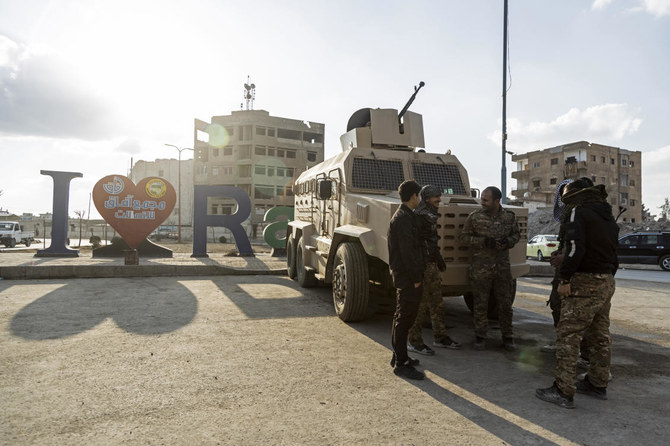
RAQQA, Syria: In a square that a few years ago was a grim stage for the Daesh group’s brutal rule in the Syrian city of Raqqa, Mahmoud Dander sat deep in thought.
He wants to leave Syria, but has a problem: The 75-year-old has no money. He recalled the old days before protests and wars led to his country’s collapse and national currency crash: Syria wasn’t thriving back then, but he had work, his children had university degrees and decent futures, and food was always on the table.
That’s all gone now. “We have fallen, just like our currency,” he said.
Raqqa, the former de facto capital of the self-proclaimed Daesh caliphate and home to about 300,000 people, is now free, but many of its residents try to leave. Those with property are trying to sell it to save up for the journey to Turkey. Those without money struggle to get by.
At least 3,000 people left Raqqa for Turkey in 2021, according to the city’s civil council co-chair Mohammed Nour.
Their reasons span the spectrum of post-war life in Syria, one of the world’s most complex conflict zones. They include economic collapse and widespread unemployment following one of the worst years of drought, as well as fears of an Daesh comeback and a proliferation of criminal gangs. And there is the looming specter of conflict between rival powers that control various parts of northern Syria, including Turkey, Russia and Syrian government forces.
On the surface, the city’s slow recovery from Daesh rule is evident. Cafes and restaurant are full of patrons. Kurdish-led forces stand guard at every major intersection.
But poverty is rampant in the majority Arab city administered by US-backed Kurdish-led forces. People line up for basics such as bread. Unemployed young men sit around. Water and electricity are limited. Many live among bombed-out ruins. Local officials say at least 30 percent of the city remains destroyed.
Poverty and unemployment drive young men into the arms of Daesh. Kurdish investigators say new Daesh recruits captured last month had been lured by money. At the same time, the Kurdish-led city administration received applications from 27,000 job seekers last year, but had no jobs.
Milhem Daher, a 35-year-old engineer, is in the process of selling his home, businesses and properties to pay a smuggler to take him and his family of eight to Turkey, a key route for Syrian migrants trying to win asylum in Europe.
He plans to leave as soon as he has enough money.
Daher had survived Raqqa’s recent violent history, including the outbreak of Syria’s civil war in 2011, and the 2014 takeover by Daesh militants who turned the city into the capital of their caliphate spanning parts of Syria and Iraq. A US-led coalition dropped thousands of bombs on the once vibrant city to drive out Daesh, liberating it in 2017. Daesh lost its last territorial foothold in Syria in 2019.
Daher emerged from the dark chapter ready to invest, but said he faced many obstacles, including a lack of resources and export markets. “If you sell to locals, it won’t generate profit,” he said.
For his first project, Daher bought seeds to cultivate vegetables. When it was time to harvest, traders weren’t interested in paying the asking price.
He purchased trucks to lift rubble amid reconstruction efforts. But the quality of the vehicles quickly degraded as a result of poor fuel in the market and lack of materials for upkeep. A potato chip factory and Internet service company also floundered.
Finally, Daher bought livestock, but a devastating drought led to shortages in animal feed. His cattle died.
Now he is selling off what remains of these failed businesses to start a new life. He needs $10,000.
In Raqqa, having money can also be a problem as kidnappings-for-ransom are on the rise.
