IRBIL, Iraq: Complexes of McMansions, fast food restaurants, real estate offices and half-constructed high-rises line wide highways in Irbil, the seat of the semi-autonomous Kurdish region in northern Iraq.
Many members of the political and business elite live in a suburban gated community dubbed the American Village, where homes sell for as much as $5 million, with lush gardens consuming more than a million liters of water a day in the summer.
The visible opulence is a far cry from 20 years ago. Back then, Irbil was a backwater provincial capital without even an airport.
That rapidly changed after the 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq that toppled Saddam Hussein. Analysts say that Iraqi Kurds – and particularly the Kurdish political class – were the biggest beneficiaries in a conflict that had few winners.
That’s despite the fact that for ordinary Kurds, the benefits of the new order have been tempered by corruption and power struggles between the two major Kurdish parties and between Irbil and Baghdad, the Iraqi capital.
In the wake of the invasion, much of Iraq fell into chaos, as occupying American forces fought an insurgency and as multiple political and sectarian communities vied to fill the power vacuum left in Baghdad. But the Kurds, seen as staunch allies of the Americans, strengthened their political position and courted foreign investments.
Irbil quickly grew into an oil-fueled boom town. Two years later, in 2005, the city opened a new commercial airport, constructed with Turkish funds, and followed a few years after that by an expanded international airport.
Traditionally, the “Kurdish narrative is one of victimhood and one of grievances,” said Bilal Wahab, a fellow at the Washington Institute think tank. But in Iraq since 2003, “that is not the Kurdish story. The story is one of power and empowerment.”
With the Ottoman Empire’s collapse after World War I, the Kurds were promised an independent homeland in the 1920 Treaty of Sevres. But the treaty was never ratified, and “Kurdistan” was carved up. Since then, there have been Kurdish rebellions in Iran, Iraq and Turkey, while in Syria, Kurds have clashed with Turkish-backed forces.
In Iraq, the Kurdish region won de facto self-rule in 1991, when the United States imposed a no-fly zone over it in response to Saddam’s brutal repression of Kurdish uprisings.
“We had built our own institutions, the parliament, the government,” said Hoshyar Zebari, a top official with the Kurdistan Democratic Party who served as foreign minister in Iraq’s first post-Saddam government. “Also, we had our own civil war. But we overcame that,” he said, referring to fighting between rival Kurdish factions in the mid-1990s.
Speaking in an interview at his palatial home in Masif, a former resort town in the mountains above Irbil that is now home to much of the KDP leadership, Zabari added, “The regime change in Baghdad has brought a lot of benefits to this region.”
Iraqi President Abdul Latif Rashid, from the rival Patriotic Union of Kurdistan, also gave a glowing assessment of the post-2003 developments. The Kurds, he said, had aimed for “a democratic Iraq, and at the same time some sort of … self-determination for the Kurdish people.”
With the US overthrow of Saddam, he said, “We achieved that ... We became a strong group in Baghdad.”
The post-invasion constitution codified the Kurdish region’s semi-independent status, while an informal power-sharing arrangement now stipulates that Iraq’s president is always a Kurd, the prime minister a Shiite and the parliament speaker a Sunni.
But even in the Kurdish region, the legacy of the invasion is complicated. The two major Kurdish parties have jockeyed for power, while Irbil and Baghdad have been at odds over territory and the sharing of oil revenues.
Meanwhile, Arabs in the Kurdish region and minorities, including the Turkmen and Yazidis, feel sidelined in the new order, as do Kurds without ties to one of the two key parties that serve as gatekeepers to opportunities in the Kurdish region.
As the economic boom has stagnated in recent years, due to both domestic issues and global economic trends, an increasing number of Kurdish youths are leaving the country in search of better opportunities. According to the International Labor Organization, 19.2 percent of men and 38 percent of women aged 15-24 were unemployed and out of school in Irbil province in 2021.
Wahab said Irbil’s post-2003 economic success has also been qualified by widespread waste and patronage in the public sector.
“The corruption in the system is really undermining the potential,” he said.
In Kirkuk, an oil-rich city inhabited by a mixed population of Kurds, Turkmen and Sunni Arabs where Baghdad and Irbil have vied for control, Kahtan Vendavi, local head of the Iraqi Turkmen Front party, complained that the American forces’ “support was very clear for the Kurdish parties” after the 2003 invasion.
Turkmen are the third largest ethnic group in Iraq, with an estimated 3 million people, but hold no high government positions and only a handful of parliamentary seats.
In Kirkuk, the Americans “appointed a governor of Kurdish nationality to manage the province. Important departments and security agencies were handed over to Kurdish parties,” Vendavi said.
