RIYADH: There is a very strong internal and international consensus in favor of continuation of the truce in Yemen, with all of the regional countries supporting a peaceful resolution, not a return to war, Timothy Lenderking, the US special envoy for Yemen, has told Arab News.
If the Houthis opt for a military solution, they will be completely isolated, he said during an interview with Arab News in Riyadh, where he arrived on Saturday as part of a diplomatic push to extend a UN-mediated truce in Yemen into a permanent arrangement.
Lenderking is also expected to continue to rally support for UN efforts to raise awareness of the threat posed by the stricken oil storage vessel, Safer, in the Red Sea, and the funding required to address the ticking environmental time bomb.
After more than seven years of war and humanitarian crisis, the truce between the Houthis, who control most of northern Yemen, and the UN-recognized government has been extended from two to six months and has largely held.
Lenderking considers the extension an opportunity for the Iran-backed Houthis to show good faith and good will, and respond to the desire of the Yemeni people for peace.
“From what we know after talking to Yemenis inside Yemen and around the world, there is no appetite for a return to war. There is no capacity for anybody to wish to see this happen,” he said.

US Special Envoy Lenderking being interviewed by Arab News' Aisha Fareed in Riyadh. (AN photo by Huda Bashatah)
Lenderking, a career member of the senior foreign service who was picked for the special envoy’s post by US President Joe Biden on Feb. 4, 2021, said that the US recognizes the leadership the Yemen government has shown in terms of flexibility with facilitating the entry of oil derivatives ships into the port of Hodeidah.
Deploring the fuel crisis that resulted from the Houthis’ “altering of the standard operating procedures” by which oil supplies move into Yemen, he said: “It created a problem, and immediately produced long gas lines in Sanaa such as we had seen before the truce.”
Washington does not support any bureaucratic procedures that obstruct the movement of oil, Lenderking clarified, adding that free movement of oil without any impediments into Yemen is, for the US, a fundamental and longstanding position.
Acknowledging that the government’s role in facilitating the entry of oil tankers into Hodeidah port is a vital part of the truce (which went into effect on April 2 this year), he said the movement of oil has an immediate and positive impact on Yemenis.
“It reduces the fuel lines, powers the food mills, and brings fuel to hospitals and schools and indeed the entire transportation network. It’s one of the cornerstones of what we feel has been a very successful truce,” he said.

Lenderking said the movement of oil into Yemen, thanks to the truce, is having an immediate and positive impact on the lives of ordinary people. (AFP)
Illustrating his point, Lenderking said that 21,000 passengers have flown from Sanaa airport on commercial airlines for the first time since 2016, and there will be more destinations becoming available.
Also as a result of the truce, he said, there are 60 percent fewer civilian casualties in Yemen — yet another development that he believes demonstrates what the agreement can bring in terms of tangible benefit to the Yemeni people.
The Houthis have publicly committed to the terms of the truce when it was extended on Aug. 2, and according to Lenderking, the US is counting on them to continue to support the deal going forward in October in an expanded format.
“We see all of those (pillars of the truce including the fuel ships and commercial flights) expanding after October, bringing additional benefit to the Yemenis and really changing their lives in a very positive way,” he said.
Lenderking said that the international consensus exists among the Permanent Members of the UN Security Council, notably the Chinese, the US, the Russians, who all see this conflict in the same way — that the pressing issues must be resolved in a political context through negotiation.

Houthi fighters, reportedly funded and armed by Iran, have contributed largely to the destruction of Yemen. (AFP file)
He said that even Iran has welcomed the truce in each of its iterations and that there is a considerable amount of international attention focused on Yemen at this moment, particularly heading into October.
Elaborating on Iran’s role in the conflict, Lenderking said that the relationship between the Houthis and Iran has been mostly a “lethal” one, with the Iranians having encouraged the Houthis at times to launch attacks.
