DUBAI: Although mental health issues present a significant challenge to productivity, a benchmark survey in Saudi Arabia has revealed yawning gaps between the services that human resources departments claim to provide and what employees believe is actually on offer, with employees largely unwilling to discuss workplace stress.
For the report, entitled “State of Wellness at the Workplace,” researchers talked to 4,000 employees in the Kingdom’s public and private sectors to assess where challenges arise in the workplace and how to fix them.
The study, which was compiled by Tuhoon, a Saudi tech startup founded in 2021, was carried out in collaboration with the Saudi National Center for Mental Health and the Ministry of Health.
“The surveys were filled out anonymously, which made workers more receptive to talk about their issues,” Tuhoon CEO Fares Ghandour told Arab News.
“We found females are more willing to talk on a personal level but they opt out of discussing their mental health in the workspace as they do not wish to be perceived as weaklings. We also found workers above the age of 45 are less likely to talk about their mental health than younger generations.”
Tuhoon recently launched a smartphone app designed to help users improve their mental health, manage stress and get better quality of sleep through personalized, culturally relevant audio content.
This content includes meditation and mindfulness exercises, sleep stories, masterclasses, book summaries, deep-focus music, and emergency playlists. It is curated by doctors, clinical psychologists, and certified meditation and self-awareness coaches.
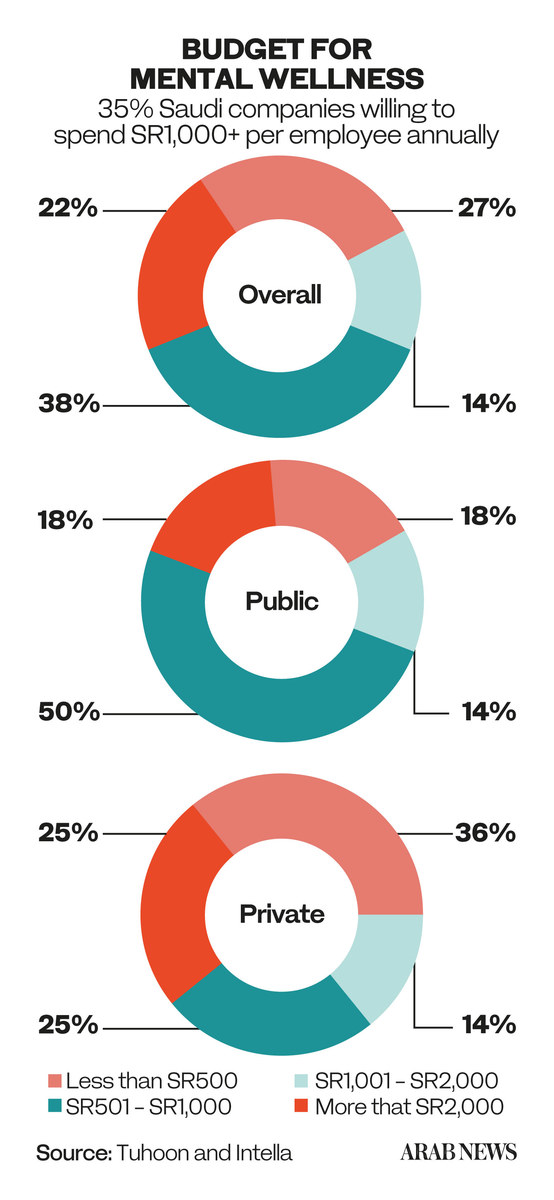
The study indicates that more than 80 percent of Saudi workplaces have no budget to support the mental health of their employees, despite the rising number of workers reporting a decline in their well-being.
The report says that the lack of mental health monitoring has taken a significant toll on the cultural and economic performance of many organizations, and the private sector is perceived as offering less assistance than the public sector.
