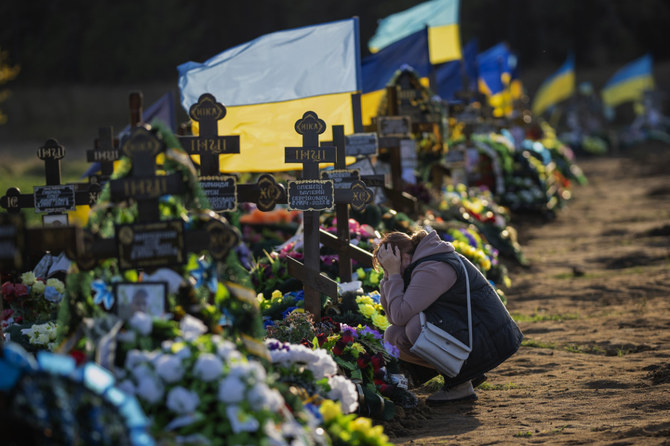
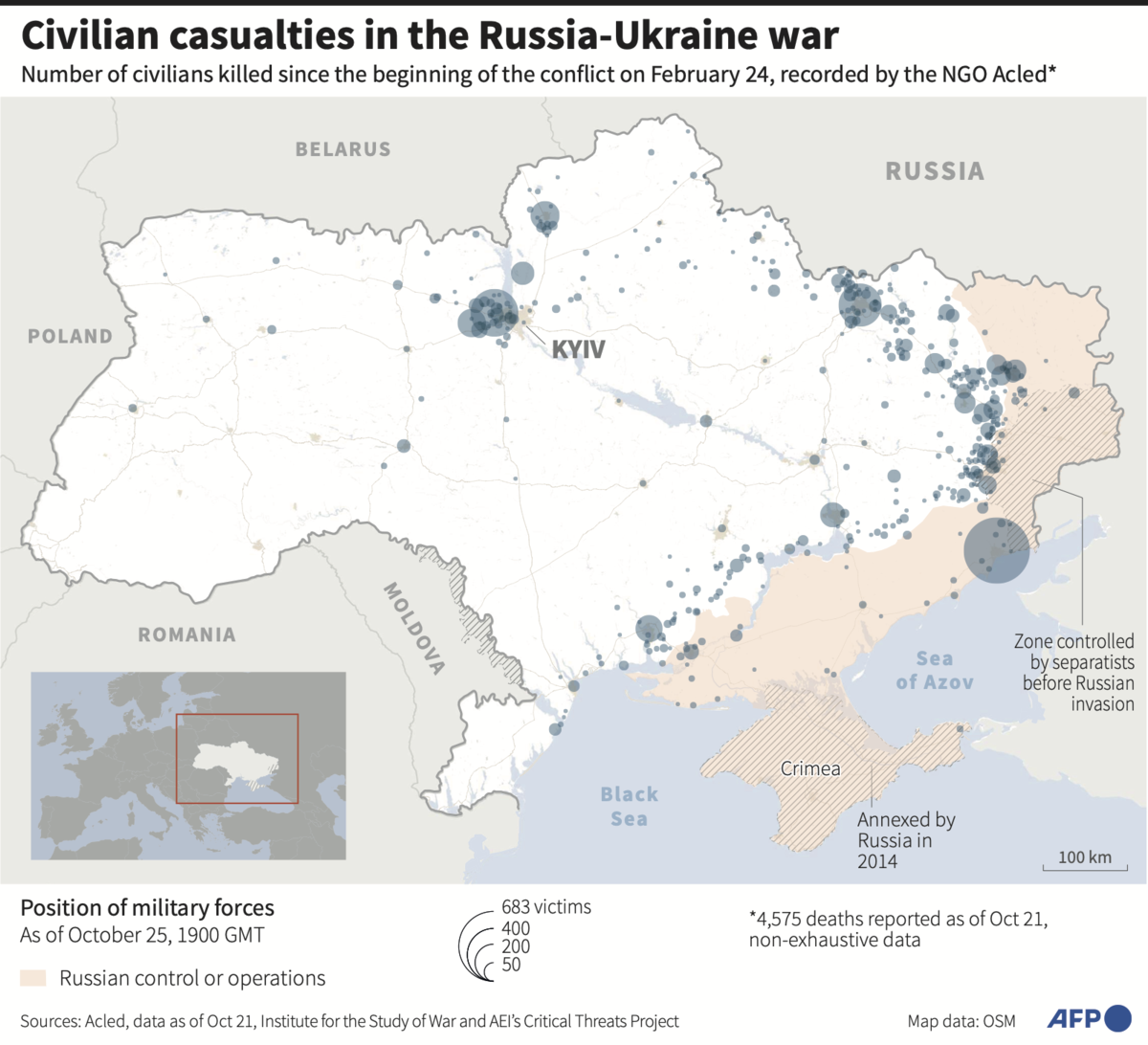
FRONT LINES NORTH OF KHERSON, Ukraine: Ukrainian troops are holding out against repeated attacks by Russian forces in two eastern towns while those at the southern front are poised to battle for the strategic Kherson region, which Russia appears to be reinforcing.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky said in a Wednesday evening video address that there would be good news from the front but he gave no details.
