JEDDAH: The saga of the Safer continues with an attempt by the UN to raise funds to salvage the stricken vessel that has been anchored close to Yemen’s Red Sea coast since 1988.
The plan is to raise $144 million, of which $80 million will pay for offloading the cargo of oil on board the Safer. To this end, the governments of the US and the Netherlands, represented by Dutch Ambassador to the US Andre Haspels, jointly hosted a meeting on Friday that was attended by Tim Lenderking, the US special envoy for Yemen, and representatives from the diplomatic community in Washington.
“We urge public and private donors to consider generous contributions to help prevent a leak, spill or explosion, whose effects would destroy livelihoods, tourism and commerce in one of the world’s vital shipping lanes,” a joint statement read, referring to the abandoned vessel.
The UN-coordinated plan’s objective is to avert an economic, humanitarian and environmental catastrophe that could affect not just Yemen, where 17 million people depend on humanitarian aid, but the wider region as well.
“The Safer is a ticking time bomb and it’s time to resolve the problem,” political analyst Dr. Hamdan Al-Shehri told Arab News.
“The vessel has been lying around for seven years unattended. It is the international community’s responsibility to put pressure on the Houthis on all levels to resolve the many issues confronting Yemen and Yemenis, including the Safer dispute.”
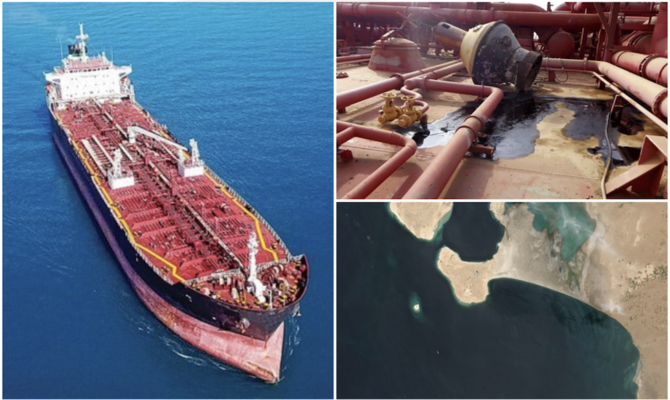
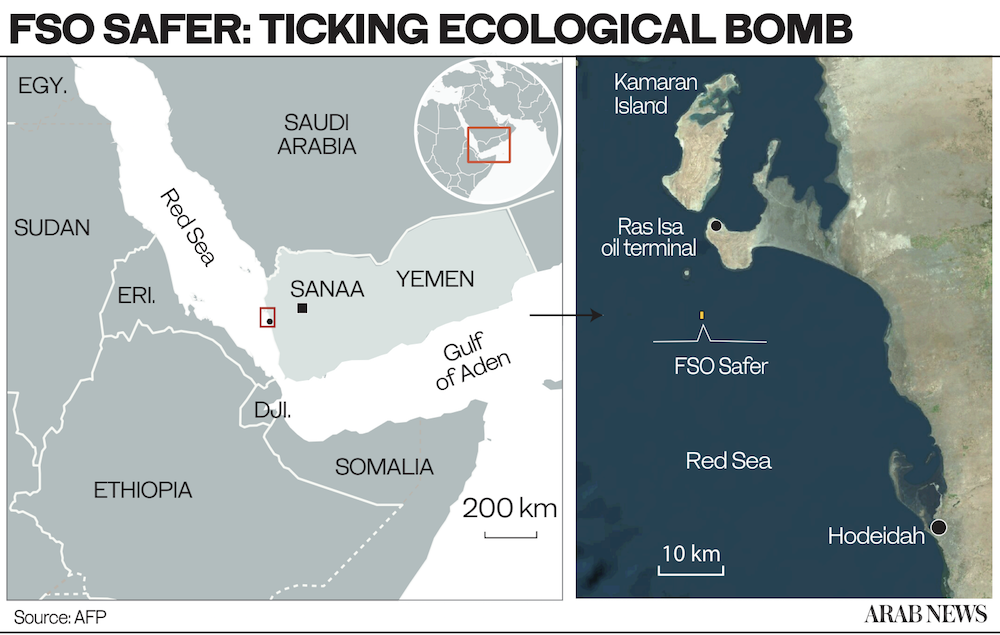
The ship, decaying off the port of Ras Isa in the absence of any maintenance, is believed to contain 1.1 million barrels of oil — four times the amount that leaked into Alaska’s Prince William Sound as a result of the Exxon Valdez disaster in 1989.