Some Kurdish groups also lost out in the post-2003 order, which consolidated the power of the two major parties.
Ali Bapir, head of the Kurdistan Justice Group, a Kurdish Islamist party, said the two ruling parties “treat people who do not belong to (them) as third- and fourth-class citizens.”
Bapir has other reasons to resent the US incursion. Although he had fought against the rule of Saddam’s Baath Party, the US forces who arrived in 2003 accused him and his party of ties to extremist groups. Soon after the invasion, the US bombed his party’s compound and then arrested Bapir and imprisoned him for two years.
Kurds not involved in the political sphere have other, mainly economic, concerns.
Picnicking with her mother and sister and a pair of friends at the sprawling Sami Abdul Rahman Park, built on what was once a military base under Saddam, 40-year-old Tara Chalabi acknowledged that the “security and safety situation is excellent here.”
But she ticked off a list of other grievances, including high unemployment, the end of subsidies from the regional government for heating fuel and frequent delays and cuts in the salaries of public employees like her.
“Now there is uncertainty if they will pay this month,” she said.
Nearby, a group of university students said they are hoping to emigrate.
“Working hard, before, was enough for you to succeed in life,” said a 22-year-old who gave only her first name, Gala. “If you studied well and you got good grades … you would have a good opportunity, a good job. But now it’s very different. You must have connections.”
In 2021, hundreds of Iraqi Kurds rushed to Belarus in hopes of crossing into Poland or other neighboring EU countries. Belarus at the time was readily handing out tourist visas in an apparent attempt to pressure the European Union by creating a wave of migrants.
Those who went, Wahab said, were from the middle class, able to afford plane tickets and smuggler fees.
“To me, it’s a sign that it’s not about poverty,” he said. “It’s basically about the younger generation of Kurds who don’t really see a future for themselves in this region anymore.”
Kurds remain biggest winners from US-led invasion of Iraq
https://arab.news/5svzg
Kurds remain biggest winners from US-led invasion of Iraq
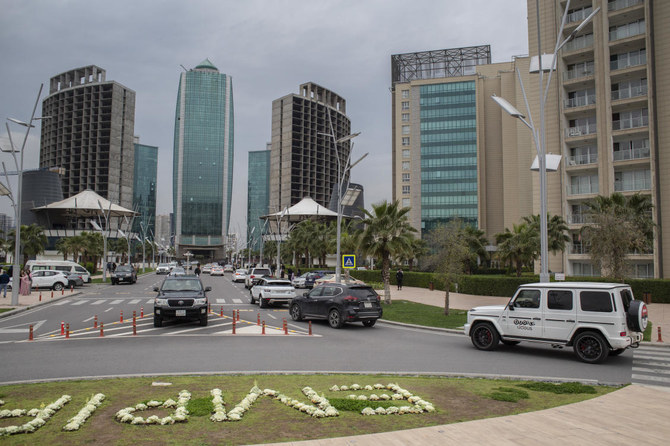

- Irbil, the seat of the semi-autonomous Kurdish region in northern Iraq, was once a backwater provincial capital
- That rapidly changed after the 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq that toppled Saddam Hussein
Israeli missiles hit site in Iran, Iran and US media report

DUBAI/WASHINGTON: Israeli missiles have hit a site in Iran, ABC News reported late on Thursday, citing a US official.
Commercial flights began diverting their routes early Friday morning over western Iran without explanation as one semiofficial news agency in the Islamic Republic claimed there had been “explosions” heard over the city of Isfahan.
The incident comes as tensions remain high in the wider Middle East after Iran’s unprecedented missile-and-drone attack on Israel last weekend. Most of the drones and missiles were downed before reaching Israeli territory.
Dubai-based carriers Emirates and FlyDubai began diverting around western Iran about 4:30 a.m. local time. They offered no explanation, though local warnings to aviators suggested the airspace may have been closed.
The semiofficial Fars news agency reported on the sound of explosions over Isfahan near its international airport. It offered no explanation for the blast. However, Isfahan is home to a major air base for the Iranian military, as well as sites associated with its nuclear program.
