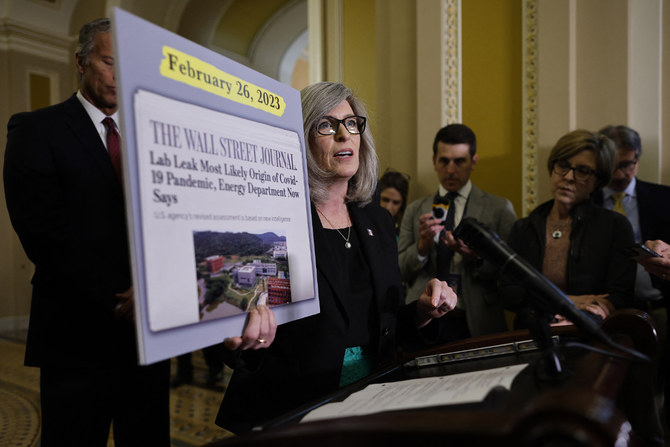WASHINGTON: COVID-19’s origins remain hazy. Three years after the start of the pandemic, it’s still unclear whether the coronavirus that causes the disease leaked from a lab or spread to humans from an animal.
This much is known: When it comes to COVID-19 misinformation, any new report on the virus’ origin quickly triggers a relapse and a return of misleading claims about the virus, vaccines and masks that have reverberated since the pandemic began.
It happened again this week after the Energy Department confirmed that a classified report determined, with low confidence, that the virus escaped from a lab. Within hours, online mentions of conspiracy theories involving COVID-19 began to rise, with many commenters saying the classified report was proof they were right all along.
Far from definitive, the Energy Department’s report is the latest of many attempts by scientists and officials to identify the origin of the virus, which has now killed nearly 7 million people after being first detected in the central Chinese city of Wuhan in late 2019.
The report has not been made public, and officials in Washington stressed that a variety of US agencies are not in agreement on the origin. On Tuesday, FBI Director Christopher Wray told Fox News that the FBI “has for quite some time now” assessed that the pandemic’s origins are “most likely a potential lab incident in Wuhan.”
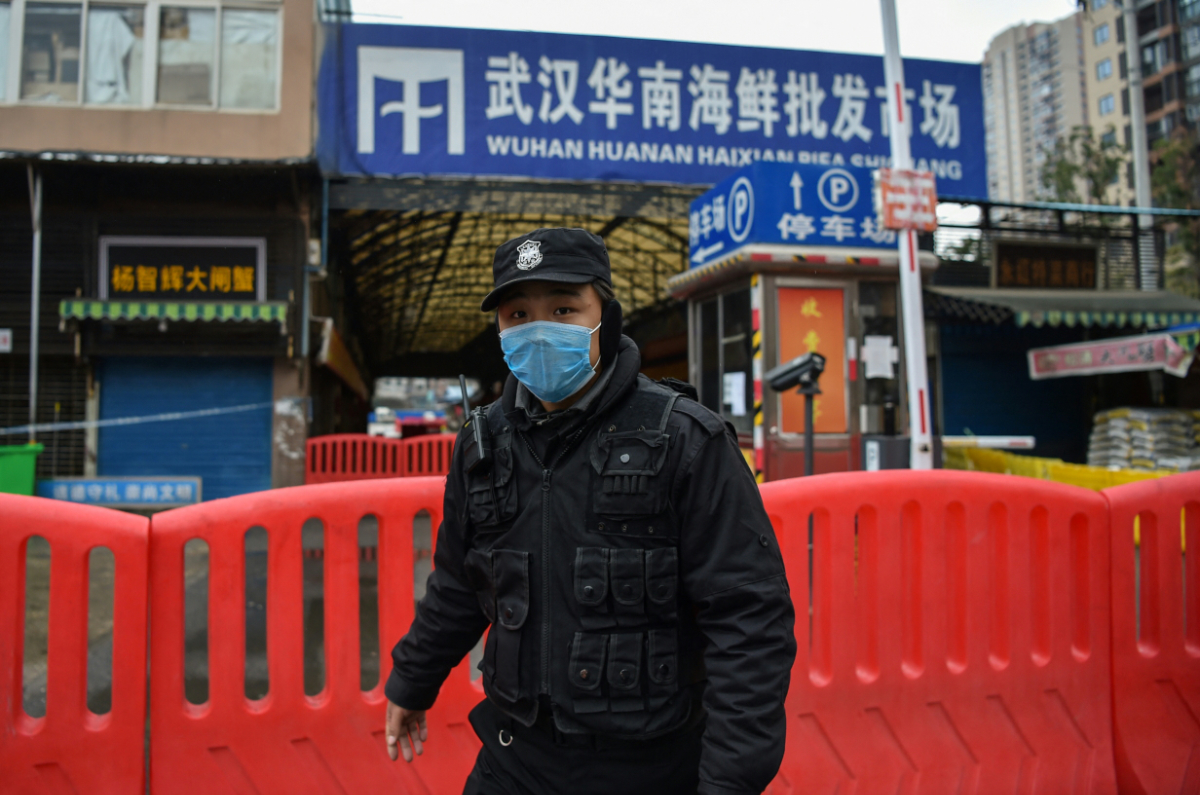

In this January 24, 2020 photo, a police officer stands guard outside the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, where the coronavirus was detected in Wuhan on Jan. 24, 2020. (AFP)
But others in the US intelligence community disagree, and there’s no consensus. Many scientists believe the likeliest explanation is that the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 jumped from animals to humans, possibly at Wuhan’s Huanan market, a scenario backed up by multiple studies and reports. The World Health Organization has said that while an animal origin remains most likely, the possibility of a lab leak must be investigated further before it can be ruled out.
People should be open-minded about the evidence used in the Energy Department’s assessment, according to virologist Angela Rasmussen. But she said that without evaluating the classified report, she can’t assess if it’s persuasive enough to challenge the conclusion that the virus spread from an animal.
“The vast majority of the evidence continues to support natural origin,” Rasmussen told The Associated Press Wednesday. “I’m a scientist. I need to see the evidence rather than take the FBI director’s word for it.”