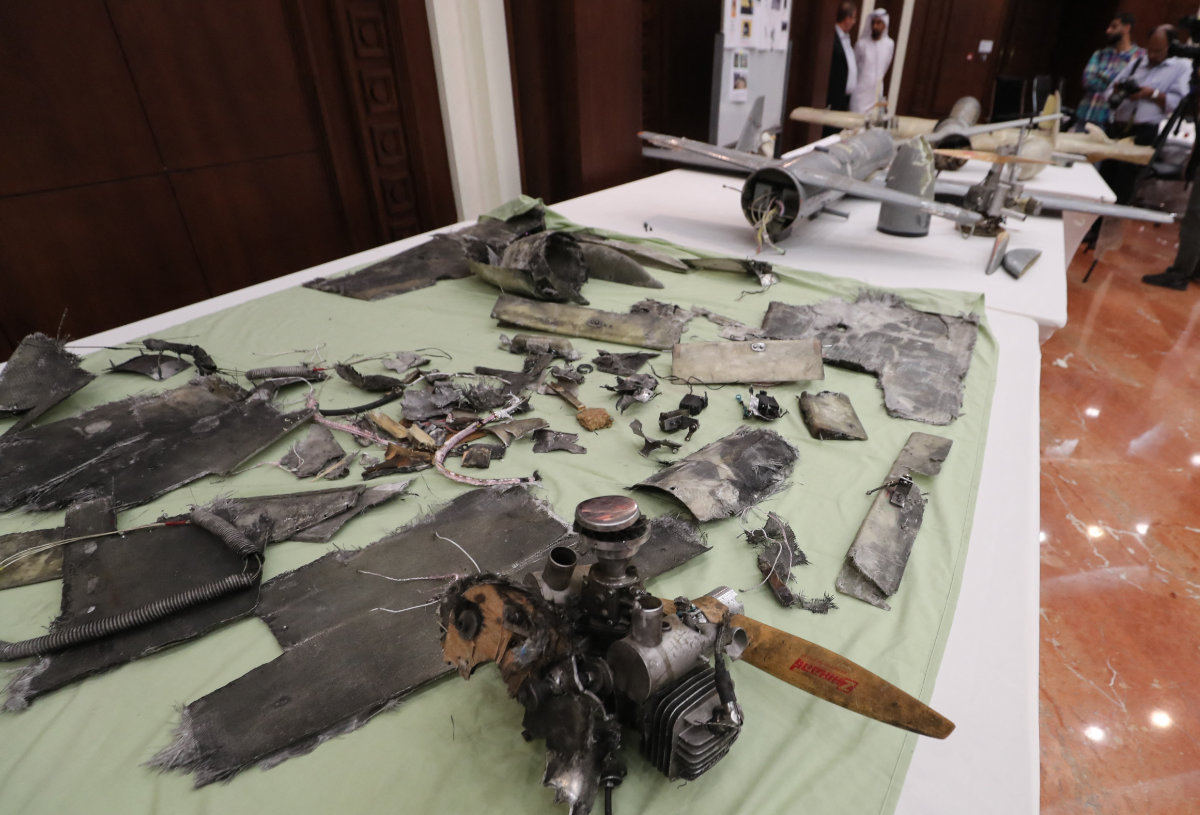

A picture taken on June 19, 2018 shows debris of Iranian-made Ababil drones, which the UAE military says were used by Houthi rebels in Yemen in battles against coalition forces. (AFP)
“They’ve supported the Houthis in developing their military capability, their UAV capability. And that’s been very negative,” he said. “This fuels rather than tempers the conflict.”
Nevertheless, Lenderking expressed hope that Tehran would match its words — welcoming the truce and backing an extended cease-fire — with action by supporting the current positive trajectory.
“There is a lot at stake here,” he said. “When we talk about the Yemen conflict, you have not only the livelihoods and the terrible humanitarian situation in Yemen, but you also have the American lives in Saudi Arabia and around the Gulf that are put at risk by attacks on these countries.
“We’ve seen oil and other infrastructure in these countries attacked by the Houthis.”
BIO
Name: Timothy A. Lenderking
Designation: Deputy assistant secretary of state for Arabian Gulf Affairs in the Near East Bureau, Department of State
Previous posts: Deputy chief of mission, US Embassy in Riyadh Senior democracy adviser, US Embassy in Baghdad
Education: Masters in history and international relations, University of Washington (1989)
All things considered, Lenderking says now is the moment for Yemen and its leaders to embrace the possibility of peace — through the truce, a durable cease-fire and political negotiations.
