying to push.”
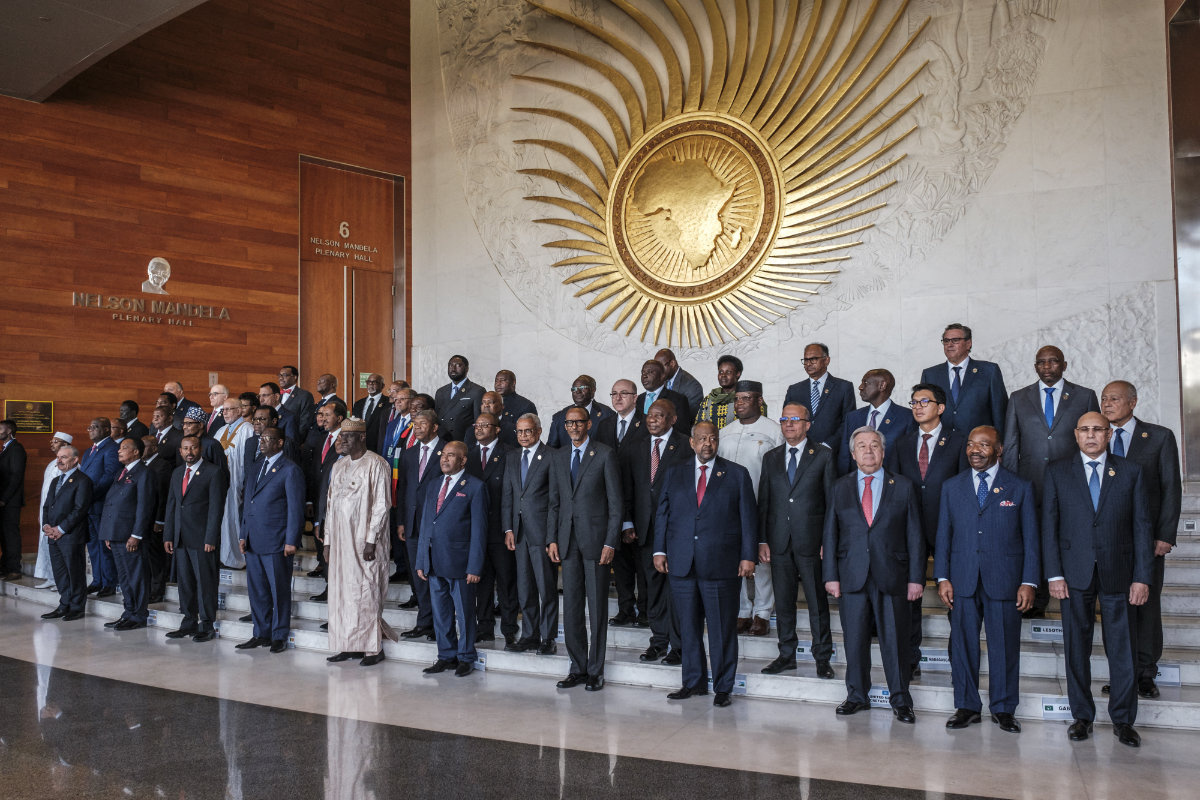

Leaders of African Union member states join a family photo session during a recent assembly in the city of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The Union needs to strengthen itself, grow more assertive and become a vocal advocate of African interests, says Eritrean Ambassador Sophia Tesfamariam (AFP/File photo)
To start with, according to Tesfamariam, the AU needs to strengthen itself, grow more assertive and become a vocal advocate of African interests. Next, she underscored the need for Africans to take responsibility for their own issues, strengthen regional and continental institutions, and find their own solutions to problems.
She criticized the current financial dependency in Africa on external entities, arguing that it often leads to the dictation of terms by donors that might not align with Africa’s interests.
“Africans themselves have got to take responsibility,” said Tesfamariam. “We need to start looking at ourselves, to do some soul-searching and say, why are we not doing more to strengthen our own regional and continental institutions?