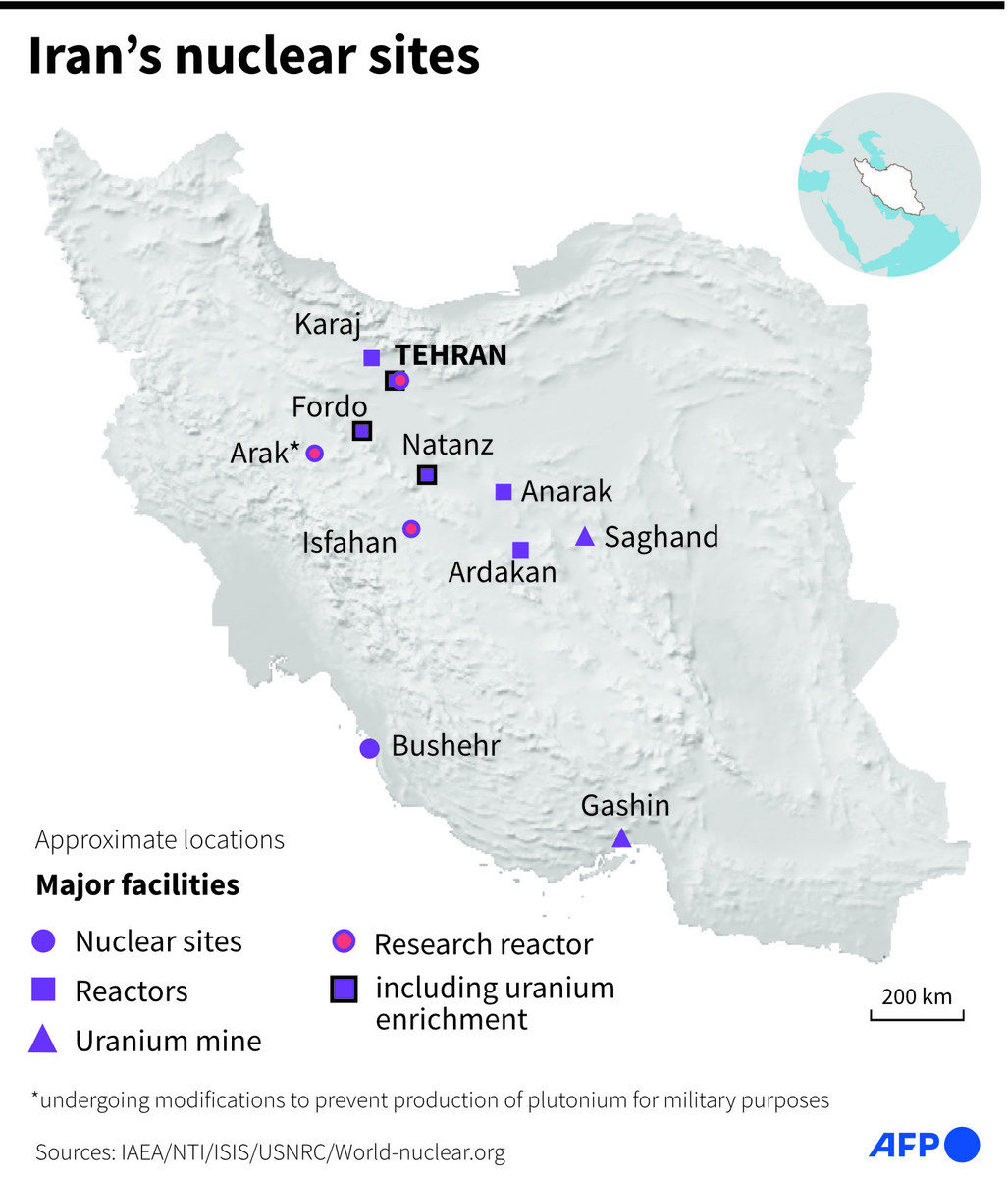
“Flights over Isfahan, Shiraz and Tehran cities have been suspended,” state media reported.
Iran’s government offered no immediate comment.
Isfahan is some 350 kilometers (215 miles) south of Iran’s capital, Tehran.
Iran told the United Nations Security Council on Thursday that Israel “must be compelled to stop any further military adventurism against our interests” as the UN secretary-general warned that the Middle East was in a “moment of maximum peril.”
Israel had said it was going to retaliate against Iran’s April 13 missile and drone attack.
Hamas slams US veto of Palestinian UN membership bid

PALESTINIAN TERRITORIES: Palestinian militant group Hamas condemned on Friday the US veto that ended a long-shot Palestinian bid for full United Nations membership.
“Hamas condemns the American veto at the Security Council of the draft resolution granting Palestine full membership in the United Nations,” the Gaza Strip rulers said in a statement, which comes amid growing international concern over the toll inflicted by the war in the besieged Palestinian territory.
The veto by Israel’s main ally and military backer had been expected ahead of the vote, which took place more than six months into Israel’s offensive in Gaza, in retaliation for the deadly October 7 attack by Hamas militants.