Many of those citing the report as proof, however, seemed uninterested in the details. They seized on the report and said it suggests the experts were wrong when it came to masks and vaccines, too.
“School closures were a failed & catastrophic policy. Masks are ineffective. And harmful,” said a tweet that’s been read nearly 300,000 times since Sunday. “COVID came from a lab. Everything we skeptics said was true.”
Overall mentions of COVID-19 began to rise after The Wall Street Journal published a story about the Energy Department report on Sunday. Since then, mentions of various COVID-related conspiracy theories have soared, according to an analysis conducted by Zignal Labs, a San Francisco-based media intelligence firm, and shared with The Associated Press.
While the lab leak theory has bounced around the Internet since the pandemic began, references to it soared 100,000 percent in the 48 hours after the Energy Department report was revealed, according to Zignal’s analysis, which combed through social media, blogs and other sites.
Many of the conspiracy theories contradict each other and the findings in the Energy Department report. In a tweet on Tuesday, US Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene, a Republican from Georgia, called COVID-19 a “man made bioweapon from China.” A follower quickly challenged her: “It was made in Ukraine,” he responded.
With so many questions remaining about a world event that has claimed so many lives and upended even more, it’s not at all surprising that COVID-19 is still capable of generating so much anger and misinformation, according to Bret Schafer, a senior fellow at the Alliance for Securing Democracy, a Washington-based organization that has tracked government propaganda about COVID-19.
“The pandemic was so incredibly disruptive to everyone. The intensity of feelings about COVID, I don’t think that’s going to go away,” Schafer said. “And any time something new comes along, it breathes new life into these grievances and frustrations, real or imagined.”
Chinese government officials have in the past used their social media accounts to amplify anti-US conspiracy theories, including some that suggested the US created the COVID-19 virus and framed its release on China.
So far, they’ve taken a quieter approach to the Energy Department report. In their official response, China’s government dismissed the agency’s assessment as an effort to politicize the pandemic. Online, Beijing’s sprawling propaganda and disinformation network was largely silent, with just a few posts criticizing or mocking the report.
“BREAKING,” a pro-China YouTuber wrote on Twitter. “I can now announce, with ‘low confidence,’ that the COVID pandemic began as a leak from Hunter Biden’s laptop.”