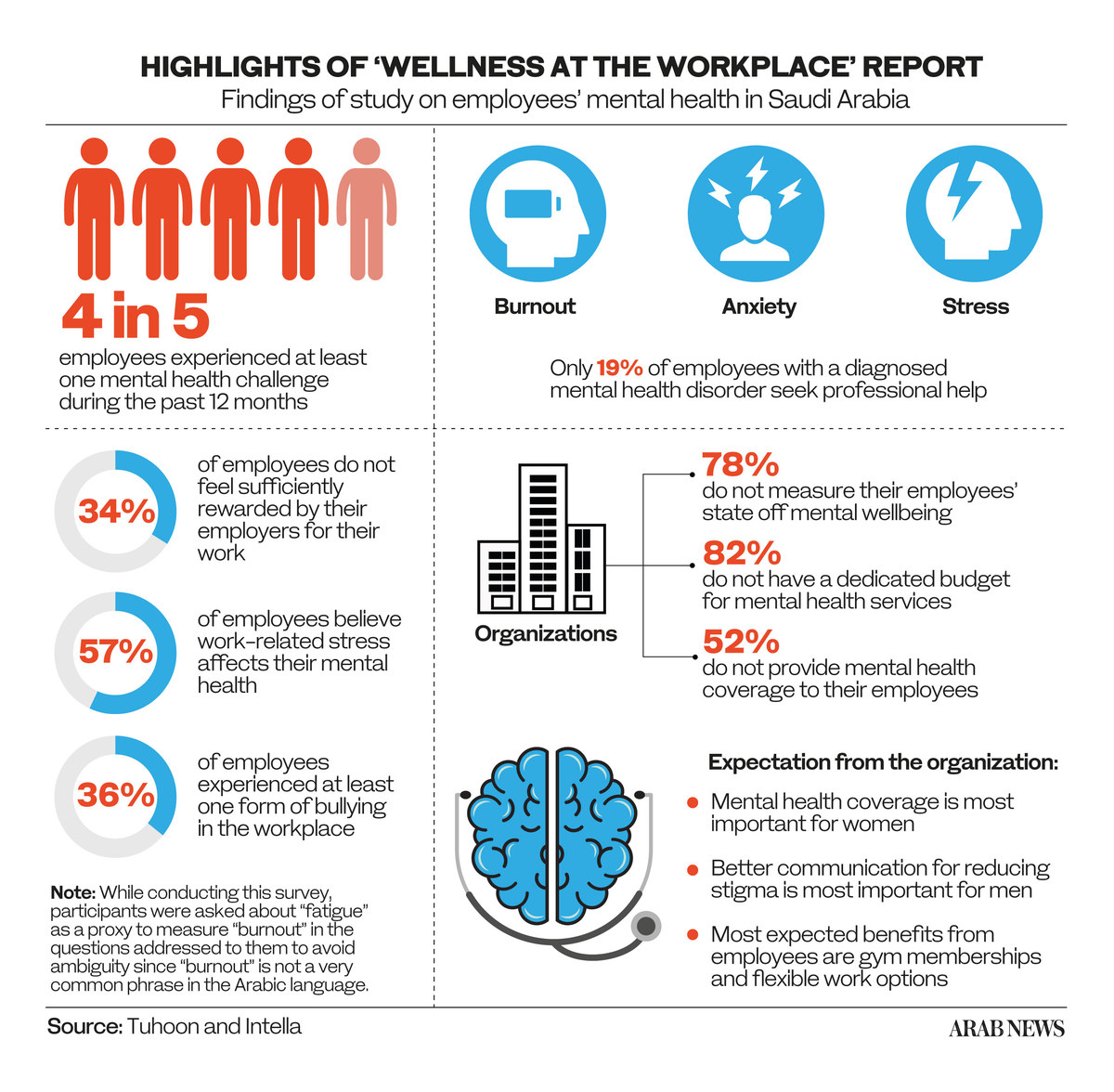
According to the report, most workplaces are failing to prioritize the mental health of employees. It says that 78 percent of organizations do not measure their workers’ mental health at all, 82 percent have no dedicated resources for mental health services, and 52 percent do not provide health insurance cover for mental health.