Real estate developer Imam Al-Hasan, 37, was taken from his home and held for days by attackers in military fatigues. To secure his release, he paid $400,000, money belonging to him and traders who trusted him with their life savings. He complained to the local authorities, but he said nothing was done. A month after the ordeal, bruises are still visible on his face and legs.
Al-Hasan, too, is selling his home and belongings. “There is nothing left for me here,” he said.
Two of Al-Hasan’s relatives who left in September and recently arrived in Europe said that apart from economic uncertainty it was the threat of more violence that pushed them to leave.
“At any moment the situation could explode, how can I stay there?” said Ibrahim, 27. He and Mohammed, 41, spoke under the condition that only their first names be used, citing security concerns for their wives and children still living in the city.
Like many others, their journey from northeastern Syria to Europe began via tunnels along the town of Ras Al-Ain, which straddles the border with Turkey.
The smuggler had charged $2,000 per person. From there, the path to Europe was riddled with risk.
Ibrahim arrived in Germany last week after an arduous journey that began in Belarus. Mohammed walked for treacherous miles before setting off for Greece by boat. He ended up in The Netherlands in October.
Mohammed is waiting for a chance to bring his family from Raqqa to Europe, he said in a phone interview. For now, he is without work.
Back in Raqqa, Reem Al-Ani, 70, prepares tea for two. Her son is the only one of four children who has remained in Syria. The others are spread across the world.
The stairs leading to their apartment are riddled with bullet holes, remnants of battles to dislodge Daesh. The ceilings are charred from smoke.
She has grown accustomed to a silent house. “I miss them,” she said of her children.
Nearby, in Naim Square, the elderly Dander says he barely makes ends meet, surviving on his rapidly diminishing pension from his previous government job.
His three children have university degrees in engineering and literature, and one was a teacher, he said. But none have been able to find work. He wishes he had the money to help them leave.
“I spend every day thinking about how to get out,” he said.
Poverty, fear drive exodus from Syria’s one-time Daesh capital
https://arab.news/9mf6a
Poverty, fear drive exodus from Syria’s one-time Daesh capital

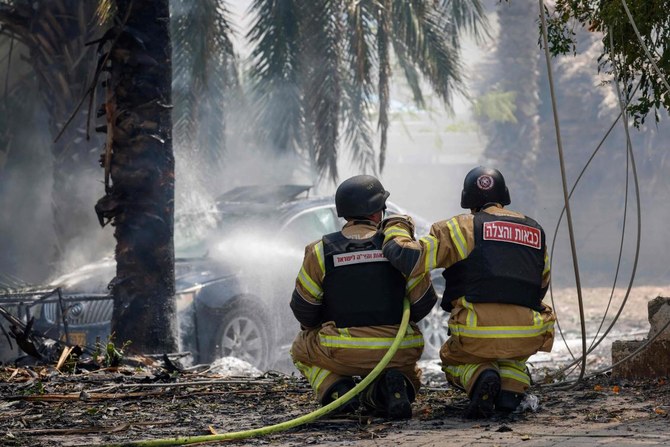
Hezbollah attacks northern Israel with drones

- Hezbollah fighters launched ‘explosive-laden drones targeting enemy soldiers and officers’
- At least 390 people have been killed, in Lebanon, in nearly seven months of cross-border violence
Israel and Hezbollah have exchanged regular cross-border fire since Palestinian militant group Hamas’s unprecedented October 7 attack on southern Israel sparked war in the Gaza Strip.
In recent weeks Hezbollah has stepped up its attacks, which it says are in support of Gazans and its ally Hamas, and Israel’s military has struck deeper into Lebanese territory.
Hezbollah fighters on Tuesday launched “explosive-laden drones targeting enemy soldiers and officers,” the group said in a statement.
At the same time, other drones “targeted one of the Iron Dome (air defense system) platforms,” the militants said, adding in separate statements that they carried out other attacks on northern Israel, including with guided missiles.
Israel’s army said on Tuesday that two soldiers had been killed a day earlier in the north.
On Monday, Hezbollah claimed a drone attack on troops near northern Israel’s Metula, with the Israeli military saying “a UAV (drone) was identified crossing from Lebanon” into the area.
In Lebanon, at least 390 people have been killed in nearly seven months of cross-border violence, mostly militants but also more than 70 civilians, according to an AFP tally.
