IRBIL, Iraqi Kurdistan: In the early hours of Nov. 7, three quadcopter drones armed with explosives detonated inside the grounds of the official residence of Iraq’s prime minister, Mustafa Al-Kadhimi, injuring seven members of his security detail.
Al-Kadhimi, who escaped with only light injuries, promptly released a statement appealing for calm. The question as to who was behind the attack, however, remained unanswered and open to speculation.
Topping the list of likely conspirators are fighters affiliated with Iraq’s vast network of Iran-backed Al-Hashd Al-Shaabi militias, also known as the Popular Mobilization Forces.
Established in 2014 during the war against Daesh, these groups have since morphed into something of a fifth column within the Iraqi state, officially absorbed into the state security apparatus, but largely operating under their own chain of command.

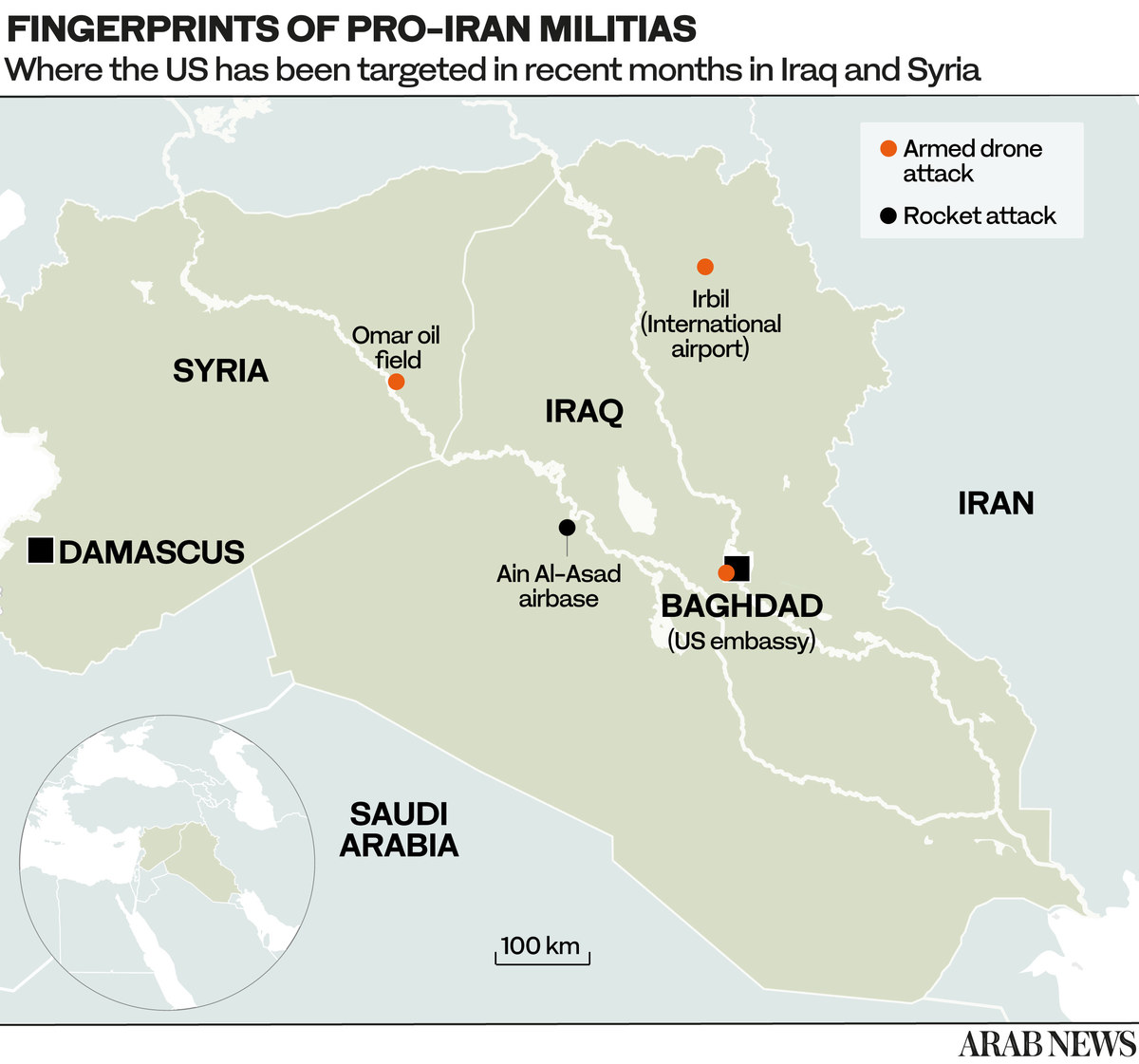
They have carried out similar drone attacks in recent months, targeting US troops stationed in Iraq and the semi-autonomous Kurdistan region with the aim of forcing their withdrawal.
If Al-Hashd Al-Shaabi was indeed responsible for the attempt on Al-Kadhimi’s life, it raises the question: Did Iran sanction the attack?
Kyle Orton, an independent Middle East analyst, believes the identity of the culprit or culprits behind the attack on Al-Kadhimi’s residence is murky by design, giving the Iran-backed militias the luxury of plausible deniability.
“Iran’s militia network, especially in Iraq over the last few years, has worked to create various splinter groups to claim responsibility for some of their more politically sensitive attacks,” Orton told Arab News.