Commissioned in 1976 as an oil tanker and converted a decade later into a floating storage and offloading (FSO) facility, the Safer ceased production, offloading and maintenance in 2015 with the eruption of war and the capture of western Yemen by the Houthis.
The ship is currently moored about 4.8 nautical miles off the coast of Yemen’s Hodeidah governorate. Given the steady deterioration in its structural integrity, there is an imminent risk of an oil spill owing to leakage or explosion.
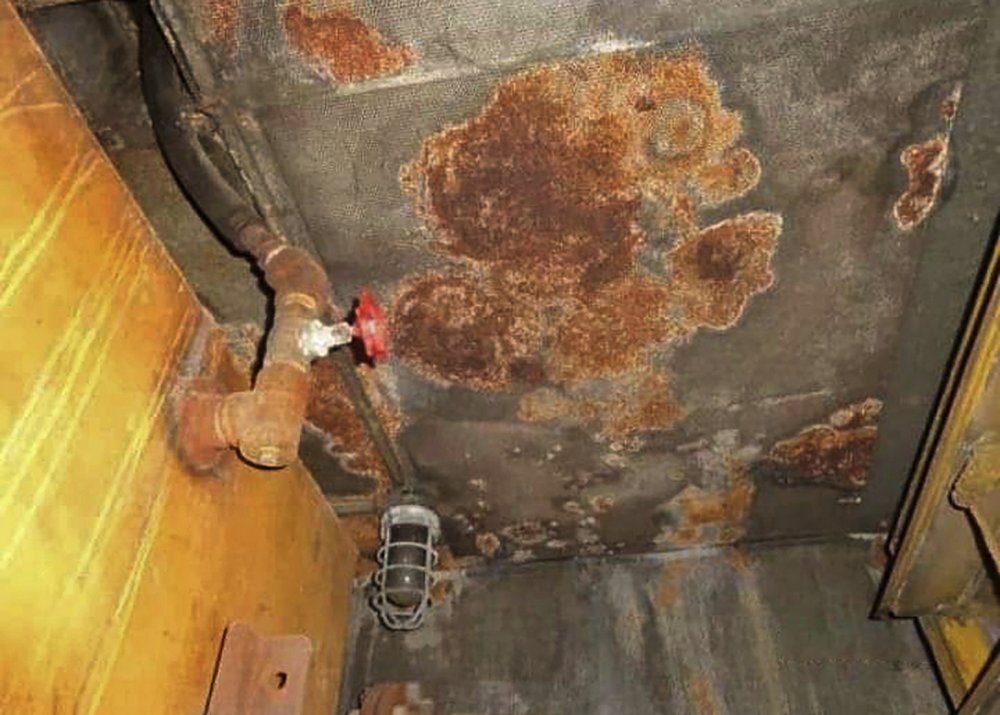

Damage to the Safer (above) has raised fears of an imminent oil spill owing to leakage or explosion. (AFP/File Photo)
In March, after years of on-again, off-again talks between the major parties concerned, the Iran-aligned Houthis apparently agreed to allow the UN to offload the oil stored in barrels on the Safer. Mohammed Ali Al-Houthi, the head of the Houthis’ Supreme Revolutionary Committee, confirmed the signing of a memorandum of understanding with the UN via Twitter.