Israel says 13 soldiers and nine civilians have been killed on its side of the border.
Tens of thousands of people have been displaced on both sides.
UN says its access to Gaza’s Rafah crossing ‘denied’ by Israel

- UN says only has one day of fuel reserves in Gaza
GENEVA: Israeli authorities have denied the UN access to the closed Rafah crossing, the main entry point for humanitarian aid into the Gaza Strip, the United nations said Tuesday .
Jens Laerke, spokesman for the UN’s humanitarian agency OCHA, said there was only a one-day buffer of fuel to run humanitarian operations inside the besieged Palestinian territory.
“We currently do not have any physical presence at the Rafah crossing as our access... has been denied by COGAT,” he said, referring to the Israeli agency that oversees supplies into the Palestinian territories.
“We have been told there will be no crossings of personnel or goods in or out for the time being. That has a massive impact on how much stock do we have.
“There’s a very, very short buffer of one day of fuel available.
“As fuel only comes in through Rafah, the one day buffer is for the entire operation in Gaza.”
If no fuel comes in, “it would be a very effective way of putting the humanitarian operation in its grave,” said Laerke.
“Currently, the two main arteries for getting aid into Gaza are currently choked off,” he said, referring to the Rafah crossing from Egypt and the Kerem Shalom crossing from Israel.
‘Unlike anything we have studied’: Gaza’s destruction in numbers
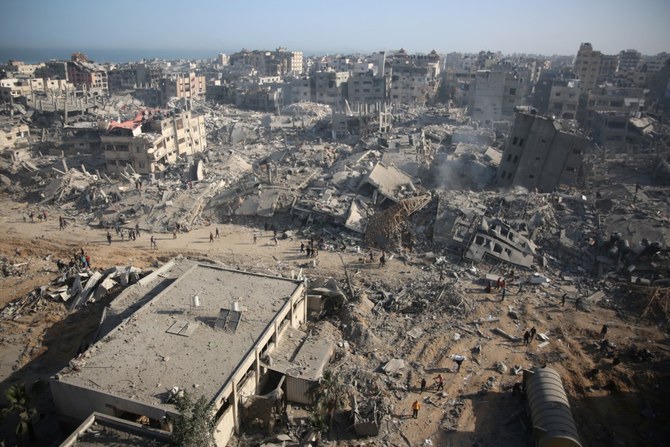

- The level of destruction in northern Gaza has surpassed that of the German city of Dresden, which was firebombed by Allied forces in 1945 in one of the most controversial Allied acts of World War II
Paris: As well as killing more than 34,000 people and causing catastrophic levels of hunger and injury, the seven-month war between Israel and Hamas has also caused massive material destruction in Gaza.
“The rate of damage being registered is unlike anything we have studied before. It is much faster and more extensive than anything we have mapped,” said Corey Scher, a PhD candidate at the City University of New York, who has been researching satellite imagery of Gaza.
As Israel launches an offensive on Rafah, the last population center in Gaza yet to be entered by its ground troops, AFP looks at the territory’s shattered landscape seven months into the war sparked by Hamas’s unprecedented October 7 attack.
Gaza is one of the most densely populated places on the planet, where before the war 2.3 million people had been living on a 365-square-kilometer strip of land.
According to satellite analyzes by Scher and Jamon Van Den Hoek, an associate professor of geography at Oregon State University, 56.9 percent of Gaza buildings were damaged or destroyed as of April 21, totaling 160,000.
“The fastest rates of destruction were in the first two to three months of the bombardment,” Scher told AFP.
In Gaza City, home to some 600,000 people before the war, the situation is dire: almost three-quarters (74.3 percent) of its buildings have been damaged or destroyed.
During the war, Gaza’s hospitals have been repeatedly attacked by Israel, which accuses Hamas of using them for military purposes, a charge the militant group denies.
In the first six weeks of the war sparked by the Hamas attack, which killed more than 1,170 people according to an AFP tally of Israeli official figures, “60 percent of health care facilities... were indicated as damaged or destroyed,” Scher said.
The territory’s largest hospital, Al-Shifa in Gaza City, was targeted in two offensives by the Israeli army, the first in November, the second in March.