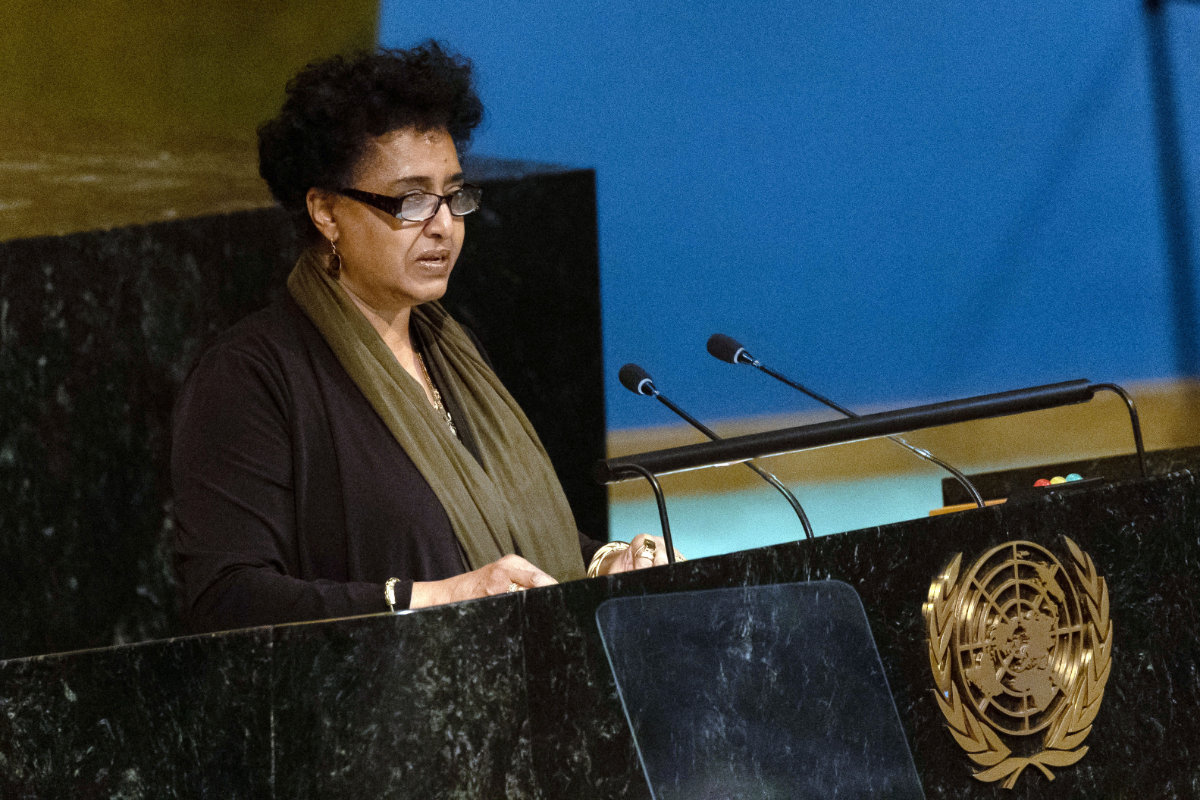

A file photo shows Eritrea's UN Ambassador Sophia Tesfamariam speaking during a UN General Assembly meeting. (AFP/File photo)
“These institutions can’t just be a talking shop anymore. In practical terms, what are we doing to respond to the needs of our people, of our region? How do we form partnerships — not ‘who-gives-and-who-receives’ kind of partnerships but real partnerships, where we share interests and then do things together for the benefit of global security?”
While conceding that efforts to make a dent in the “entrenched” international architecture is still “a work in progress,” Tesfamariam added: “We are not giving up now.”
She pledged to continue to work to amplify Africa’s voice in international forums, taking heart from the fact that “over the years we’ve been able to find more like-minded people.”
She added: “I am not here alone. If I felt alone before, I now have a mutual grievance society at the UN whose members feel exactly the way Eritrea feels — that same frustration with the UN and its ineptitude in some of the things, and with our failure to coalesce as a group to make a difference, to bring change to some of the issues that we have raised here.”