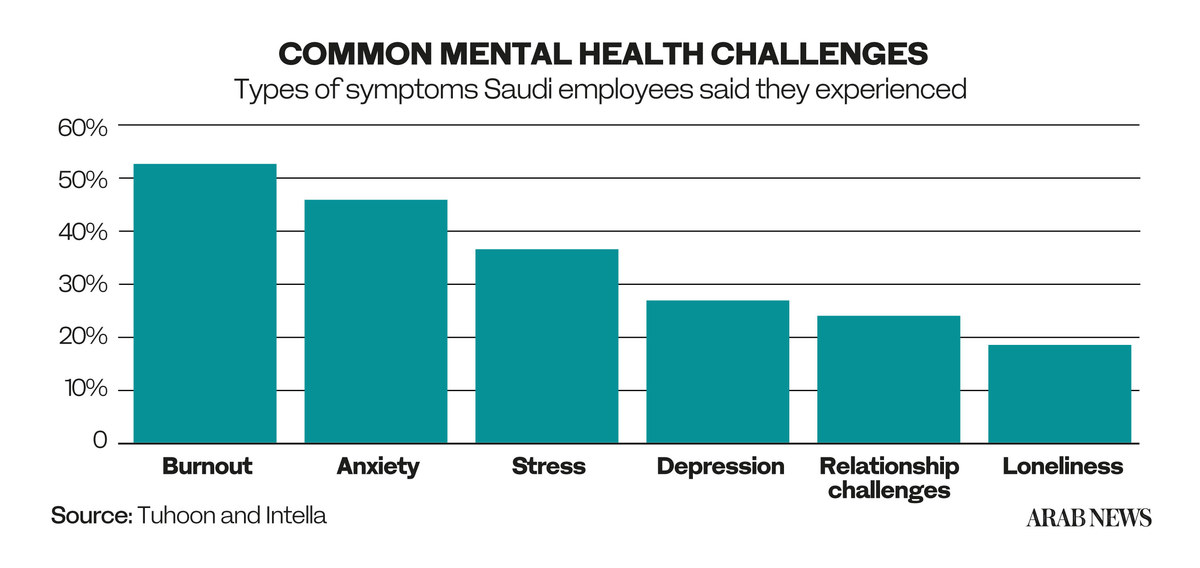
It also says that at least four out of five employees experienced at least one mental health problem in the past year. The most common symptoms were anxiety, burnout and stress, as well as depression, relationship challenges and loneliness.
The available data on the issue of wellness in Saudi workplaces, including details of programs and benefits employers offer their workers, remains limited but the culture surrounding mental health does appear to be improving.
However, the Arab world in general lags in this regard which Ghandour says is why he founded Tuhoon.
“I have been investing in tech businesses for nine years,” he told Arab News. “I decided I wanted to build and invest in something I am passionate about, and the mental health cause is dear to me.
“I approached Dr. Naif Almutawa, a clinical psychologist, and Aymane Sennoussi, who became co-founders, and I put my time, energy and effort into making Saudi Arabia and the Arab world a happier and healthier place.”
Mental health problems are among the leading causes of disability worldwide, with depression topping the list. They can affect people regardless of age, culture and socioeconomic status.
The World Health Organization estimates a quarter of the global population will suffer a mental health issue at some point during their lives, and that about 12 billion working days are lost each year to depression and anxiety at an annual cost of $1 trillion in lost productivity.
The Tuhoon survey of Saudi workplaces posed the question: “How would you rate your mental health over the past 12 months on a scale, from 0 to 4?” It found that 24 percent of respondents ranked their mental health as below average.

Almost a quarter of respondents ranked their mental health below average, with 44 percent of Saudi women and 32 percent of Saudi men in the workplace prone to burnout. (Shutterstock)
Among the respondents, women were 62 percent more likely to develop a mental health problem than men, while 44 percent of women in work were found to be prone to burnout and anxiety compared with 32 percent of men.