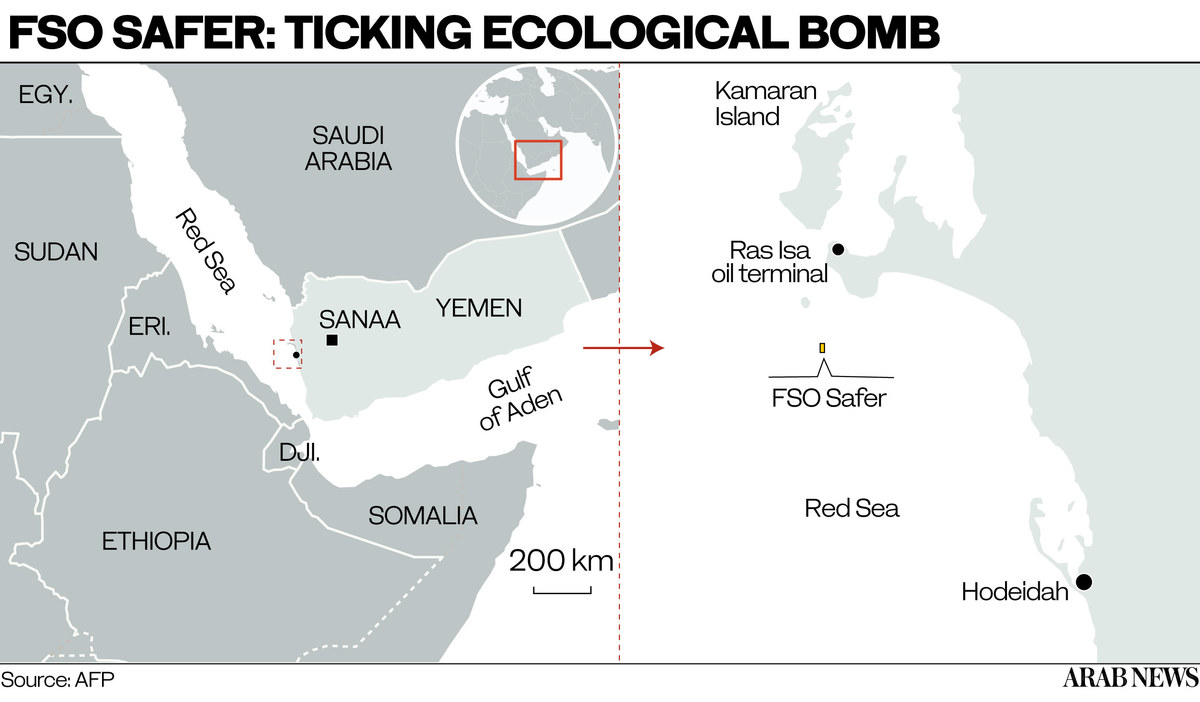
Besides the war, another issue related to Yemen that is of growing international concern is the fate of the derelict vessel FSO Safer. In recent months, the UN, with the support of the US and the Netherlands, has raised $70 million in contributions for the safe transfer of the oil stored in the Safer.
The Safer, decaying off the port of Ras Isa north of Hodeidah, is believed to contain 1.1 million barrels of oil — four times the amount that leaked into Alaska’s Prince William Sound as a result of the Exxon Valdez disaster in 1989.