“It isn’t clear whether these groups actually exist beyond social media — at most, they are cells answerable to preexisting Iranian Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps-run militias.”
The IRGC and its extraterritorial Quds Force exert tight control over their Iraqi militia proxies, their personnel, training, finances and access to weaponry, including explosive-laden drones, and demand total ideological loyalty to Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei.
Such a brazen attack “does not proceed if Tehran does not want it to,” said Orton. “Again, exactly how this came about — whether it was an order from IRGC Quds Force leader Esmail Qaani or a Qaani non-veto of a militia initiative — we will probably never know.”
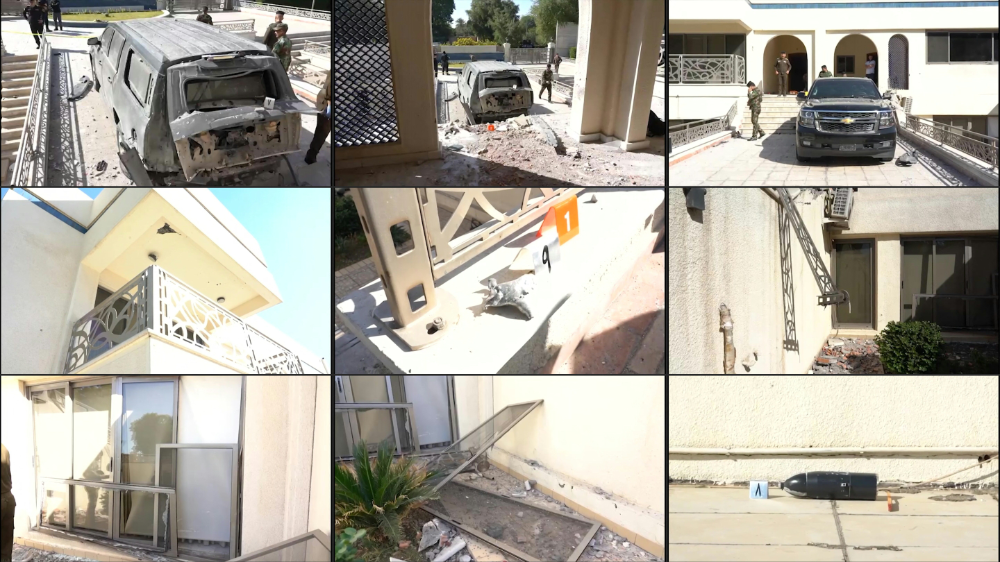

Security forces inspect the aftermath of a drone strike on the prime minister's residence. (AFP)
Then there is the question of whether the militias actually intended to assassinate Al-Kadhimi or simply wanted to intimidate him and send a message.
In May 2020, militiamen encircled Al-Kadhimi’s residence in Baghdad’s fortified Green Zone in an apparent attempt to apply pressure on him. That was most likely because Al-Kadhimi has consistently sought to strengthen Iraqi state institutions, curtail the power of these militias, and restore genuine Iraqi sovereignty since he assumed office.
Orton, however, has little doubt the attackers were out to kill Al-Kadhimi on Nov. 7. “There has been a lot of analysis suggesting that this was a warning to Al-Kadhimi, rather than an attempt to assassinate him, but this strikes me as too clever by half,” he told Arab News.