The research also revealed that 57 percent believed work-related stress affected their mental well-being.
Of the 50 human resources departments that were surveyed, 59 percent said their organizations did not provide mental health insurance coverage, and 82 percent said their companies did not have an employee assistance program. EAPs are designed to help workers resolve professional and personal problems that might be affecting their productivity.
The results of the Saudi surveys compare with the findings of a 2022 workplace report entitled “Mental Health in America” in which one-third of HR professionals said their organization provided no mental health services to employees, 27 percent said their organization was not sure of the proper benefits to provide, and 18 percent said their organization was unsure of what plan or insurance to offer workers.
In the UK, according to a 2022 study by the Chartered Institute of Personnel Development, there is weak leadership on the issue of mental health in the workplace, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. Figures show that only 29 percent of employers are able to spot early signs of mental health problems in their workers. Less than half (42 percent) of employers said that their leaders focus and encourage positive mental health by actions and behavior.
Good mental health is viewed as a key measure of prosperous and successful nations and organizations.
The Kingdom’s public sector scored higher (45 percent) than the private sector (36 percent) in terms of the proportion of employers that offered health insurance coverage that includes mental health services. Ghandour believes this is because the public sector plays such a major role in the Saudi economy, and so employees are looked after relatively well in an effort to maintain high productivity levels.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
According to studies by the Arab Barometer research network, however, more than half of residents in the Arab world find it hard to find decent mental health services. And globally, organizations struggle in the execution of HR policies designed to support mental health.
In 2019, the Saudi National Mental Health Survey found that 34 percent of people had experienced a mental health issue at some point in their lives, with blue collar-workers more open to reporting the challenges they faced than their white-collar counterparts.
It also found the most prevalent mental illnesses in the Kingdom were separation anxiety disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, social phobia, and obsessive compulsive disorder.
Better-educated Saudis were more prone to such conditions.
Some 80 percent of respondents afflicted by a serious mental illness said they had not sought any treatment, while 8.9 percent said they had gone to a religious adviser or non-medical healer for help.
Experts say that to promote a healthier work culture, employers need to prioritize well-being, work to reduce the stigma that still surrounds mental illness, and provide mental health coverage for employees.
Tuhoon believes workplaces need to start viewing mental health as a collective issue rather than an individual problem. It recommends nine cost-effective steps to improve workplace mental health and, as a result, boost productivity.
These steps include workshops to raise awareness of the issue, and webinars on topics such as stress management, dealing with burnout, and increasing connectivity between workers. It also suggests offering additional days off to increase morale, training managers to spot mental health problems in workers, and creating a more welcoming and trusting work environment.

I decided I wanted to build and invest in something I am passionate about, and the mental health cause is dear to me,” said Fares Ghandour, CEO of Tuhoon. (Supplied)
Furthermore, Tuhoon urges employers to promote workplace behaviors that reduce burnout by encouraging workers to take time off if needed, offering a more flexible work environment, promoting a healthy balance between work and personal life, and creating a “check in” culture.
Additional recommendations include encouraging employers to use mental health assessments as a tool to measure stress and challenges, and to connect workers with helpful resources if needed.
Tuhoon says mental health “first aid” courses could also provide staff with the skills they need to detect the early signs of stressors and provide solutions and rapid responses to help distressed workers.
This could further reduce the stigma surrounding mental health in the workplace. Appointing “mental health ambassadors” would also contribute to more open and supportive conversations in the workplace.
Regarding the well-being of women in particular, Tuhoon urges employers to adjust workplace policies and encourage female employees to report harassment and sexual assault through the provision of a proper platform for doing so. Salaries and promotions must also be fairly determined regardless of gender.
Finally, employers and employees are encouraged to show gratitude in the workplace and introduce mechanisms through which workers feel able to talk about things or people they are grateful for inside and outside of work.
Tuhoon believes this could lead to enhanced job satisfaction, fewer sick days, the promotion of a positive and more trusting work environment, and increased productivity.


