The World Health Organization said the second operation reduced the hospital to an “empty shell” strewn with human remains.
Five hospitals have been completely destroyed, according to figures compiled by AFP from the OpenStreetMap project, the Hamas health ministry and the United Nations Satellite Center (UNOSAT). Fewer than one in three hospitals — 28 percent — are partially functioning, according to the UN.
The territory’s largely UN-run schools, where many civilians have sought refuge from the fighting, have also paid a heavy price.
As of April 25, UNICEF counted 408 schools damaged, representing at least 72.5 percent of its count of 563 facilities.
Of those, 53 school buildings have been completely destroyed and 274 others have been damaged by direct fire.
The UN estimates that two-thirds of the schools will need total or major reconstruction to be functional again.
Regarding places of worship, combined data from UNOSAT and OpenStreetMap show 61.5 percent of mosques have been damaged or destroyed.
The level of destruction in northern Gaza has surpassed that of the German city of Dresden, which was firebombed by Allied forces in 1945 in one of the most controversial Allied acts of World War II.
According to a US military study from 1954, quoted by the Financial Times, the bombing campaign at the end of World War II damaged 59 percent of Dresden’s buildings.
In late April, the head of the UN mine clearance program in the Palestinian territories, Mungo Birch, said there was more rubble to clear in Gaza than in Ukraine, which was invaded by Russia more than two years ago.
The UN estimated that as of the start of May, the post-war reconstruction of Gaza would cost between 30 billion and 40 billion dollars.
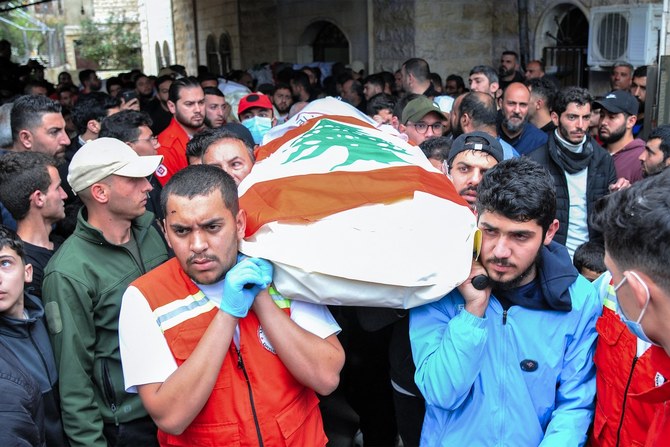
HRW: Israel attack on Lebanon rescuers was ‘unlawful’

- The rights group urged the United States to “immediately suspend arms sales and military assistance to Israel
Beirut: Human Rights Watch said Tuesday an Israeli strike in Lebanon that killed seven first responders was “an unlawful attack on civilians,” and urged Washington to suspend weapons sales to Israel.
The Israel-Lebanon border area has witnessed near-daily exchanges between the Israeli army and Hamas ally Hezbollah since the Palestinian militant group attacked southern Israel on October 7 sparking war in Gaza.
“An Israeli strike on an emergency and relief center” in the southern village of Habariyeh on March 27 “killed seven emergency and relief volunteers” and constituted an “unlawful attack on civilians that failed to take all necessary precautions,” HRW said in a statement.
“If the attack on civilians was carried out intentionally or recklessly, it should be investigated as an apparent war crime,” it added.
The Israeli military did not immediately comment when contacted by AFP.
But at the time the military said the target was “a military compound” and that the strike killed a “significant terrorist operative” from Jamaa Islamiya, a Lebanese group close to Hamas, and other “terrorists.”
HRW said in the statement that it found “no evidence of a military target at the site,” and said the Israeli strike “targeted a residential structure that housed the Emergency and Relief Corps of the Lebanese Succour Association, a non-governmental humanitarian organization.”
Jamaa Islamiya later denied it was connected to the emergency responders, and the association told AFP it had no affiliation with any Lebanese political organization.
HRW said “the Israeli military’s admission” it had targeted the center in Habariyeh indicated a “failure to take all feasible precautions to verify that the target was military and avoid loss of civilian life... making the strike unlawful.”
The rights group said those killed were volunteers, adding that 18-year-old twin brothers were among the dead.