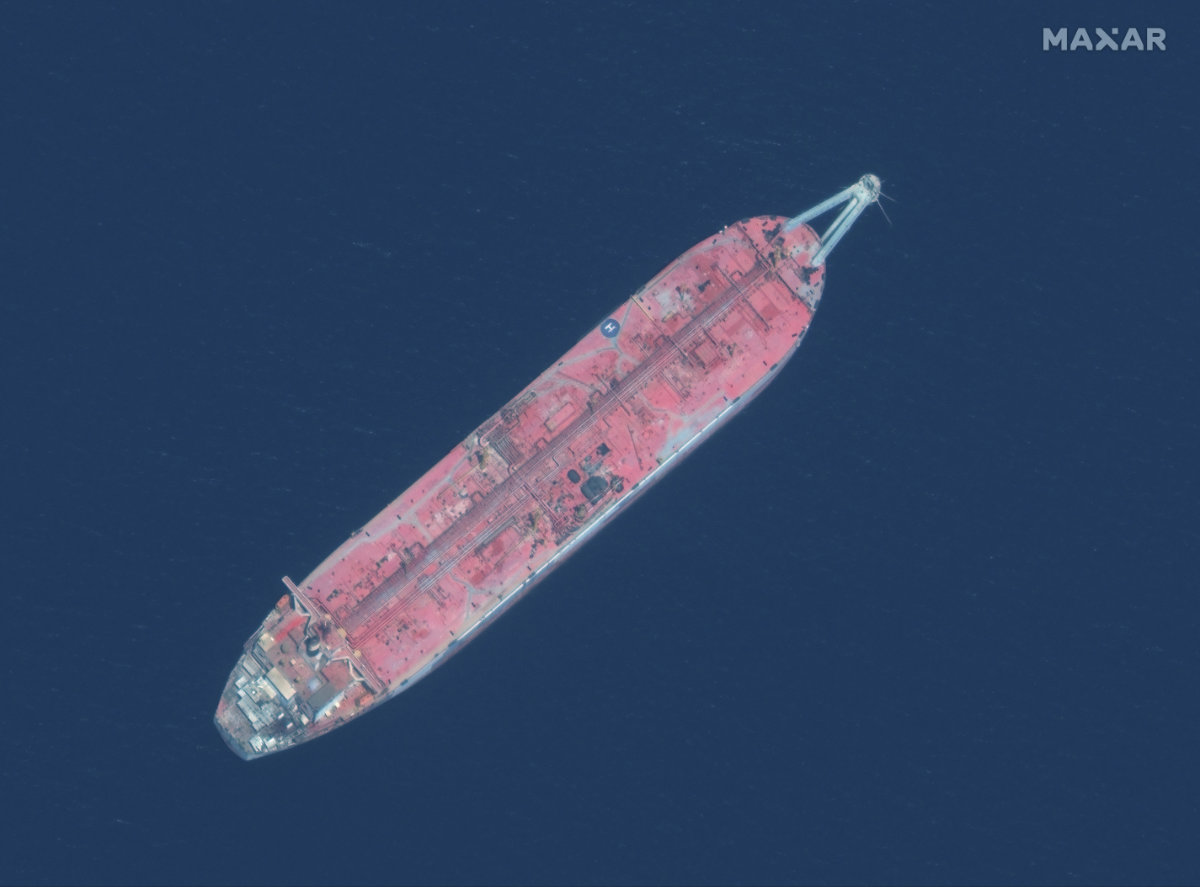

There is growing international concern surrounding the fate of the derelict vessel FSO Safer. (AFP)
The vessel’s structure has been left exposed to humidity and corrosion with little or no maintenance since the war started in 2015.
Lenderking, who is spearheading the salvage effort, is optimistic about preventing what he has described as a “looming disaster.”
He said that there is considerable support not only from countries in this region but also from Europe and the US, which is one of the largest donors to the initiative, with a pledge of $10 million, alongside Saudi Arabia and other countries.
“Obviously, an oil spill of a magnitude four times the size of the Exxon Valdez will be devastating for the coastline of the Red Sea, through which so much of international commerce traverses,” Lenderking said. “It will exacerbate the humanitarian situation in Yemen if the ports along the western coast are blocked to oil ships.”
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
According to Lenderking, the private sector has done a good job, but could do more to support the dismantling effort, which he said would benefit international commerce, maritime diversity and trade, in addition to helping Yemen rebound from the humanitarian crisis.
The first phase envisages the removal of the oil from the Safer onto a more secure vessel. However, neither the funding ($80 million) of this phase has been completed, nor is a reliable political agreement in place.
Still, Lenderking believes that the salvage initiative has been worthwhile, noting that a great deal of progress has been made since it was launched and expressing satisfaction with the leadership that Saudi Arabia, the US, the Netherlands, the UN and other donors have shown in the matter.

Lenderking is optimistic about preventing what he has described as a “looming disaster” off the western Yemeni coast. (AFP)
“We’re not there yet, and of course the key is to actually move the oil off the Safer before the tanker explodes or starts to leak, and that’s really the concern and that could happen at any time,” he said. “I mean experts have been warning about this for years.”
Lenderking pointed out that is the first time has been an agreement to move oil off the Safer and put it onto a safer vessel, an objective he is “confident” will be met this year.
“That’s a realistic goal, and I believe at the UN General Assembly later this month there will be an event which marks the progress made, and calls on donors to continue to support this effort,” he said.




