He did not mention what was happening in Kherson, which officials and military analysts have predicted will be one of the most consequential battles of the war since Russia invaded Ukraine eight months ago.
The most severe fighting in eastern Ukraine was taking place near Avdiivka, outside Donetsk, and Bakhmut, Zelensky said.
“This is where the craziness of the Russian command is most evident. Day after day, for months, they are driving people to their deaths there, concentrating the highest level of artillery strikes,” he said.
Russian forces have repeatedly tried to seize Bakhmut, which sits on a main road leading to the Ukrainian-held cities of Sloviansk and Kramatorsk.
The looming battle for Kherson city at the mouth of the Dnipro River will determine whether Ukraine can loosen Russia’s grip on the south.
Fresh recruits inserted
While much of the front line remains off limits to journalists, at one section of the front north of the Russian-occupied pocket on the west bank of the Dnipro, Ukrainian soldiers said Russian shelling was stepping up again after having tailed off in recent weeks.
Radio intercepts indicated freshly mobilized recruits had been sent to the front and Russian forces were firmly dug in.
“They have good defensive lines with deep trenches, and they are sitting deep underground,” said Vitalii, a Ukrainian soldier squatting in a weed-choked irrigation canal, concealed from any prowling enemy drones by overhanging trees.
Ukrainian forces advanced along the Dnipro River in a dramatic push in the south at the start of this month, but progress appears to have slowed. Russia has been evacuating civilians on the west bank but says it has no plans to pull out its troops.
Oleksii Reznikov, Ukraine’s defense minister, said wet weather and rough terrain were making Kyiv’s counter-offensive in Kherson harder than it was in the northeast, where it pushed Russia back in September.
At the front, intermittent artillery fire echoed from both sides, with towers of smoke rising in the distance.
A Ukrainian helicopter gunship swept low over the fields, loosed rockets at the Russian positions and wheeled around spitting flares to distract any heat-seeking anti-aircraft rockets fired at it.
“In this area, they are very active. They shell every day and are digging trenches and preparing for defense,” a unit commander at the front, who asked to be quoted by his nickname, Nikifor, said of the Russians.
His location in Mykolaiv province could not be identified under Ukrainian military regulations.
The unit holds a network of well fortified trenches dug into tree lines opposite the Russian fortifications, and rain has turned the dirt tracks that access them to mud, especially where tank treads have churned them up.
Australia said it was sending 30 more armored vehicles and deploying 70 soldiers to Britain to help train Ukrainian troops there to bolster Kyiv’s war effort.
“We’re mindful that Ukraine needs to now be supported over the longer term if we’re going to put Ukraine in a position where it can resolve this conflict on its own terms,” Defense Minister Richard Marles told ABC television.
Nuclear rehearsal
Since Russia began losing ground in a counter-offensive in September, Russian President Vladimir Putin has taken a series of steps to intensify the conflict, calling up hundreds of thousands of Russian reservists, proclaiming the annexation of occupied land and repeatedly threatening to use nuclear weapons to defend Russia.
This month, Russia launched a new campaign of strikes using missiles and Iranian-made drones against Ukraine’s energy infrastructure, also hitting parks and homes across the country.
In Russia, the military staged a high-profile rehearsal for nuclear war, with state television broadcasts dominated by footage of submarines, strategic bombers and missile forces practicing launches in retaliation for an atomic attack.
Moscow has conducted a diplomatic campaign this week to promote an accusation that Kyiv is preparing to release nuclear material with a so-called “dirty bomb,” an allegation the West calls baseless and a potential pretext for Russian escalation.
Despite the rising tensions, United Nations aid chief Martin Griffiths said he was “relatively optimistic” that a UN-brokered deal that allowed a resumption of Ukraine Black Sea grain exports would be extended beyond mid-November.


