Twelve countries voted in favor of the draft resolution, which was introduced by Algeria and “recommends to the General Assembly that the State of Palestine be admitted to membership of the United Nations.” Britain and Switzerland abstained.
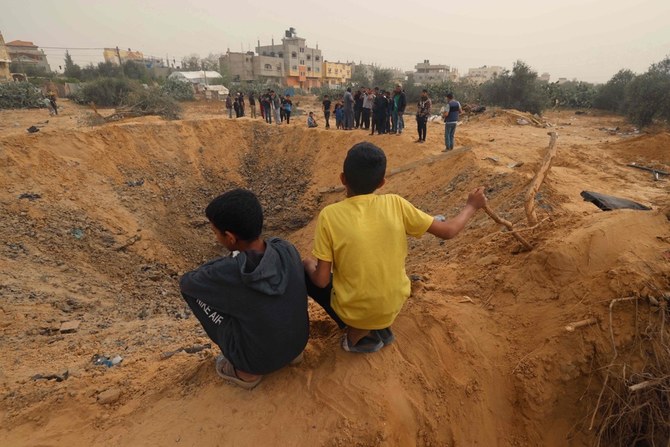
Gazans search for remains after deadly Rafah strike

An Israeli strike hit the home where a displaced Palestinian family was sheltering in the southern city of Rafah, relatives and neighbors told AFP as they scraped at the soil with their hands.
Al-Arja said the blast killed at least 10 people.
“We retrieved the remains of children and women, finding arms and feet. They were all torn to pieces.
“This is horrifying. It’s not normal,” he said, hauling concrete and broken olive branches from the wreckage. “The entire world is complicit.”
Soon after the war began on Oct. 7, Israel told Palestinians living in the north of Gaza to move to “safe zones” in the territory’s south, like Rafah.
But Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has since vowed to invade the city, where around 1.5 million people live in shelters, more than half the territory’s population.
“How is Rafah a safe place?” said Zeyad Ayyad, a relative of the victims. He sighed as he cradled a fragment of the remains.
“I heard the bombing last night and then went back to sleep. I did not think it hit my aunt’s house.”
The search for remains was long and painful. The strike left a huge crater and children picked through the rubble while neighbors removed debris, tarpaulin, a pink top.
“We can see them under the rubble and we’re unable to retrieve them,” Al-Arja said.
“These are people who came from the north because it was said the south is safe.”
“They struck without any warning,” he said.
In a separate strike on the house in Rafah’s Al-Salam neighborhood overnight on Tuesday, rescue crews recovered the corpses of eight family members, including five children and two women, Gaza’s civil defense service said.
“An Israeli rocket hit a house of displaced people,” said resident Sami Nyrab.
“My sister’s son-in-law, her daughter, and her children were having dinner when an Israeli missile demolished their house over their heads.”
Dubai clears up after epic rains swamp glitzy city

- The rains were the heaviest experienced by the UAE in the 75 years that records have been kept
DUBAI: Dubai was busy on Thursday clearing its waterlogged roads and drying out flooded homes two days after a record storm deposited a year’s worth of rainfall in a day.
Dubai International Airport, a major travel hub, struggled to clear a backlog of flights, and many roads were still flooded in the aftermath of Tuesday’s deluge.
The rains were the heaviest experienced by the UAE in the 75 years that records have been kept.
They brought much of the country to a standstill and caused significant damage.
Flooding trapped residents in traffic, offices, and homes.
Many reported leaks at their homes, while footage circulated on social media showed malls overrun with water pouring from roofs.
Traffic remained heavily disrupted.
A highway through Dubai was reduced to a single lane in one direction, while the main road connecting Dubai with Abu Dhabi was closed in the Abu Dhabi direction.
“This was like nothing else. It was like an alien invasion,” said Jonathan Richards, a Dubai resident from Britain.
“I woke up the other morning to people in kayaks, pet dogs, pet cats, and suitcases outside my house.”
Another resident, Rinku Makhecha, said the rain swamped her newly renovated house, which she moved into two weeks ago.
“My entire living room is just like ... all my furniture is floating right now,” she said.
In Dubai’s streets, some vehicles, including buses, could be seen almost entirely submerged in water.
Long queues formed at petrol stations.
Dubai Airport had not resumed normal operation after the storm flooded taxiways, forcing flight diversions, delays, and cancellations.
Dubai Airport Chief Operating Officer Majed Al Joker told Al Arabiya TV he expected Dubai International Airport to reach 60 to 70 percent capacity by the end of Thursday and full operational capacity within 24 hours.
