WASHINGTON: President Vladimir Putin’s threat to use a nuclear weapon in Ukraine if Russian “territorial integrity” is threatened has sparked deep discussion in the West as to how it would respond.
“Those who are trying to blackmail us with nuclear weapons should know that the wind can also turn in their direction,” Putin said, adding: “This is not a bluff.”
However analysts aren’t convinced the Russian president is willing to be the first to unleash nuclear weapons since the US bombed Japan in 1945.
AFP spoke with several experts and officials about the possible scenarios that could arise should Russia carry out a nuclear attack.
Analysts say Moscow would likely deploy one or more “tactical” or battlefield nuclear bombs.
These are small weapons, ranging from 0.3 kilotons to 100 kilotons of explosive power, compared to the 1.2 megatons of the largest US strategic warhead or the 58 megaton bomb Russia tested in 1961.
Tactical bombs are designed to have a limited impact on the battlefield, compared to strategic nuclear weapons which are designed to fight and win all-out wars.
But “small” and “limited” are relative: The atom bomb the US dropped on Hiroshima in 1945 to devastating effect was just 15 kilotons.
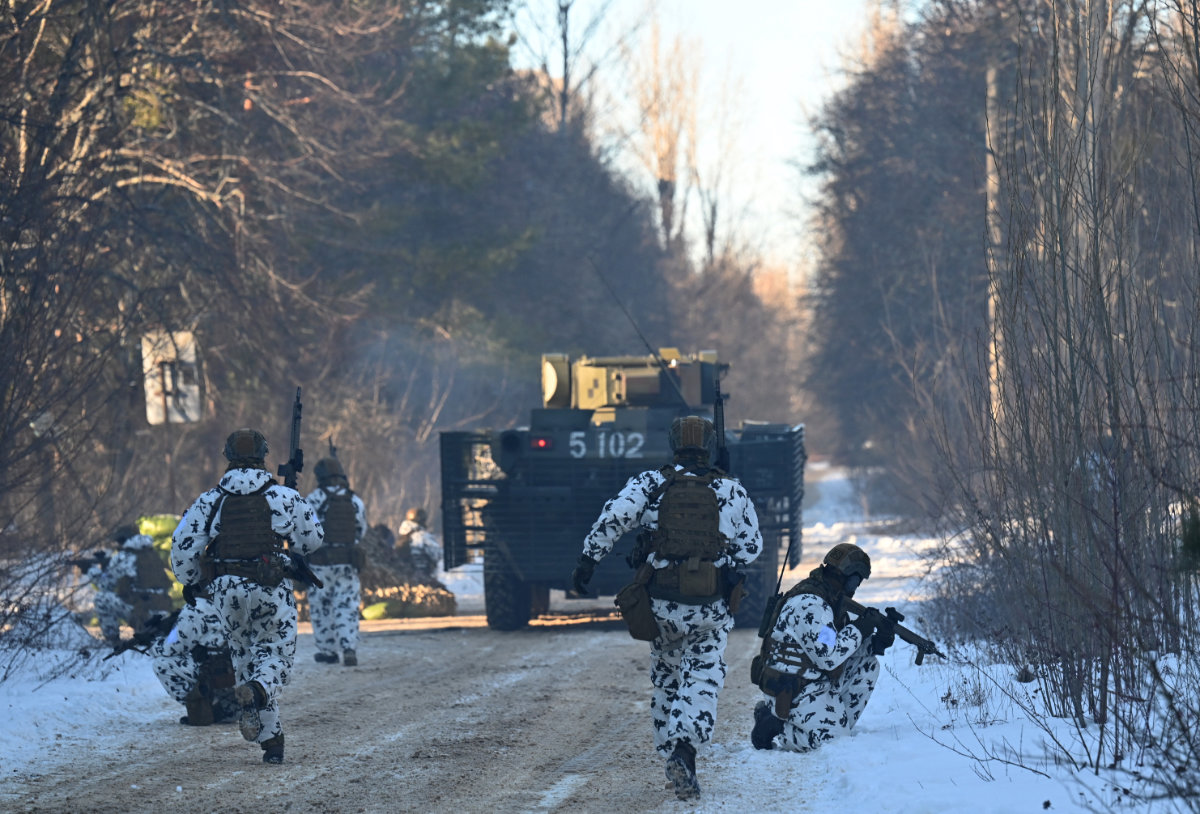

Ukrainian troops take part in a joint tactical and special exercises in a ghost city of Pripyat, near Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant on Feb. 4, 2022. (AFP file)
Analysts say Russia’s goal in using a tactical nuclear bomb in Ukraine would be to frighten it into surrender or submission to negotiations, and to divide the country’s Western backers.
Mark Cancian, a military expert with the CSIS International Security Program in Washington, said Russia would not likely use nuclear weapons on the front lines.
Capturing 20 miles (32 kilometers) of territory could require 20 small nuclear bombs — small gains for the huge risks of introducing nuclear weapons and nuclear fallout.
“Just using one will not be enough,” Cancian said.
Moscow could instead send a strong message and avoid significant casualties by detonating a nuclear bomb over water, or exploding one high over Ukraine to generate an electromagnetic pulse that would knock out electronic equipment.
Or Putin could opt for greater destruction and death: attacking a Ukraine military base, or hitting an urban center like Kyiv, generating mass casualties and possibly killing the country’s political leadership.
Such scenarios “would likely be designed to split the NATO alliance and global consensus against Putin,” Jon Wolfsthal, a former white House nuclear policy expert, wrote Friday on Substack.
But “it is unclear if it would succeed, and could just as easily be seen as desperation as resolve,” he said.
The West has remained ambiguous on how it would respond to a tactical nuclear strike, and the choices are complicated.
The United States and NATO do not want to appear weak in front of an implicit nuclear threat.
But they also would want to avoid the possibility that the war in Ukraine — not a NATO member — could escalate into a much broader, devastating global nuclear war.
Experts say the West would have no option but to respond, and that a response should come from NATO as a group, rather than the United States alone.
Any response should “ensure both that Putin’s military situation did not improve from such a strike, and that his political, economic and personal position suffered as a result,” said Wolfsthal.
The United States has positioned about 100 of its own tactical nuclear weapons in NATO countries and could respond in kind against Russian forces.
That would demonstrate resolve and remind Moscow of the danger of its actions, according to Matthew Kroenig of the Atlantic Council.
However, he said, “it might also provoke a Russian nuclear reprisal, raising the risk of a larger nuclear exchange and further humanitarian disaster.”
Another risk is that some NATO members might reject a nuclear response, serving Putin’s aims of weakening the alliance.
Answering a Russian nuclear attack in a more conventional military or diplomatic way, and supplying Ukraine with more lethal arms to attack Russia, could be more effective, experts say.
“Russian nuclear use might provide an opening to convince countries that have so far been reluctant — such as India and possibly even China — to participate in escalating sanctions,” said Kroenig.
In addition, the United States could offer Ukraine NATO aircraft, Patriot and THAAD anti-missile batteries, and ATACMS long-range missiles that could be used by Ukraine forces to strike deep inside Russia.
“Whatever restrictions we have on Ukraine forces — and I think we have some restrictions — I think we take all of those off,” said Cancian.
