If Al-Hashd Al-Shaabi was indeed responsible for the attempt on Al-Kadhimi’s life, it raises the question: Did Iran sanction the attack?
“Al-Kadhimi was injured in the attack and it strains credulity to believe that the IRGC agents who did this had calculated it to injure seven of his bodyguards and wound the prime minister, but kill nobody.”
The timing of the attack was also hardly coincidental. In October, Iraq held parliamentary elections, which had been a core demand of the popular grassroots protest movement that began in October 2019 against rampant corruption, unemployment and Iranian influence.
Several of Tehran’s consulates and missions across the country were torched by Iraq’s young protesters, who have increasingly come to view Iran as a foreign occupying power. Iran-backed militias responded by killing hundreds of demonstrators.
The protest movement nevertheless succeeded in forcing then-prime minister Adel Abdul-Mahdi to step down, clearing the way for new elections. However, the Oct. 10 ballot saw the country’s lowest ever turnout at just 41 percent.

The IRGC and its extraterritorial Quds Force exert tight control over their Iraqi militia proxies. (AFP)
Iran-backed political factions fared poorly. The Fatah Alliance won a paltry 17 seats, a substantial loss compared to the 48 they secured in 2018. Al-Sadr’s alliance, Sayirun, meanwhile, increased its share, taking 73 of the parliament’s 329 seats.
Given the desire of Al-Sadr and his supporters to reduce foreign influence in Iraq, the result came as a blow to Iran’s regional strategy. Insisting that the election had been rigged, militia supporters came out in strength to demand a manual recount.
Qais Al-Khazali, leader of the Iran-backed Asaib Ahl Al-Haq militia, joined the protests against the result the night before the drone attack on the prime minister’s residence, during which he accused Al-Kadhimi of orchestrating the “fraudulent” election results.
“The timing is surely related to the aftermath of the election,” said Orton. “The attacks on people close to Al-Kadhimi, particularly senior officers, a number of whom were murdered, began months ago, when the militias could see Al-Kadhimi forging a coalition against them ahead of the elections.”
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
Orton believes that Al-Kadhimi will stay the course in his efforts to cement the authority of the Iraqi state. “The prime minister is likely to continue his policy of trying to rein in the militias through legal instruments, whether it’s indictments for attacks on demonstrators or corruption,” he said.
But, as the Nov. 7 attack shows, Al-Kadhimi’s success is not necessarily guaranteed. “If Iran feels seriously threatened in Iraq, it has tools beyond a no-confidence motion in parliament to change the Iraqi prime minister,” Orton said.
Not everyone is convinced that the perpetrators intended to kill Al-Kadhimi, or that the message was intended solely for him.
“Certain Iran-backed militias with connections to both Kataib Hezbollah and Asaib Ahl Al-Haq were trying to send Al-Kadhimi a message to back off,” Nicholas Heras, senior analyst and program head for State Resilience and Fragility in the Human Security Unit at the Newlines Institute, told Arab News.
“But they’re also trying to signal more widely, to Al-Sadr, that they can choose violence if they are frozen out of the political spoils in Iraq.”
Al-Sadr has burnished his credentials as an Iraqi nationalist by repeatedly calling for militias in the country to be disarmed and for their weapons to be handed over to state security forces.
“This attack likely occurred with the knowledge of Iran, but Iran likely tried to discourage it, and the attack happened anyway,” Heras said.

Al-Kadhimi has consistently sought to strengthen Iraqi state institutions, curtail the power of these militias
The question now is how Al-Kadhimi ought to respond to the attack. “Al-Kadhimi’s next move is fraught with peril,” said Heras. “He can escalate and take on these militias head-on and risk a civil conflict within the Iraqi Shiite community.
“But if he backs down and does not respond, he creates a bad precedent of tacit acceptance of this behavior that could establish a norm in Iraq for years to come.
“Therefore, Al-Kadhimi is most likely to go the route of police action, with arrests and trials.”
Twitter: @pauliddon