The airport struggled to get food to stranded passengers, with nearby roads flooded and overcrowding limited access to those who had confirmed bookings.
While some roadways into hard-hit communities remain flooded, delivery services across Dubai, whose residents are used to ordering everything at the click of a mouse, slowly began returning to the streets.
Following Tuesday’s events, questions were raised about whether cloud seeding, a process that the UAE frequently conducts, could have caused the heavy rains.
A UAE government agency overseeing cloud seeding — manipulating clouds to increase rainfall — denied conducting such operations before the storm.
President Sheikh Mohammed bin Zayed Al-Nahyan said in a statement that he had ordered authorities to assess the damage and support families impacted by the storm.
Dubai’s Crown Prince Sheikh Hamdan bin Rashid Al-Maktoum said on X that the safety of citizens, residents, and visitors was the utmost priority.
“At a meeting with government officials in Dubai, we set directives to prepare comprehensive plans in response to natural crises such as the unexpected current weather conditions,” he said.
Hezbollah says 2 fighters killed in Israeli strikes

- GPS interference affecting both sides of Lebanese border, source says
BEIRUT: Two Hezbollah fighters were killed on Wednesday as Israel intensified strikes on south Lebanon following an attack by the Iran-backed group that wounded 14 Israeli soldiers.
Israel and Hezbollah have exchanged near-daily cross-border fire since Palestinian militant group Hamas attacked southern Israel on Oct. 7, triggering war in the Gaza Strip.
A security source said: “Hezbollah’s complex attack against the Israeli army in Wadi Al-Aramshe early on Wednesday, which led to the injury of 14 Israeli soldiers, including six with serious injuries, was absorbed by the Israeli side after the painful blow it directed at the party by assassinating three of its field officials.”
The Israeli army responded to the Wadi Al-Aramshe operation on Wednesday night by targeting the town of Iaat in the Bekaa Valley, 5 km from Baalbek. A drone strike hit a warehouse belonging to a member of the Al-Zein family, resulting in light wounds to one civilian.
Israel continues to jam GPS around the Lebanese southern border region, especially during military operations.
A security source said: “This interference negatively affects both the Israeli army and Hezbollah in targeting objectives.”
Hezbollah announced a series of operations since dawn on Thursday, targeting Israeli military sites opposite the Lebanese border.
The group targeted an Israeli force attempting to withdraw a military vehicle that was targeted on Wednesday at Metula, opposite the Lebanese town of Kfarkela.
At dawn, Israeli soldiers in Al-Malikiyah, opposite the Lebanese town of Aitaroun, were targeted by Hezbollah using missiles.
The group also targeted Israeli soldiers in Al-Marj.
“After careful monitoring and anticipation of the enemy’s movement at Al-Marj … they were targeted with missile weapons and suffered a direct hit; some died while others were injured,” the group said in a statement.
Hezbollah attacked Israeli soldiers using missiles in the Hanita forest, opposite the Lebanese town of Alma Al-Shaab.
On Thursday, the party mourned two members killed in Wednesday night’s shelling of Kfarkela. Mohammed Jamil Al-Shami from Kfarkela and Ali Ahmed Hamadeh from Doueir were killed in the Israeli operation.
The Israeli army targeted Lebanese towns with heavy shelling until dawn on Thursday. The town of Khiam was a priority target; correspondents in the area counted seven strikes and 128 artillery and phosphorous shells impacting between 8 p.m. and 4 a.m.
A young man from Habboush, Ahmed Hassan Al-Ahmed, was killed in the shelling and mourned by residents of his town.
Jets struck Hezbollah targets in Khiam, including infrastructure and two military buildings, the Israeli army said.
Israeli drones targeted a house on the outskirts of Markaba and in Blida on Thursday, with casualties reported.
The Israeli army also targeted Kfarkela with two missiles from a drone, and with artillery and phosphorous shells. From Metula opposite the border, Israeli soldiers combed the town with heavy machine guns.
The outskirts of Dhayra, Al-Bustan and Aita Al-Shaab were hit by gunfire from the Israeli position in Birkat Risha and other positions adjacent to the Blue Line.
German airline Lufthansa announced on Thursday it had extended the suspension of flights to Beirut and Tehran until April 30.
The decision was taken on the night of the Iranian attack on Israel last weekend.
UNIFIL spokesman Andrea Tenenti said that the organization’s peacekeepers “remain in their positions and carry out their duties, as well as our civilian staff.”
He added: “The safety and security of UN staff and their families are our priority.”



