The UN-coordinated plan, which is backed by the Yemeni government, consists of two simultaneously operative tracks. The first involves the installation of a long-term replacement for the Safer within an 18-month period, while the second entails the transfer of the cargo of oil to a temporary vessel over a period of four months.
The UN intends to keep the Safer and the temporary vessel in place until all the oil is transferred to the permanent replacement vessel. Afterwards, the rusting vessel would be towed to a yard and sold for scrap.
In April, Lenderking, Dutch Ambassador to Yemen Peter Derrek Hoff and UN Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator for Yemen David Gressly toured the region as part of a UN-led mission to raise awareness of the threat posed by the Safer and raise funds for the UN plan.
A month later, a scheme devised by Gressly to oversee the UN’s attempts to raise $80 million from donors began. So far, however, the world body has been able to raise only $40 million.
Meanwhile, the clock is ticking on the salvage plan.
INNUMBERS
* 181 million - Liters of oil stored in the decaying FSO Safer.
* 1.7 million - People in fishing industry in harm’s way in event of leak or explosion.
“If we do not receive sufficient funding urgently, the weather window to transfer the oil will close,” Auke Lootsma, resident representative of the UN Development Program in Yemen, said.
“By October, high winds and volatile currents make the operation more dangerous and increase the risk of the ship breaking up.”
A massive oil spill from the Safer would devastate fishing communities on the Red Sea coast and wreak havoc on the water, reefs and mangroves of the littoral states, notably Saudi Arabia, Eritrea, Djibouti, Somalia, and Yemen itself.
It would also lead to the disruption or even closure of the ports of Hodeidah and As Salif, which would greatly hinder commercial activity across Yemen and the country’s ability to receive humanitarian aid.
In any event, the cost of cleanup alone is expected to be $20 million.
“When the Houthis seized power in that part of Yemen in 2015, they took over the Safer but they lacked the know-how to maintain it,” Al-Shehri said. “Since then, they have been using the alarming structural state of the vessel as a bargaining chip, with the goal of grabbing the proceeds of the oil sold in the market or selling the oil in the black market for further gain.”

Representatives from Saudi Arabia, Djibouti, Egypt, Jordan, Sudan and Yemen sent a letter in 2020 addressed to the president of the Security Council, drawing attention to the risks the floating cargo posed to the region. (Reuters/File Photo)
He added: “With regard to the Safer, the Houthis will not agree to do the right thing easily, but with pressure they might. This would prevent a catastrophe whose repercussions would be felt thousands of miles away. The flow of humanitarian aid through the vital shipping lanes of the Bab Al-Mandeb Strait would be disrupted.”
Having said that, Al-Shehri cited two developments — the signing of the memorandum between the Houthis and the two-month ceasefire currently in force, the first nationwide truce since 2016 — as auguring well for the future of Yemen. In his opinion, the opening of the road to Taiz could help put an end to ongoing factional feuds and, with luck, even to the Houthi occupation.
“But to truly show their good intentions, the Houthis must cooperate with the international community and the legitimate government of Yemen plus its people and regional neighbors. They must also stop using the ship for political leverage,” he said.
“If the Houthis don’t show this spirit of cooperation, this would have dire consequences not only for Yemen but the entire region.”
Significantly, the UN ambassadors of Djibouti, Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Sudan and Yemen sent a letter in 2020 addressed to the president of the Security Council, drawing attention to the risks the floating cargo posed to the region and calling for immediate action to stave off two nightmare scenarios.