“Family members... the Lebanese Succour Association, and the civil defense all said that the seven men were civilians and not affiliated with any armed group,” it added.
However, it noted that social media content suggested at least two of those killed “may have been supporters” of Jamaa Islamiya.
HRW said images of weapons parts found at the site included the remains of an Israeli bomb and remnants of a “guidance kit produced by the US-based Boeing Company.”
“Israeli forces used a US weapon to conduct a strike that killed seven civilian relief workers in Lebanon who were merely doing their jobs,” HRW’s Lebanon researcher, Ramzi Kaiss, said.
The rights group urged the United States to “immediately suspend arms sales and military assistance to Israel given evidence that the Israeli military is using US weapons unlawfully.”
Mid-level Israeli team to head to Cairo to assess Hamas position, Israeli official says

- Current ceasefire proposal is not acceptable to Israel
- Israel military takes control of Rafah crossing, special forces scanning area
- Hamas says Rafah operation aims to undermine ceasefire efforts
JERUSALEM: A team of mid-ranking Israeli officials will travel to Cairo in coming hours to assess whether Hamas can be persuaded to shift on its latest ceasefire offer, a senior Israeli official said, reiterating the current proposal was unacceptable to Israel.
“This delegation is made up of mid-level envoys. Were there a credible deal in the offing, the principals would be heading the delegation,” the official told Reuters, referring to the senior officials from the intelligence services Mossad and Shin Bet who are leading the Israeli side.
The visit to the Egyptian capital will take place hours after Israeli tanks took control of the Palestinian side of the Rafah border crossing between Egypt and Gaza.
Israeli jets have carried out repeated strikes on eastern Rafah, the southern Gaza city where more than 1 million Palestinians displaced by the seven-month war have been sheltering.
Egypt’s state-aligned Al Qahera News TV reported that there were still efforts to contain the escalation between the two sides and said Egyptian officials had asked Israel to stop the Rafah operation immediately.
Hamas issued a statement saying the operation was designed to undermine ceasefire efforts.
The Israeli official, who spoke on condition of anonymity, said Israel’s demonstrated determination to move against Rafah had pushed Hamas into putting out its latest proposal hastily.
The proposal took the basic framework of a proposal from April 27, based around a halt in fighting and a return of some of the more than 130 Israeli hostages in exchange for Palestinian prisoners in Israel, and stretched it to “unacceptable extremes,” the official said.
However, another official said Hamas had agreed to the phased ceasefire and hostage release deal Israel proposed on April 27 with only minor changes that did not affect the main parts of the proposal.
The new demand would not allow Israel to veto the release of specific Palestinian prisoners, including Marwan Barghouti, a leader from the Fatah faction currently serving a life sentence for his role in mounting deadly attacks against Israelis.
“Hamas wants them all to be eligible and for Israel to have no say in the matter,” the official said.
It would also lift restrictions on the import into Gaza of so-called dual use materials that can be used for both civilian and military purposes. “Hamas says these should be allowed in for the rehabilitation of Gaza, but we know that their intention is to manufacture munitions.”
In addition, Hamas was now offering to release only 18 hostages in the first phase of a truce, instead of the 33 who would have been released under previous proposals, with the remainder to come in a subsequent phase.
“That means Israel would get only 18 hostages if it sticks to its refusal to call off the offensive,” the official said.
Rafah crossing closed
A Gaza border authority spokesperson told Reuters the Rafah crossing, a major route for aid into the devastated enclave, was closed because of the presence of Israeli tanks. Israel’s Army Radio had earlier announced its forces were there.
The United States has been pressing Israel not to launch a military campaign in Rafah until it had drawn up a humanitarian plan for the Palestinians sheltering there, which Washington says it has yet to see.
Israel said the vast majority of people had been evacuated form the area of military operations.
Instructed by Arabic text messages, phone calls and flyers to move to what the Israeli military called an “expanded humanitarian zone” around 20 km (12 miles) away, some Palestinian families began trundling away in chilly spring rain.
Some piled children and possessions onto donkey carts, while others left by pick-up or on foot through muddy streets.
As families dismantled tents and folded belongings, Abdullah Al-Najar said this was the fourth time he had been displaced since the fighting began seven months ago.
“God knows where we will go now. We have not decided yet.”