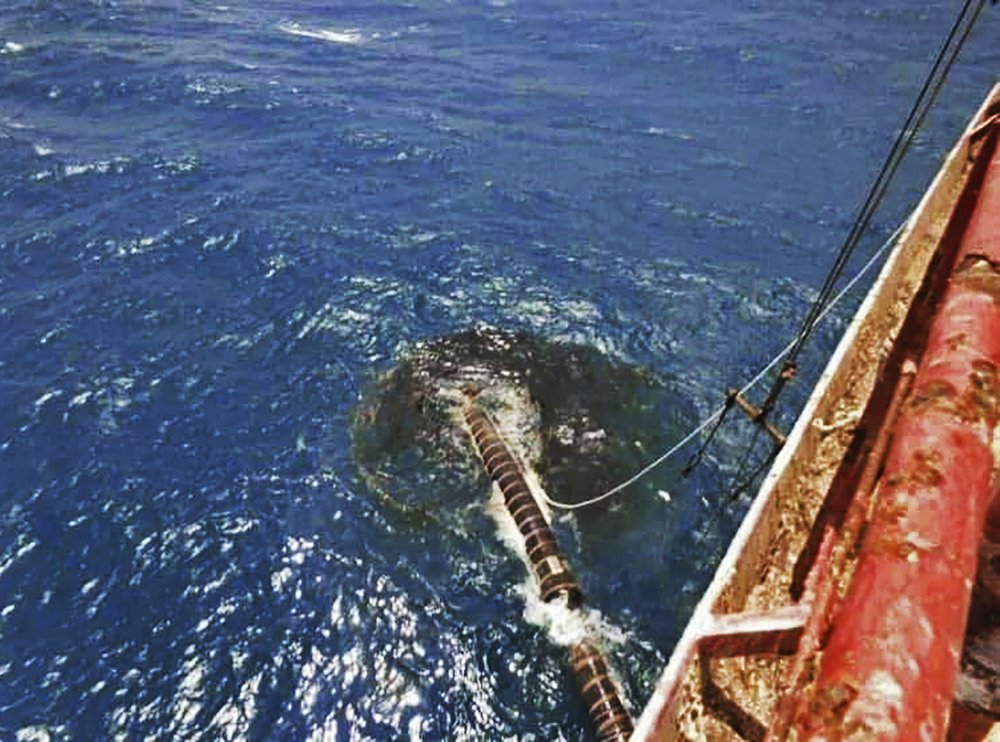

The external piping system of the FSO Safer and the hose failure that led to a spill, moored off Ras Issa port, Yemen. (AFP/File Photo)
The first would be the ecological disaster resulting from the spillage of 181 million liters into the marine life-rich Red Sea. The second would be the havoc caused by dark clouds of toxic gases released by an explosion. In addition to damage to the health of some 3 million people in Hodeidah, 4 percent of productive agricultural lands in Yemen would suffer destruction of standing crops of beans, fruits and vegetables to the tune of more than $70 million.
The spill could lead to the closure of Hodeidah port for several months, which in turn would prevent the delivery of much-needed fuel and essential goods to the local population, cause fuel prices to soar by up to 800 percent and double the cost of goods in an already poverty-stricken nation.
Expectedly, a statement issued by the UN and the Netherlands government on May 11 made it clear that the timing and funding of the oil spill-prevention plan were of the essence.
And in comments to the media on Wednesday, Linda Thomas-Greenfield, the US ambassador to the UN, said: “We know what the consequences are, we know the danger that is there, and we have encouraged others to contribute to the funding to this effort. But let’s be clear: The problem with the Safer is the Houthis, who have not allowed even the UN or others (access to inspect the ship.)”
Suggesting that the onus is on the Houthis to prove their sincerity, she added: “We can get all the money in the world, (but if) they don’t allow access, then we are still in the same place where we started. So, it is a two-pronged effort to get this (job) done.”
In the same vein, Dr. Al-Shehri points out that a settlement of the Safer standoff has been a long-standing priority of the regional actors, notably Saudi Arabia, which has been calling for a resolution of the many issues keeping Yemen embroiled in pointless conflict.
“The international community is responsible for all the chaos,” he told Arab News. “Its passive attitude is interpreted by the Houthis as a green light for continuing with their activities, so only the international community can, and must, resolve this matter once and for all. The solution is in its hands.”



















